Human GCDH Recombinant Protein (RPES5067)
- SKU:
- RPES5067
- Product Type:
- Recombinant Protein
- Species:
- Human
Frequently bought together:
Description
system_update_altDatasheet
Human GCDH Recombinant Protein
Glutaryl-CoA Dehydrogenase Mitochondrial (GCDH) is an enzyme that acts upon glutaryl-coenzyme A, creating crotonyl-coenzyme A. It plays a role in the metabolism of lysine, hydroxylysine and tryptophan. It uses electron transfer flavoprotein as its electron acceptor. Isoform Short is inactive Glutaryl-CoA and electron-transfer flavoprotein to (E)-but-2-enoyl-CoA, CO2 and reduced electron-transfer flavoprotein. A defect in this enzyme is associated with neurological condition glutaric acidemia type 1 and cause a progressive form of early-onset generalized dystonia.
| Product Name: | Human GCDH Recombinant Protein (RPES5067) |
| Product Code: | RPES5067 |
| Size: | 10µg |
| Species: | Human |
| Expressed Host: | E.coli |
| Synonyms: | Glutaryl-CoA Dehydrogenase Mitochondrial, GCD, GCDH |
| Accession: | Q92947 |
| Sequence: | Arg45-Lys438 |
| Fusion tag: | N-6His |
| Endotoxin: | <1.0 EU per µg as determined by the LAL method. |
| Protein Construction: | Recombinant Human Glutaryl-CoA Dehydrogenase, Mitochondrial is produced by our E.coli expression system and the target gene encoding Arg45-Lys438 is expressed with a 6His tag at the N-terminus. |
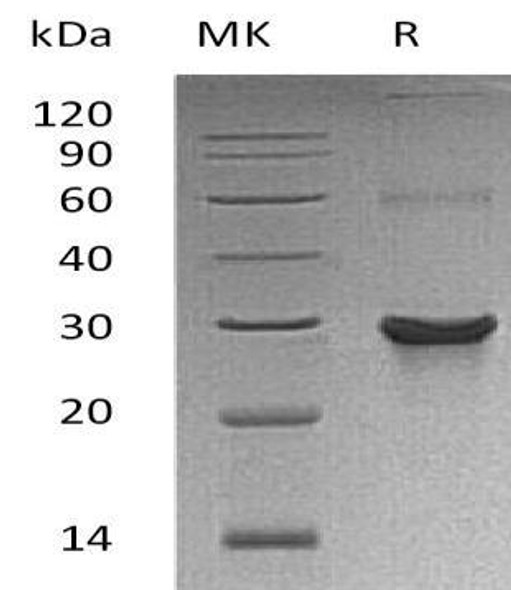
| Purity: | > 95 % as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Mol Mass: | 45.0 kDa |
| AP Mol Mass: | 41 kDa |
| Formulation: | Supplied as a 0.2 µm filtered solution of 20mM HEPES, 150mM NaCl, pH 7.4. |
| Shipping: | This product is provided as liquid. It is shipped at frozen temperature with blue ice/gel packs.Upon receipt, store it immediately at<-20°C. |
| Stability and Storage: | Store at < -20°C, stable for 6 months. Please minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |