Human Amyloid Beta 40 / AB 1-40 ELISA Kit
- SKU:
- HUFI02244
- Product Type:
- ELISA Kit
- Size:
- 96 Assays
- Uniprot:
- P05067
- Sensitivity:
- 4.688pg/ml
- Range:
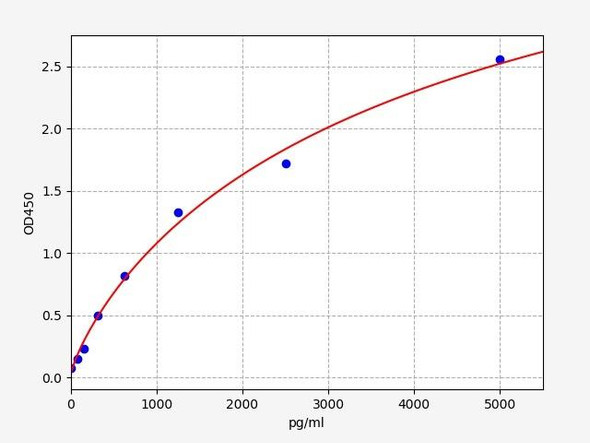
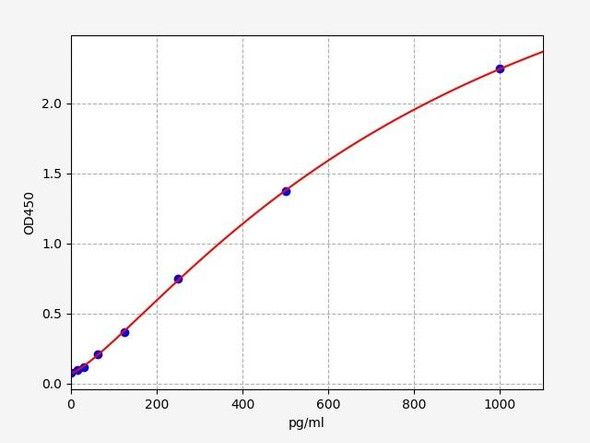
- 7.813-500pg/ml
- ELISA Type:
- Sandwich
- Synonyms:
- ABeta40, Amyloid Beta 40, Abeta 40, Beta-amyloid protein 40, ABeta, 1-40
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Research Area:
- Cell Death
Description
Human Amyloid Beta 40 / AB 1-40 ELISA Kit
Amyloid Beta 40 / AB 1-40 encodes a cell surface receptor and transmembrane precursor protein that is cleaved by secretases to form a number of peptides. Amyloid Beta 40 / AB 1-40 forms the protein basis of the amyloid plaques found in the brains of patients with Alzheimer disease. Amyloid Beta 40 / AB 1-40 has also been shown to have bacteriocidal and antifungal activities. Mutations in Amyloid Beta 40 / AB 1-40 gene have been implicated in autosomal dominant Alzheimer disease and cerebral amyloid angiopathy.
