A Quick Guide to Myelin
The myelin sheath is an insulating layer around nerve cells. It is made up of a substance called myelin, which is produced by special cells called oligodendrocytes. Myelin protects the nerve cells and to keep them maintain their function. Myelin is important for the proper function of the nervous system. It helps to speed up nerve impulses and prevents them from becoming mixed up. Without myelin, nerve impulses would move slowly and would be easily confused. Myelin is also important for the repair of damaged nerves. When a nerve is damaged, the myelin sheath around it is also damaged. The oligodendrocytes that produce myelin can also repair the myelin sheath. This process is called myelination.
Key Takeaways
- Myelin is a white, fatty substance made up of lipids and proteins.
- Oligodendrocytes produce myelin, which insulates nerve cells, speeds up nerve impulses, and prevents interference.
- Myelin damage can result from autoimmune diseases, injury, infection, or toxins.
- Various drugs and therapies are used to treat myelin damage, depending on the cause.
- Multiple sclerosis is a debilitating condition associated with myelin damage, but symptom management is possible.
- Myelin restoration is crucial for maintaining nervous system function and involves oligodendrocyte precursor cells.
What is Myelin?
Myelin is a white, fatty substance that is made up of lipids and proteins. It is produced by oligodendrocytes, which are specialized cells found in the central nervous system. The myelin sheath is composed primarily of myelin, a type of lipid that wraps around the axons of nerve cells. This protective sheath acts as an insulator, significantly increasing the speed of electrical impulses along the nerve fibers. Recent research has shed light on the importance of specific lipids in myelin structure. One essential lipid component found in myelin is called galactosylceramide, responsible for stabilizing the membrane structure. Additionally, the presence of cholesterol in myelin has been linked to the regulation of membrane fluidity, influencing nerve conduction velocity and overall nervous system health.
As mentioned earlier, myelin is made up of approximately 70% lipids and 30% proteins. These lipids play a crucial role in the formation and maintenance of the myelin sheath, while the proteins provide structural support and perform various functions required for efficient nerve impulse transmission. One crucial protein found in myelin is myelin basic protein (MBP). MBP not only plays a significant role in stabilizing the myelin sheath but also facilitates the compaction of multiple layers of myelin around the axon. Mutations in the MBP gene have been associated with demyelinating disorders like multiple sclerosis (MS), highlighting the critical role this protein plays in maintaining a healthy nervous system.
Myelin is prominently found in the white matter of the brain and the spinal cord. White matter is so-called due to its pale appearance, caused by the abundance of myelin that surrounds the nerve fibers in this region. The myelin sheath acts as an essential factor in enhancing the efficiency of signal propagation between different regions of the central nervous system.
Neuron Anatomy
The Role of Axons
The role of axons in the neuron is to enable nerve impulses to pass from one neuron to another. This enables messages to be sent to and from the CNS. The myelin sheath surrounds the axons. Axons link the dendrites on one end of the neuron to the axon terminal on the opposite end of the neuron.
The role of axons in the neuron is crucial for facilitating the transmission of nerve impulses between neurons, enabling communication within the nervous system. When a neuron receives an electrical signal through its dendrites, this impulse travels along the axon like a fast-paced messenger, relaying information to other neurons or effector cells. Additionally, the length and diameter of axons can influence the speed at which these nerve impulses travel, allowing for efficient and rapid communication throughout the nervous system.
The myelin sheath, an essential component of the nervous system, plays a vital role in supporting and protecting axons. It consists of multiple layers of specialized cells, such as oligodendrocytes in the central nervous system (CNS) and Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Myelin acts as an insulating layer around the axons, much like the plastic coating around an electric wire, preventing electrical signals from dissipating and maintaining the signal's strength during transmission. This insulation enhances the speed of nerve impulses, allowing for rapid and efficient communication between neurons. Moreover, the presence of the myelin sheath is critical in preventing signal interference and ensuring accurate information transfer along the neural pathways.
