Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Nucleoprotein Antibody (CAB21042)
- SKU:
- CAB21042
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
Frequently bought together:
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Nucleoprotein Antibody (CAB21042) |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB21042 |
| Antibody Size: | 50µL, 100µL |
| Application: | Western blotting, Immunofluorescence |
| Reactivity: | SARS-CoV-2 |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-420 of coronavirus Nucleoprotein (P0DTC9). |
| Application: | Western blotting, Immunofluorescence |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IF 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | SARS-CoV-2 |
| Positive Samples: | 293T |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-420 of coronavirus Nucleoprotein (P0DTC9). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 0.05% BSA, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | MSDN GPQN QRNA PRIT FGGP SDST GSNQ NGER SGAR SKQR RPQG LPNN TASW FTAL TQHG KEDL KFPR GQGV PINT NSSP DDQI GYYR RATR RIRG GDGK MKDL SPRW YFYY LGTG PEAG LPYG ANKD GIIW VATE GALN TPKD HIGT RNPA NNAA IVLQ LPQG TTLP KGFY AEGS RGGS QASS RSSS RSRN SSRN STPG SSRG TSPA RMAG NGGD AALA LLLL DRLN QLES KMSG KGQQ QQGQ TVTK KSAA EASK KPRQ KRTA TKAY NVTQ AFGR RGPE QTQG NFGD QELI RQGT DYKH WPQI AQFA PSAS AFFG MSRI GMEV TPSG TWLT YTGA IKLD DKDP NFKD QVIL LNKH IDAY KTFP PTEP KKDK KKKA DETQ ALPQ RQKK QQTV TLLP AADL DDFS KQLQ QSMS SADS TQA |
| Cellular Location: | |
| Calculated MW: | 45KDa |
| Observed MW: | 50KDa |
| Synonyms: | |
| Background: | Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is an enveloped, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA virus that causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Virus particles include the RNA genetic material and structural proteins needed for invasion of host cells. Once inside the cell the infecting RNA is used to encode structural proteins that make up virus particles, nonstructural proteins that direct virus assembly, transcription, replication and host control and accessory proteins whose function has not been determined.~ The structural proteins of SARS-CoV-2 include the envelope protein (E), spike or surface glycoprotein (S), membrane protein (M) and the nucleocapsid protein (N). The nucleocapsid phosphoprotein is a structural protein that binds to, protects the viral RNA genome and is involved in packaging the RNA into virus particles. The N protein has been suggested as an antiviral drug target. |
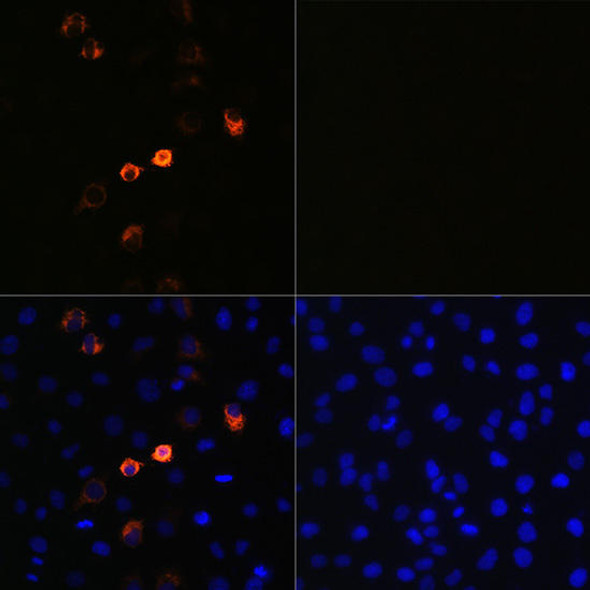
 | Immunofluorescence analysis of 293T-N and 293T cells using SARS-CoV-2 Nucleoprotein Rabbit mAb at dilution of 1:100, 1:400, 1:1600, 1:3200 (40x lens). Blue: DAPI for nuclear staining. |
 | Western blot analysis of extracts of normal 293T cells and 293T transfected with Nucleoprotein Protein, using SARS-CoV-2 Nucleoprotein antibody at 1:10000 dilution. Secondary antibody: HRP Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) at 1:10000 dilution. Lysates/proteins: 25ug per lane. Blocking buffer: 3% nonfat dry milk in TBST. Detection: ECL Basic Kit. Exposure time: 0. 8s. |