| Product Name: | Human Amyloid Beta 40 / AB 1-40 ELISA Kit |
| Product Code: | HUFI02244 |
| Size: | 96 Assays |
| Alias: | Abeta40, Amyloid Beta 40, Abeta 40, Beta-amyloid protein 40, Abeta, 1-40 |
| Detection method: | Sandwich ELISA, Double Antibody |
| Application: | This immunoassay kit allows for the in vitro quantitative determination of Human Abeta40 concentrations in serum plasma and other biological fluids. |
| Sensitivity: | 4.688pg/ml |
| Range: | 7.813-500pg/ml |
| Storage: | 4°C for 6 months |
| Note: | For Research Use Only |
| Recovery: | Matrices listed below were spiked with certain level of Human Abeta40 and the recovery rates were calculated by comparing the measured value to the expected amount of Human Abeta40 in samples. | ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Linearity: | The linearity of the kit was assayed by testing samples spiked with appropriate concentration of Human Abeta40 and their serial dilutions. The results were demonstrated by the percentage of calculated concentration to the expected. | ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| CV(%): | Intra-Assay: CV<8% Inter-Assay: CV<10% |
| Component | Quantity | Storage |
| ELISA Microplate (Dismountable) | 8×12 strips | 4°C for 6 months |
| Lyophilized Standard | 2 | 4°C/-20°C |
| Sample/Standard Dilution Buffer | 20ml | 4°C |
| Biotin-labeled Antibody(Concentrated) | 120ul | 4°C (Protect from light) |
| Antibody Dilution Buffer | 10ml | 4°C |
| HRP-Streptavidin Conjugate(SABC) | 120ul | 4°C (Protect from light) |
| SABC Dilution Buffer | 10ml | 4°C |
| TMB Substrate | 10ml | 4°C (Protect from light) |
| Stop Solution | 10ml | 4°C |
| Wash Buffer(25X) | 30ml | 4°C |
| Plate Sealer | 5 | - |
Other materials and equipment required:
- Microplate reader with 450 nm wavelength filter
- Multichannel Pipette, Pipette, microcentrifuge tubes and disposable pipette tips
- Incubator
- Deionized or distilled water
- Absorbent paper
- Buffer resevoir
| Uniprot | P05067 |
| UniProt Protein Function: | APP: a cell surface receptor that influences neurite growth, neuronal adhesion and axonogenesis. Cleaved by secretases to form a number of peptides, some of which bind to the acetyltransferase complex Fe65/TIP60 to promote transcriptional activation. The Abeta peptide is released from the cell, its extracellular deposition and accumulation form the main components of amyloid plaques in Alzheimer's disease. Mutations in this gene have been implicated in autosomal dominant Alzheimer disease and cerebroarterial amyloidosis. Can promote transcription activation through binding to Fe65-Tip60 and inhibits Notch signaling through interaction with Numb. Couples to apoptosis-inducing pathways such as those mediated by G(O) and JIP. Inhibits G(O) alpha ATPase activity. Acts as a kinesin I membrane receptor, mediating the axonal transport of beta-secretase and presenilin 1. Involved in copper homeostasis/oxidative stress through copper ion reduction. In vitro, copper-metallated APP induces neuronal death directly or is potentiated through Cu(2+)-mediated low-density lipoprotein oxidation. Can regulate neurite outgrowth through binding to components of the extracellular matrix such as heparin and collagen I and IV. Induces a RAGE-dependent pathway that activates p38 MAPK, resulting in internalization of amyloid-beta peptide and leading to mitochondrial dysfunction in cultured cortical neurons. Provides Cu(2+) ions for GPC1 which are required for release of nitric oxide (NO) and subsequent degradation of the heparan sulfate chains on GPC1. Binds, via its C-terminus, to the PID domain of several cytoplasmic proteins, including APBB family members, the APBA family, JIP1, SHC1 and, NUMB and DAB1. Binding to DAB1 inhibits its serine phosphorylation. Associates with microtubules in the presence of ATP and in a kinesin-dependent manner. Amyloid beta-42 binds nAChRA7 in hippocampal neurons. Beta-amyloid associates with HADH2. Soluble APP binds, via its N-terminal head, to FBLN1. Expressed in all fetal tissues examined with highest levels in brain, kidney, heart and spleen. Weak expression in liver. In adult brain, highest expression found in the frontal lobe of the cortex and in the anterior perisylvian cortex- opercular gyri. Moderate expression in the cerebellar cortex, the posterior perisylvian cortex-opercular gyri and the temporal associated cortex. Weak expression found in the striate, extra- striate and motor cortices. Expressed in cerebrospinal fluid, and plasma. 