Axons serve as the structural bridges that connect different parts of the nervous system. They establish connections between the dendrites of one neuron to the axon terminals of another, forming a complex network that enables the seamless exchange of information. This interconnected web of axons, known as neural circuits or pathways, is responsible for carrying out various functions such as sensory perception, motor control, and cognitive processing. Remarkably, the human brain alone contains billions of these intricate connections, forming the basis of our thoughts, memories, emotions, and actions.
Nodes of Ranvier
Nodes of ranvier are spaces in between the myelin sheath. It helps to send a nerve impulse from one neuron to another. They help to speed up nerve impulses by providing a pathway for electrical signals to travel along. Without nodes of ranvier, nerve impulses would move slowly and would be easily confused. Nodes of ranvier are also important for the repair of damaged nerves. When a nerve is damaged, the nodes of ranvier around it are also damaged. The process by which the nodes of ranvier accelerates the nerve signals is achieved through a mechanism known as saltatory conduction. The nodes of ranvier consist of sodium channels which allow for the rapid influx of sodium ions. This creates an electrical potential difference which causes the nerve signal to 'jump' from nodes to nodes, thereby increasing the speed of conduction. Without myelin, saltatory conduction would not be possible and impulses would be conducted slower through the neuron. Myelin provides insulation to the axon and nodes of Ranvier serve as 'gaps' in between the myelin sheath which help to increase the speed of saltatory conduction.
Myelin Damage
Myelin damage can occur for a variety of reasons. One reason is that the myelin sheath can be damaged by the immune system. This can happen in people with autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis. In multiple sclerosis, the immune system damages myelin. This disrupts nerve impulses traveling between neurons. Damage to the myelin sheath can also occur due to injury or a disease process. When the myelin sheath is disrupted, it can no longer do its job properly. This can result in inaccurate nerve function. A variety of neurological disorders can occur as a result of a disrupted Myelin sheath.
There are several drugs used in the treatment of myelin damage, each targeting different aspects of the condition. Immune-suppressing drugs, such as corticosteroids (e.g., prednisone) and disease-modifying therapies (e.g., interferon-beta and glatiramer acetate), are often prescribed to control the inflammatory response in autoimmune disorders like multiple sclerosis (MS). These medications help reduce the frequency and severity of relapses by curbing the immune system's attack on the myelin sheath. Additionally, some drugs, like natalizumab and fingolimod, work by modulating immune cell migration, preventing them from entering the central nervous system and causing further damage. Furthermore, emerging therapies focus on promoting myelin repair and regeneration. Agents like clemastine and opicinumab are being investigated in clinical trials for their potential to encourage remyelination, which could improve nerve function in patients with myelin damage. It's important to note that treatment plans are highly individualized, and healthcare providers work closely with patients to determine the most appropriate drugs based on the specific condition and its severity, ensuring the best possible outcomes. Regular monitoring and communication with healthcare professionals are essential to assess treatment efficacy and manage any potential side effects effectively.
