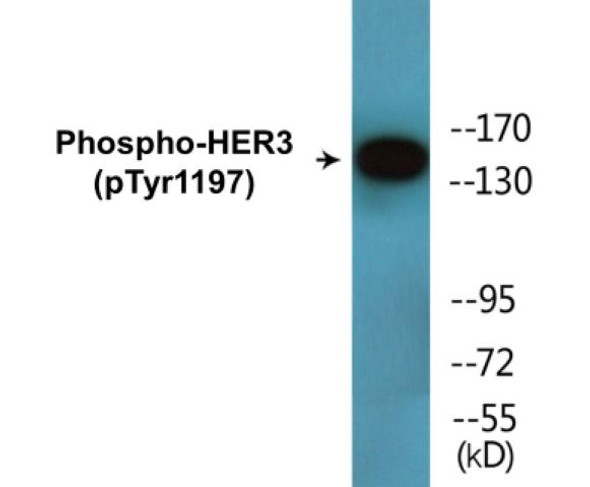
Phospho-EGFR (Tyr1197) In-Cell ELISA
- SKU:
- CBCAB00464
- Product Type:
- ELISA Kit
- ELISA Type:
- Cell Based Phospho Specific
- Research Area:
- Immunology
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Detection Method:
- Colorimetric
Description
Phospho-EGFR (Tyr1197) Cell-Based ELISA
| Product Description: | The Phospho-EGFR (Tyr1197) Colorimetric Cell-Based ELISA Kit allows for qualitative detection of Phospho-EGFR(Tyr1197) in plated and fixed cells. |
| Target Synonyms: | Epidermal growth factor receptor; Proto-oncogene c-ErbB-1; Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-1; EGFR; ERBB1 |
| Detection Target: | Phospho-IRAK1(Thr209) |
| Reactivity: | H:Y1197, M:Y1197, R:Y1196 |
| Pack Size: | 2 x 96 assays |
| Detection Method: | Colorimetric 450 nm |
| Format: | Cell-Based ELISA/In-Cell ELISA |
| Storage and Stability Guarantee: | 4°C/6 Months |
| Sample Type: | Plated & fixed cells |
| Range: | 5000 cells/well minimum |
| Time: | 4.5 hours |
Phospho-EGFR (Tyr1197) Cell-Based ELISA Protein Information
| UniProt Protein Function: | EGFR: a receptor tyrosine kinase. This is a receptor for epidermal growth factor (EGF) and related growth factors including TGF-alpha, amphiregulin, betacellulin, heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor, GP30, and vaccinia virus growth factor. EGFR is involved in the control of cell growth and differentiation. It is a single-pass transmembrane tyrosine kinase. Ligand binding to this receptor results in receptor dimerization, autophosphorylation (in trans), activation of various downstream signaling molecules and lysosomal degradation. It can be phosphorylated and activated by Src. Activated EGFR binds the SH2 domain of phospholipase C-gamma (PLC-gamma), activating PLC-gamma-mediated downstream signaling. Phosphorylated EGFR binds Cbl, leading to its ubiquitination and degradation. Grb2 and SHC bind to phospho-EGFR and are involved in the activation of MAP kinase signaling pathways. Phosphorylation on Ser and Thr residues is thought to represent a mechanism for attenuation of EGFR kinase activity. EGFR is overexpressed in breast, head and neck cancers, correlating with poor survival. Activating somatic mutations are seen in lung cancer, corresponding to the minority of patients with strong responses to the EGFR inhibitor Iressa (gefitinib). Mutations and amplifications are also seen in glioblastoma, and upregulation is seen in colon cancer and neoplasms. In xenografts, inhibitors synergize with cytotoxic drugs in the inhibition of many tumor types. Inhibitors include: Iressa/ZD1839, Erbitux, Tarceva, and lapatinib. Four alternatively spliced isoforms have been described. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Tumor suppressor; Protein kinase, tyrosine (receptor); Protein kinase, TK; Kinase, protein; Membrane protein, integral; EC 2.7.10.1; TK group; EGFR family Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 7p12 Cellular Component: extracellular space; endoplasmic reticulum membrane; nuclear membrane; cell surface; focal adhesion; basolateral plasma membrane; integral to membrane; lipid raft; Golgi membrane; membrane; perinuclear region of cytoplasm; cytoplasm; apical plasma membrane; plasma membrane; AP-2 adaptor complex; endosome membrane; nucleus; receptor complex; endosome Molecular Function:identical protein binding; epidermal growth factor receptor activity; epidermal growth factor binding; nitric-oxide synthase regulator activity; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity; receptor signaling protein tyrosine kinase activity; protein phosphatase binding; protein kinase binding; actin filament binding; integrin binding; protein binding; transmembrane receptor activity; enzyme binding; MAP kinase kinase kinase activity; protein heterodimerization activity; ubiquitin protein ligase binding; protein-tyrosine kinase activity; double-stranded DNA binding; chromatin binding; glycoprotein binding; ATP binding Biological Process: circadian rhythm; diterpenoid metabolic process; positive regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process; nerve growth factor receptor signaling