10 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. Isoform APP695 is the predominant form in neuronal tissue, isoform APP751 and isoform APP770 are widely expressed in non- neuronal cells. Isoform APP751 is the most abundant form in T-lymphocytes. Appican is expressed in astrocytes. The splice isoforms that contain the BPTI domain possess protease inhibitor activity. Belongs to the APP family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Receptor, misc.; Membrane protein, integral; Cell surface; Transcription factor; Apoptosis Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 21q21.3 Cellular Component: Golgi apparatus; extracellular space; cell surface; integral to plasma membrane; integral to membrane; coated pit; intercellular junction; cytosol; ER to Golgi transport vesicle; lipid raft; ciliary rootlet; perinuclear region of cytoplasm; nuclear envelope lumen; cytoplasm; synapse; dendritic shaft; neuromuscular junction; endosome; receptor complex; intracellular membrane-bound organelle; extracellular region; dendritic spine; axon; apical part of cell; plasma membrane; spindle midzone Molecular Function:serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity; heparin binding; identical protein binding; protein binding; protease activator activity; enzyme binding; DNA binding; transition metal ion binding; PTB domain binding; acetylcholine receptor binding; receptor binding Biological Process: extracellular matrix organization and biogenesis; adult locomotory behavior; mRNA polyadenylation; locomotory behavior; positive regulation of mitotic cell cycle; protein amino acid phosphorylation; regulation of translation; platelet degranulation; synaptic growth at neuromuscular junction; forebrain development; dendrite development; visual learning; collateral sprouting in the absence of injury; neuromuscular process controlling balance; cell adhesion; neurite development; cholesterol metabolic process; platelet activation; Notch signaling pathway; cellular copper ion homeostasis; regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor activity; axon cargo transport; mating behavior; regulation of multicellular organism growth; endocytosis; axon midline choice point recognition; smooth endoplasmic reticulum calcium ion homeostasis; negative regulation of neuron differentiation; neuron apoptosis; axonogenesis; suckling behavior; ionotropic glutamate receptor signaling pathway; regulation of synapse structure and activity; regulation of protein binding; innate immune response; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; response to oxidative stress; blood coagulation; neuron remodeling Disease: Alzheimer Disease |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a cell surface receptor and transmembrane precursor protein that is cleaved by secretases to form a number of peptides. Some of these peptides are secreted and can bind to the acetyltransferase complex APBB1/TIP60 to promote transcriptional activation, while others form the protein basis of the amyloid plaques found in the brains of patients with Alzheimer disease. In addition, two of the peptides are antimicrobial peptides, having been shown to have bacteriocidal and antifungal activities. Mutations in this gene have been implicated in autosomal dominant Alzheimer disease and cerebroarterial amyloidosis (cerebral amyloid angiopathy). Multiple transcript variants encoding several different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2014] |
| UniProt Code: | P05067 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 112927 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 351 |
| NCBI Accession: | P05067.3 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P05067,P09000, P78438, Q13764, Q13778, Q13793, Q16011 B2R5V1, B4DII8, D3DSD1, D3DSD2, D3DSD3, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P05067 |
| Molecular Weight: | 770 |
| NCBI Full Name: | Amyloid beta A4 protein |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | amyloid beta (A4) precursor protein |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | APP |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | AAA; AD1; PN2; ABPP; APPI; CVAP; ABETA; PN-II; CTFgamma |
| NCBI Protein Information: | amyloid beta A4 protein; preA4; protease nexin-II; peptidase nexin-II; beta-amyloid peptide; beta-amyloid peptide(1-40); beta-amyloid peptide(1-42); alzheimer disease amyloid protein; cerebral vascular amyloid peptide |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Amyloid beta A4 protein |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | ABPP; APPI; APP; Alzheimer disease amyloid protein; Cerebral vascular amyloid peptide; CVAP; PreA4; Protease nexin-II; PN-II |
| Protein Family: | Amyloid beta A4 protein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | APP |
| UniProt Entry Name: | A4_HUMAN |
*Note: Protocols are specific to each batch/lot. For the correct instructions please follow the protocol included in your kit.
Before adding to wells, equilibrate the SABC working solution and TMB substrate for at least 30 min at 37°C. When diluting samples and reagents, they must be mixed completely and evenly. It is recommended to plot a standard curve for each test.
