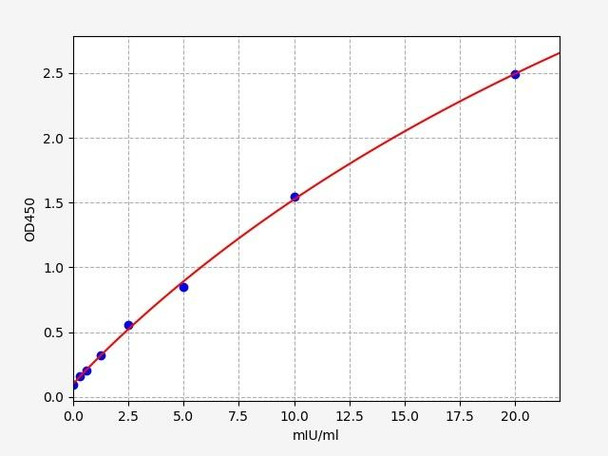
Human Beta-Gal / Beta-galactosidase ELISA Kit
- SKU:
- HUFI00547
- Product Type:
- ELISA Kit
- Size:
- 96 Assays
- Uniprot:
- P16278
- Sensitivity:
- 0.188mIU/ml
- Range:
- 0.313-20mIU/ml
- ELISA Type:
- Sandwich
- Synonyms:
- GLBeta, Galactosidase Beta, GLB1, EBP, ELNR1, Lactase, MPS4B, Acid beta-galactosidase, beta-galactosidase, Elastin receptor 1, galactosidase, beta 1
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Description
Human Beta-Gal / Beta-galactosidase ELISA Kit
GLB1 (Galactosidase Beta 1) encodes an enzyme that cleaves terminal galactose from certain oligosaccharides and glycolipids. Mutations in GLB1 are associated with classic galactosemia, a disorder characterized by accumulation of galactose-containing compounds in various tissues and the inability to metabolize dietary lactose. Gene Ontology (GO) annotations related to this gene include hydrolase activity, hydrolyzing O-glycosyl compounds and galactoside binding. An important paralog of GLB1 is GLB1L.
| Product Name: | Human Beta-Gal / Beta-galactosidase ELISA Kit |
| Product Code: | HUFI00547 |
| Size: | 96 Assays |
| Alias: | GLbeta, Galactosidase Beta, GLB1, EBP, ELNR1, Lactase, MPS4B, Acid beta-galactosidase, beta-galactosidase, Elastin receptor 1, galactosidase, beta 1 |
| Detection method: | Sandwich ELISA, Double Antibody |
| Application: | This immunoassay kit allows for the in vitro quantitative determination of Human GLB1 concentrations in serum plasma and other biological fluids. |
| Sensitivity: | 0.188mIU/ml |
| Range: | 0.313-20mIU/ml |
| Storage: | 4°C for 6 months |
| Note: | For Research Use Only |
| Recovery: | Matrices listed below were spiked with certain level of Human GLB1 and the recovery rates were calculated by comparing the measured value to the expected amount of Human GLB1 in samples. | ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Linearity: | The linearity of the kit was assayed by testing samples spiked with appropriate concentration of Human GLB1 and their serial dilutions. The results were demonstrated by the percentage of calculated concentration to the expected. | ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| CV(%): | Intra-Assay: CV<8% Inter-Assay: CV<10% |
| Component | Quantity | Storage |
| ELISA Microplate (Dismountable) | 8×12 strips | 4°C for 6 months |
| Lyophilized Standard | 2 | 4°C/-20°C |
| Sample/Standard Dilution Buffer | 20ml | 4°C |
| Biotin-labeled Antibody(Concentrated) | 120ul | 4°C (Protect from light) |
| Antibody Dilution Buffer | 10ml | 4°C |
| HRP-Streptavidin Conjugate(SABC) | 120ul | 4°C (Protect from light) |
| SABC Dilution Buffer | 10ml | 4°C |
| TMB Substrate | 10ml | 4°C (Protect from light) |
| Stop Solution | 10ml | 4°C |
| Wash Buffer(25X) | 30ml | 4°C |
| Plate Sealer | 5 | - |
Other materials and equipment required:
- Microplate reader with 450 nm wavelength filter
- Multichannel Pipette, Pipette, microcentrifuge tubes and disposable pipette tips
- Incubator
- Deionized or distilled water
- Absorbent paper
- Buffer resevoir
| Uniprot | P16278 |
| UniProt Protein Function: | GLB1: Cleaves beta-linked terminal galactosyl residues from gangliosides, glycoproteins, and glycosaminoglycans. Defects in GLB1 are the cause of GM1-gangliosidosis type 1 (GM1G1); also known as infantile GM1- gangliosidosis. GM1-gangliosidosis is an autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disease marked by the accumulation of GM1 gangliosides, glycoproteins and keratan sulfate primarily in neurons of the central nervous system. GM1G1 is characterized by onset within the first three months of life, central nervous system degeneration, coarse facial features, hepatosplenomegaly, skeletal dysmorphology reminiscent of Hurler syndrome, and rapidly progressive psychomotor deterioration. Urinary oligosaccharide levels are high. It leads to death usually between the first and second year of life. Defects in GLB1 are the cause of GM1-gangliosidosis type 2 (GM1G2); also known as late infantile/juvenile GM1- gangliosidosis. GM1G2 is characterized