pathway; activation of MAPKK activity; alkanesulfonate metabolic process; protein insertion into membrane; positive regulation of vasodilation; G1/S-specific positive regulation of cyclin-dependent protein kinase activity; positive regulation of MAP kinase activity; positive regulation of fibroblast proliferation; cell-cell adhesion; ovulation cycle; cell surface receptor linked signal transduction; hair follicle development; positive regulation of superoxide release; negative regulation of mitotic cell cycle; positive regulation of DNA repair; fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway; digestive tract morphogenesis; response to osmotic stress; phospholipase C activation; response to hydroxyisoflavone; hydrogen peroxide metabolic process; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; response to oxidative stress; regulation of nitric-oxide synthase activity; response to calcium ion; negative regulation of protein catabolic process; positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation; negative regulation of apoptosis; negative regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway; axon guidance; tongue development; embryonic placenta development; peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation; translation; protein amino acid autophosphorylation; positive regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation; signal transduction; positive regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic; learning and/or memory; positive regulation of cell proliferation; salivary gland morphogenesis; response to stress; regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation; epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway; ossification; phosphoinositide-mediated signaling; MAPKKK cascade; liver development; cell proliferation; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling cascade; cerebral cortex cell migration; calcium-dependent phospholipase A2 activation; positive regulation of vasoconstriction; innate immune response; positive regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation; astrocyte activation; positive regulation of DNA replication; positive regulation of phosphorylation; response to cobalamin; positive regulation of cell migration; lung development; positive regulation of inflammatory response Disease: Lung Cancer |
| NCBI Summary: | The protein encoded by this gene is a transmembrane glycoprotein that is a member of the protein kinase superfamily. This protein is a receptor for members of the epidermal growth factor family. EGFR is a cell surface protein that binds to epidermal growth factor. Binding of the protein to a ligand induces receptor dimerization and tyrosine autophosphorylation and leads to cell proliferation. Mutations in this gene are associated with lung cancer. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants that encode different protein isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2010] |
| UniProt Code: | P00533 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 2811086 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 1956 |
| NCBI Accession: | P00533.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P00533,O00688, O00732, P06268, Q14225, Q68GS5, Q92795 Q9BZS2, Q9GZX1, Q9H2C9, Q9H3C9, Q9UMD7, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P00533 |
| Molecular Weight: | 69,228 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | epidermal growth factor receptor |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | EGFR |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | ERBB; HER1; mENA; ERBB1; PIG61; NISBD2 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | epidermal growth factor receptor; proto-oncogene c-ErbB-1; cell growth inhibiting protein 40; cell proliferation-inducing protein 61; receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-1; avian erythroblastic leukemia viral (v-erb-b) oncogene homolog |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Proto-oncogene c-ErbB-1; Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-1 |
| Protein Family: | Pro-epidermal growth factor |
| UniProt Gene Name: | EGFR |
| UniProt Entry Name: | EGFR_HUMAN |