| Step | Protocol |
| 1. | Set standard, test sample and control (zero) wells on the pre-coated plate respectively, and then, record their positions. It is recommended to measure each standard and sample in duplicate. Wash plate 2 times before adding standard, sample and control (zero) wells! |
| 2. | Aliquot 0.1ml standard solutions into the standard wells. |
| 3. | Add 0.1 ml of Sample / Standard dilution buffer into the control (zero) well. |
| 4. | Add 0.1 ml of properly diluted sample ( Human serum, plasma, tissue homogenates and other biological fluids.) into test sample wells. |
| 5. | Seal the plate with a cover and incubate at 37 °C for 90 min. |
| 6. | Remove the cover and discard the plate content, clap the plate on the absorbent filter papers or other absorbent material. Do NOT let the wells completely dry at any time. Wash plate X2. |
| 7. | Add 0.1 ml of Biotin- detection antibody working solution into the above wells (standard, test sample & zero wells). Add the solution at the bottom of each well without touching the side wall. |
| 8. | Seal the plate with a cover and incubate at 37°C for 60 min. |
| 9. | Remove the cover, and wash plate 3 times with Wash buffer. Let wash buffer rest in wells for 1 min between each wash. |
| 10. | Add 0.1 ml of SABC working solution into each well, cover the plate and incubate at 37°C for 30 min. |
| 11. | Remove the cover and wash plate 5 times with Wash buffer, and each time let the wash buffer stay in the wells for 1-2 min. |
| 12. | Add 90 µl of TMB substrate into each well, cover the plate and incubate at 37°C in dark within 10-20 min. (Note: This incubation time is for reference use only, the optimal time should be determined by end user.) And the shades of blue can be seen in the first 3-4 wells (with most concentrated standard solutions), the other wells show no obvious color. |
| 13. | Add 50 µl of Stop solution into each well and mix thoroughly. The color changes into yellow immediately. |
| 14. | Read the O.D. absorbance at 450 nm in a microplate reader immediately after adding the stop solution. |
When carrying out an ELISA assay it is important to prepare your samples in order to achieve the best possible results. Below we have a list of procedures for the preparation of samples for different sample types.
| Sample Type | Protocol |
| Serum | If using serum separator tubes, allow samples to clot for 30 minutes at room temperature. Centrifuge for 10 minutes at 1,000x g. Collect the serum fraction and assay promptly or aliquot and store the samples at -80°C. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. If serum separator tubes are not being used, allow samples to clot overnight at 2-8°C. Centrifuge for 10 minutes at 1,000x g. Remove serum and assay promptly or aliquot and store the samples at -80°C. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Plasma | Collect plasma using EDTA or heparin as an anticoagulant. Centrifuge samples at 4°C for 15 mins at 1000 × g within 30 mins of collection. Collect the plasma fraction and assay promptly or aliquot and store the samples at -80°C. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. Note: Over haemolysed samples are not suitable for use with this kit. |
| Urine & Cerebrospinal Fluid | Collect the urine (mid-stream) in a sterile container, centrifuge for 20 mins at 2000-3000 rpm. Remove supernatant and assay immediately. If any precipitation is detected, repeat the centrifugation step. A similar protocol can be used for cerebrospinal fluid. |
| Cell culture supernatant | Collect the cell culture media by pipette, followed by centrifugation at 4°C for 20 mins at 1500 rpm. Collect the clear supernatant and assay immediately. |
| Cell lysates | Solubilize cells in lysis buffer and allow to sit on ice for 30 minutes. Centrifuge tubes at 14,000 x g for 5 minutes to remove insoluble material. Aliquot the supernatant into a new tube and discard the remaining whole cell extract. Quantify total protein concentration using a total protein assay. Assay immediately or aliquot and store at ≤ -20 °C. |
| Tissue homogenates | The preparation of tissue homogenates will vary depending upon tissue type. Rinse tissue with 1X PBS to remove excess blood & homogenize in 20ml of 1X PBS (including protease inhibitors) and store overnight at ≤ -20°C. Two freeze-thaw cycles are required to break the cell membranes. To further disrupt the cell membranes you can sonicate the samples. Centrifuge homogenates for 5 mins at 5000xg. Remove the supernatant and assay immediately or aliquot and store at -20°C or -80°C. |
| Tissue lysates | Rinse tissue with PBS, cut into 1-2 mm pieces, and homogenize with a tissue homogenizer in PBS. Add an equal volume of RIPA buffer containing protease inhibitors and lyse tissues at room temperature for 30 minutes with gentle agitation. Centrifuge to remove debris. Quantify total protein concentration using a total protein assay. Assay immediately or aliquot and store at ≤ -20 °C. |
| Breast Milk | Collect milk samples and centrifuge at 10,000 x g for 60 min at 4°C. Aliquot the supernatant and assay. For long term use, store samples at -80°C. Minimize freeze/thaw cycles. |