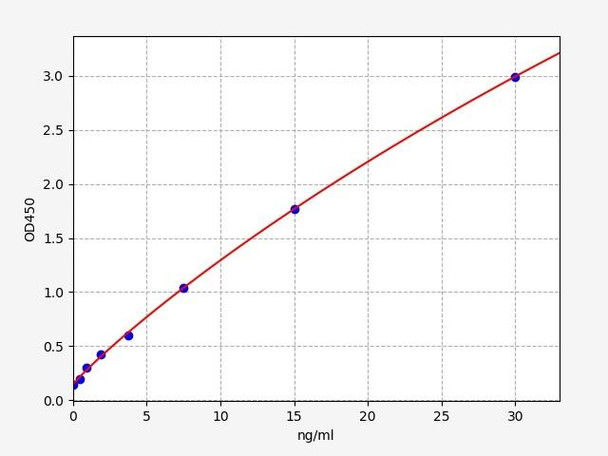
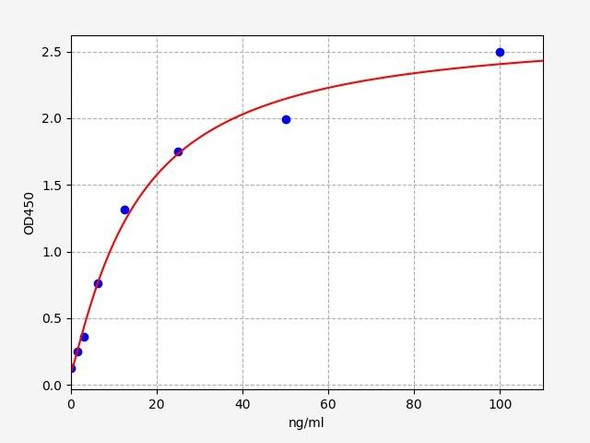
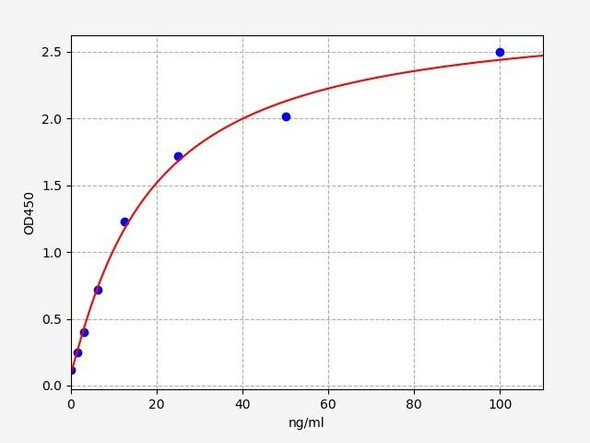
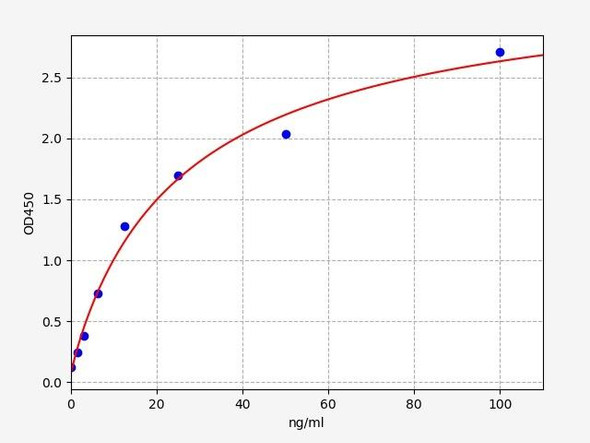
When carrying out an ELISA assay it is important to prepare your samples in order to achieve the best possible results. Below we have a list of procedures for the preparation of samples for different sample types.
| Sample Type | Protocol |
| Serum | If using serum separator tubes, allow samples to clot for 30 minutes at room temperature. Centrifuge for 10 minutes at 1,000x g. Collect the serum fraction and assay promptly or aliquot and store the samples at -80°C. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. If serum separator tubes are not being used, allow samples to clot overnight at 2-8°C. Centrifuge for 10 minutes at 1,000x g. Remove serum and assay promptly or aliquot and store the samples at -80°C. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Plasma | Collect plasma using EDTA or heparin as an anticoagulant. Centrifuge samples at 4°C for 15 mins at 1000 × g within 30 mins of collection. Collect the plasma fraction and assay promptly or aliquot and store the samples at -80°C. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. Note: Over haemolysed samples are not suitable for use with this kit. |
| Urine & Cerebrospinal Fluid | Collect the urine (mid-stream) in a sterile container, centrifuge for 20 mins at 2000-3000 rpm. Remove supernatant and assay immediately. If any precipitation is detected, repeat the centrifugation step. A similar protocol can be used for cerebrospinal fluid. |
| Cell culture supernatant | Collect the cell culture media by pipette, followed by centrifugation at 4°C for 20 mins at 1500 rpm. Collect the clear supernatant and assay immediately. |
| Cell lysates | Solubilize cells in lysis buffer and allow to sit on ice for 30 minutes. Centrifuge tubes at 14,000 x g for 5 minutes to remove insoluble material. Aliquot the supernatant into a new tube and discard the remaining whole cell extract. Quantify total protein concentration using a total protein assay. Assay immediately or aliquot and store at ≤ -20 °C. |
| Tissue homogenates | The preparation of tissue homogenates will vary depending upon tissue type. Rinse tissue with 1X PBS to remove excess blood & homogenize in 20ml of 1X PBS (including protease inhibitors) and store overnight at ≤ -20°C. Two freeze-thaw cycles are required to break the cell membranes. To further disrupt the cell membranes you can sonicate the samples. Centrifuge homogenates for 5 mins at 5000xg. Remove the supernatant and assay immediately or aliquot and store at -20°C or -80°C. |
| Tissue lysates | Rinse tissue with PBS, cut into 1-2 mm pieces, and homogenize with a tissue homogenizer in PBS. Add an equal volume of RIPA buffer containing protease inhibitors and lyse tissues at room temperature for 30 minutes with gentle agitation. Centrifuge to remove debris. Quantify total protein concentration using a total protein assay. Assay immediately or aliquot and store at ≤ -20 °C. |
| Breast Milk | Collect milk samples and centrifuge at 10,000 x g for 60 min at 4°C. Aliquot the supernatant and assay. For long term use, store samples at -80°C. Minimize freeze/thaw cycles. |