by onset between ages 1 and 5. The main symptom is locomotor ataxia, ultimately leading to a state of decerebration with epileptic seizures. Patients do not display the skeletal changes associated with the infantile form, but they nonetheless excrete elevated amounts of beta-linked galactose-terminal oligosaccharides. Inheritance is autosomal recessive. Defects in GLB1 are the cause of GM1-gangliosidosis type 3 (GM1G3); also known as adult or chronic GM1- gangliosidosis. GM1G3 is characterized by a variable phenotype. Patients show mild skeletal abnormalities, dysarthria, gait disturbance, dystonia and visual impairment. Visceromegaly is absent. Intellectual deficit can initially be mild or absent but progresses over time. Inheritance is autosomal recessive. Defects in GLB1 are the cause of mucopolysaccharidosis type 4B (MPS4B); also known as Morquio syndrome B. MPS4B is a form of mucopolysaccharidosis type 4, an autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disease characterized by intracellular accumulation of keratan sulfate and chondroitin-6-sulfate. Key clinical features include short stature, skeletal dysplasia, dental anomalies, and corneal clouding. Intelligence is normal and there is no direct central nervous system involvement, although the skeletal changes may result in neurologic complications. There is variable severity, but patients with the severe phenotype usually do not survive past the second or third decade of life. Belongs to the glycosyl hydrolase 35 family. 3 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Lipid Metabolism - sphingolipid; EC 3.2.1.23; Glycan Metabolism - glycosaminoglycan degradation; Hydrolase; Carbohydrate Metabolism - galactose; Glycan Metabolism - other glycan degradation; Glycan Metabolism - glycosphingolipid biosynthesis - ganglio series Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 3p21.33 Cellular Component: cytoplasm; Golgi apparatus; intracellular membrane-bound organelle; lysosomal lumen; vacuole Molecular Function:beta-galactosidase activity; exo-alpha-sialidase activity; protein binding Biological Process: cellular carbohydrate metabolic process; glycosaminoglycan catabolic process; glycosphingolipid metabolic process; keratan sulfate catabolic process Disease: Gm1-gangliosidosis, Type I; Gm1-gangliosidosis, Type Ii; Gm1-gangliosidosis, Type Iii; Mucopolysaccharidosis Type Ivb |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a member of the glycosyl hydrolase 35 family of proteins. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants, at least one of which encodes a preproprotein that is proteolytically processed to generate the mature lysosomal enzyme. This enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of a terminal beta-linked galactose residue from ganglioside substrates and other glycoconjugates. Mutations in this gene may result in GM1-gangliosidosis and Morquio B syndrome. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2015] |
| UniProt Code: | P16278 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 215273939 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 2720 |
| NCBI Accession: | P16278.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P16278,P16279, B2R7H8, B7Z6B0, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P16278 |
| Molecular Weight: | 72,751 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Beta-galactosidase |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | galactosidase beta 1 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | GLB1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | EBP; ELNR1; MPS4B |
| NCBI Protein Information: | beta-galactosidase |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Beta-galactosidase |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Acid beta-galactosidase; Lactase; Elastin receptor 1 |
| Protein Family: | Globulin |
| UniProt Gene Name: | GLB1 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | BGAL_HUMAN |
*Note: Protocols are specific to each batch/lot. For the correct instructions please follow the protocol included in your kit.
