Anti-2'-O-methyladenosine / Am Antibody (CAB2388)
- SKU:
- CAB2388
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Frequently bought together:
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-2'-O-methyladenosine / Am Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB2388 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
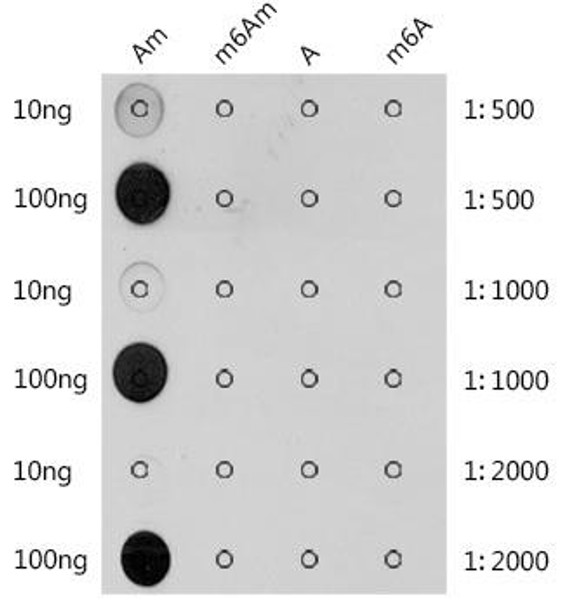
| Application: | DB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat, Other (Wide Range) |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Chemical compounds corresponding to 2'-O-methyladenosine / Am. |
| Application: | DB |
| Recommended Dilution: | DB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat, Other (Wide Range) |
| Positive Samples: |
| Immunogen: | Chemical compounds corresponding to 2'-O-methyladenosine / Am. |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | |
| Uniprot: | |
| Cellular Location: | |
| Calculated MW: | |
| Observed MW: |
| Synonyms: | Am, 2'-O-methyladenosine |
| Background: | Discovered in the 1970s, m6A is the most prevalent internal modification in polyadenylated mRNAs and long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in higher eukaryotes. m6A is widely conserved among eukaryotic species that range from yeast, plants, flies to mammals, as well as among viral RNAs with a nuclear phase. The m6A-based modification is associated with a well-defined RNA motif, RRACH (R: A/G, H: A/C/U). As a representative of the epitranscriptome, m6A mRNA modifications participate in many vital activities in the cell, including stem cell self-renewal and differentiation, mRNA transcription, alternative splicing, nuclear export, translation, degradation, and microRNA processing. These processes determine the expression or inactivation of specific genes, which is vital for growth and development.(PMID: 30416848; PMID: 24662220; PMID: 30429466) |