Myelin Related ELISA Kits
Products
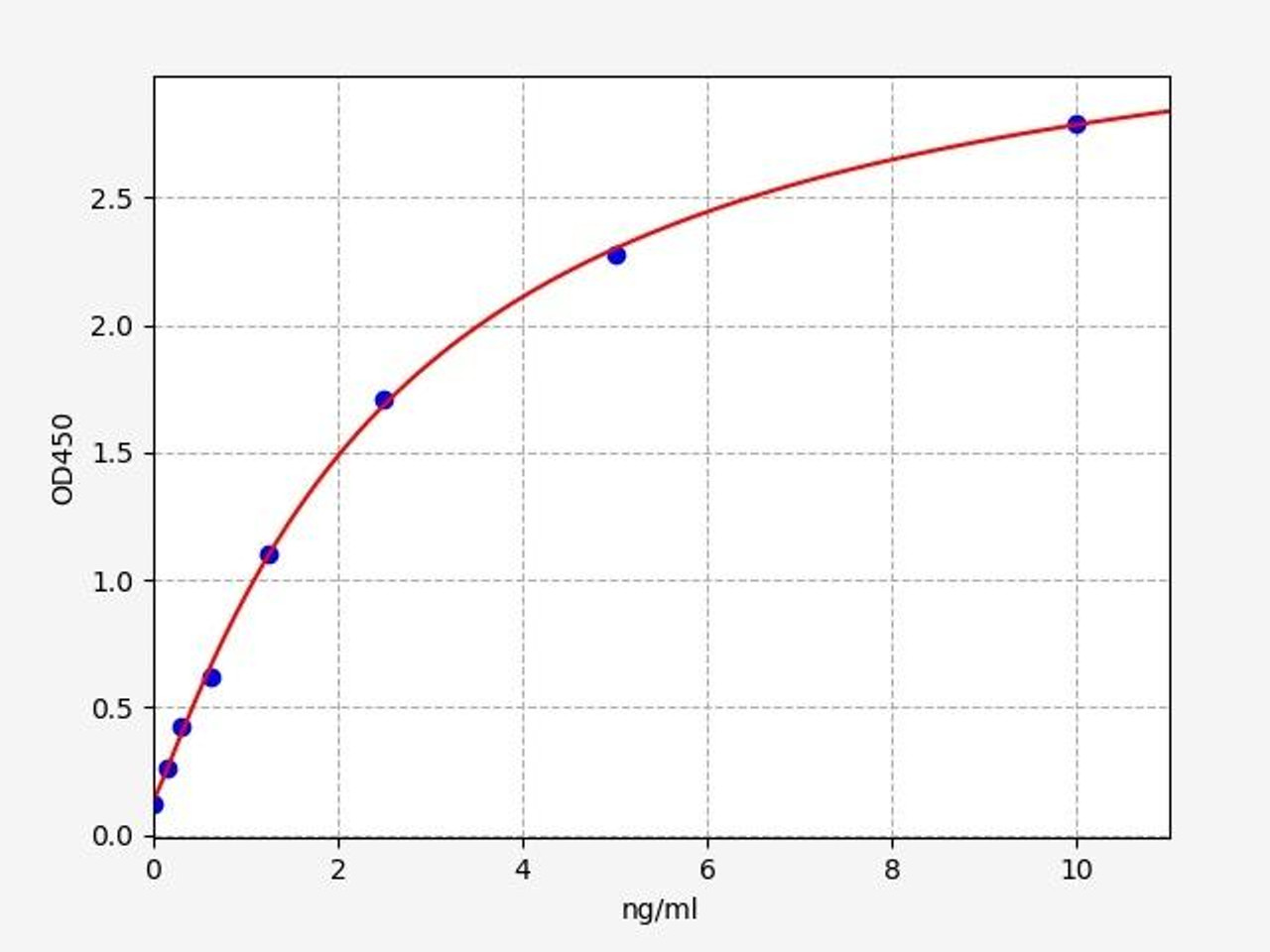
| Human MOG / Myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein ELISA Kit | |
|---|---|
| ELISA Type | Sandwich ELISA Double Antibody |
| Sensitivity | 0.094ng/ml |
| Range | 0.156-10ng/ml |
MOG / Myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein is expressed on the oligodendrocyte cell surface and the outermost surface of myelin sheaths. MOG / Myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein is a primary target antigen involved in immune-mediated demyelination.
| Human Myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG) ELISA Kit | |
|---|---|
| ELISA Type | Sandwich |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Range | 0.156-10 ng/mL |
Myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG) is a protein primarily found in the myelin sheath of nerve fibers. Changes in MAG levels can be associated with various neurological and demyelinating disorders. Researchers can use this ELISA kit to investigate MAG levels in different patient populations and healthy controls to identify potential biomarkers for diseases affecting the nervous system.