Before adding to wells, equilibrate the SABC working solution and TMB substrate for at least 30 min at 37°C. When diluting samples and reagents, they must be mixed completely and evenly. It is recommended to plot a standard curve for each test.
| Step | Protocol |
| 1. | Set standard, test sample and control (zero) wells on the pre-coated plate respectively, and then, record their positions. It is recommended to measure each standard and sample in duplicate. Wash plate 2 times before adding standard, sample and control (zero) wells! |
| 2. | Aliquot 0.1ml standard solutions into the standard wells. |
| 3. | Add 0.1 ml of Sample / Standard dilution buffer into the control (zero) well. |
| 4. | Add 0.1 ml of properly diluted sample ( Human serum, plasma, tissue homogenates and other biological fluids.) into test sample wells. |
| 5. | Seal the plate with a cover and incubate at 37 °C for 90 min. |
| 6. | Remove the cover and discard the plate content, clap the plate on the absorbent filter papers or other absorbent material. Do NOT let the wells completely dry at any time. Wash plate X2. |
| 7. | Add 0.1 ml of Biotin- detection antibody working solution into the above wells (standard, test sample & zero wells). Add the solution at the bottom of each well without touching the side wall. |
| 8. | Seal the plate with a cover and incubate at 37°C for 60 min. |
| 9. | Remove the cover, and wash plate 3 times with Wash buffer. Let wash buffer rest in wells for 1 min between each wash. |
| 10. | Add 0.1 ml of SABC working solution into each well, cover the plate and incubate at 37°C for 30 min. |
| 11. | Remove the cover and wash plate 5 times with Wash buffer, and each time let the wash buffer stay in the wells for 1-2 min. |
| 12. | Add 90 µl of TMB substrate into each well, cover the plate and incubate at 37°C in dark within 10-20 min. (Note: This incubation time is for reference use only, the optimal time should be determined by end user.) And the shades of blue can be seen in the first 3-4 wells (with most concentrated standard solutions), the other wells show no obvious color. |
| 13. | Add 50 µl of Stop solution into each well and mix thoroughly. The color changes into yellow immediately. |
| 14. | Read the O.D. absorbance at 450 nm in a microplate reader immediately after adding the stop solution. |
When carrying out an ELISA assay it is important to prepare your samples in order to achieve the best possible results. Below we have a list of procedures for the preparation of samples for different sample types.
| Sample Type | Protocol |
| Serum | If using serum separator tubes, allow samples to clot for 30 minutes at room temperature. Centrifuge for 10 minutes at 1,000x g. Collect the serum fraction and assay promptly or aliquot and store the samples at -80°C. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. If serum separator tubes are not being used, allow samples to clot overnight at 2-8°C. Centrifuge for 10 minutes at 1,000x g. Remove serum and assay promptly or aliquot and store the samples at -80°C. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Plasma | Collect plasma using EDTA or heparin as an anticoagulant. Centrifuge samples at 4°C for 15 mins at 1000 × g within 30 mins of collection. Collect the plasma fraction and assay promptly or aliquot and store the samples at -80°C. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. Note: Over haemolysed samples are not suitable for use with this kit. |
| Urine & Cerebrospinal Fluid | Collect the urine (mid-stream) in a sterile container, centrifuge for 20 mins at 2000-3000 rpm. Remove supernatant and assay immediately. If any precipitation is detected, repeat the centrifugation step. A similar protocol can be used for cerebrospinal fluid. |
| Cell culture supernatant | Collect the cell culture media by pipette, followed by centrifugation at 4°C for 20 mins at 1500 rpm. Collect the clear supernatant and assay immediately. |
| Cell lysates | Solubilize cells in lysis buffer and allow to sit on ice for 30 minutes. Centrifuge tubes at 14,000 x g for 5 minutes to remove insoluble material. Aliquot the supernatant into a new tube and discard the remaining whole cell extract. Quantify total protein concentration using a total protein assay. Assay immediately or aliquot and store at ≤ -20 °C. |
| Tissue homogenates | The preparation of tissue homogenates will vary depending upon tissue type. Rinse tissue with 1X PBS to remove excess blood & homogenize in 20ml of 1X PBS (including protease inhibitors) and store overnight at ≤ -20°C. Two freeze-thaw cycles are required to break the cell membranes. To further disrupt the cell membranes you can sonicate the samples. Centrifuge homogenates for 5 mins at 5000xg. Remove the supernatant and assay immediately or aliquot and store at -20°C or -80°C. |
| Tissue lysates | Rinse tissue with PBS, cut into 1-2 mm pieces, and homogenize with a tissue homogenizer in PBS. Add an equal volume of RIPA buffer containing protease inhibitors and lyse tissues at room temperature for 30 minutes with gentle agitation. Centrifuge to remove debris. Quantify total protein concentration using a total protein assay. Assay immediately or aliquot and store at ≤ -20 °C. |
| Breast Milk | Collect milk samples and centrifuge at 10,000 x g for 60 min at 4°C. Aliquot the supernatant and assay. For long term use, store samples at -80°C. Minimize freeze/thaw cycles. |