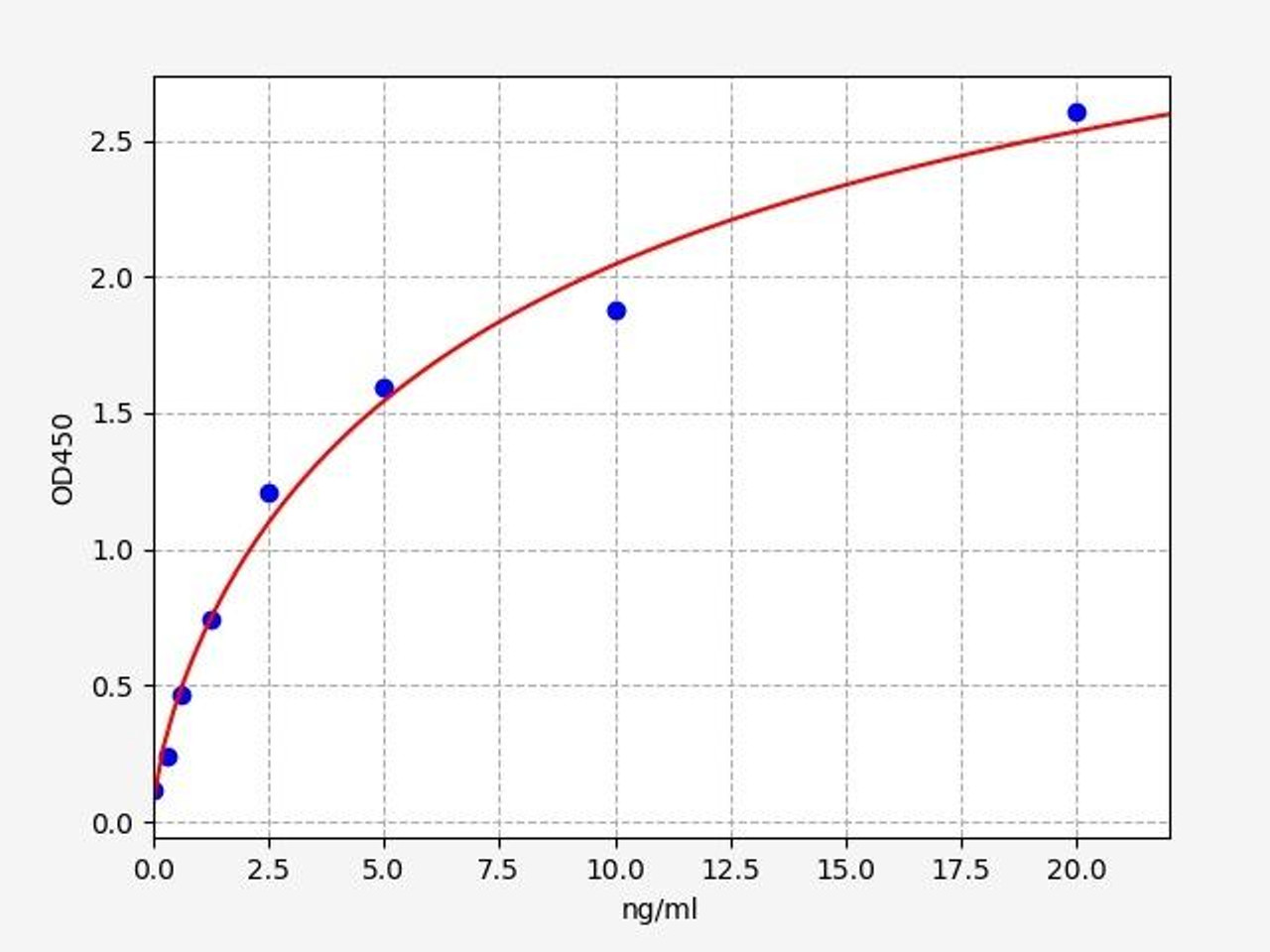
| Human MBP(myelin basic protein) ELISA Kit | |
|---|---|
| ELISA Type | Sandwich ELISA, Double Antibody |
| Sensitivity | 0.094ng/ml |
| Range | 0.156-10ng/ml |
MBP(myelin basic protein) is a major constituent of the myelin sheath of oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells in the nervous system. MBP(myelin basic protein) is conserved across species and plays a role in the early developing brain. MBP(myelin basic protein) causes remyelination of axons, and is also be involved in signaling pathways in T-cells and neural cells. MBP(myelin basic protein) might have an important role in the pathogenesis of demyelinating disease and secondary progressive multiple sclerosis.
Myelin Damage and Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis can be a very debilitating condition, and there is currently no cure. However, there are ways to manage the symptoms and to deaccelerate the disease. Some symptoms of Multiple Sclerosios include:
- Fatigue: Fatigue is one of the most common and disruptive symptoms experienced by individuals with multiple sclerosis. It can vary from mild to severe, affecting daily activities and quality of life. Managing fatigue involves maintaining a well-balanced diet, staying physically active within one's limits, and incorporating relaxation techniques like mindfulness or meditation to conserve energy.
- Vision Problems: Visual disturbances, such as blurred vision, double vision, or even temporary vision loss, may occur in multiple sclerosis. If you experience any sudden or significant changes in your vision, it is crucial to seek medical attention promptly. Eye exercises, prescribed glasses, or other visual aids can help manage some of these symptoms.
- Numbness and Tingling: Sensory issues, like numbness, tingling, or pins and needles sensations, can be early signs of multiple sclerosis. Physical therapy and regular stretching exercises may alleviate these symptoms and improve overall mobility.
- Cognitive Challenges: Multiple sclerosis can impact cognitive functions, including memory, attention, and problem-solving abilities. Cognitive exercises and brain-training activities can help maintain mental sharpness and enhance cognitive reserve.
Myelin Restoration
Myelin restoration is an essential process in the repair and maintenance of the nervous system. Without myelin, the electrical impulses that travel along the nerves would be unable to function properly, and the nerves would be damaged. Myelin is produced by oligodendrocyte precursor cells. These are specialised cells that are found in the nervous system. Oligodendrocytes are the cells responsible for regenerating myelin. Oligodendrocytes originate from oligodendrocyte precursor cells, which facilitates myelin repair. When myelin is damaged, these cells are able to repair and regenerate it. There are a number of different ways in which myelin can be damaged. One of the most common is through autoimmune disease. In autoimmune disease, the body's immune system attacks myelin, causing inflammation and damage. Other causes of myelin damage include injury, infection, and certain toxins. Myelin is produced by oligodendrocyte cells. These are a type of glial cell. Glial cells are supporting cells in the nervous system that help to protect and insulate nerve cells. Oligodendrocyte cells wrap themselves around nerve cells and produce myelin.
In conclusion, myelin is an essential and fascinating component of the nervous system that plays a crucial role in facilitating efficient and rapid signal transmission between nerve cells. This protective sheath, formed by specialized glial cells, not only enhances nerve conduction speed but also contributes to overall brain function, learning, and cognitive processes. Proper myelination is vital for the normal functioning of the nervous system and is implicated in various neurological disorders when compromised. As we continue to explore the intricate complexities of myelin biology, it becomes evident that its study holds great promise for advancing our understanding of neurological diseases and developing potential therapeutic interventions.
Written by Pragna Krishnapur
Pragna Krishnapur completed her bachelor degree in Biotechnology Engineering in Visvesvaraya Technological University before completing her masters in Biotechnology at University College Dublin.
Recent Posts
-
IgG1 Plasma Cells: The Emerging Biomarker for Predicting Cancer Immunotherapy Success
In the relentless fight against cancer, immunotherapy has emerged as a beacon of hope, harnessing t …24th Feb 2026 -
The Rise of Cancer Neuroscience: How Neural Circuits Drive Tumor Progression
For decades, we viewed cancer as a rogue army of cells, a biological glitch driven solely by geneti …23rd Feb 2026 -
CRISPR-Powered Light Sensors: A New Frontier in Ultra-Sensitive Cancer Detection
Cancer detection often relies on advanced imaging or invasive procedures, frequently catching the d …20th Feb 2026




