Blog
Trained Immunity: Reprogramming Innate Immune Memory for Future Health
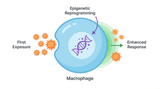
What if our first line of immune defense, the innate immune system, could learn from past encounters to fight future battles more effectively? For decades, we believed this was the exclusive domain of adaptive immunity. But a groundbreaking concept is turning this dogma on its head, revealing a hidden layer of immune memory that could revolutionize medicine as we know it.
Introduction
For years, immunology textbooks have taught us that the innate immune system is a blunt, non-specific weapon, while the adaptive immune system, with its T and B cells, holds the key to long-term memory. This is why vaccines work and why we typically only get chickenpox once.
However, a wave of recent research i
…
4th Dec 2025
Spatial Transcriptomics: Mapping the Future of Medicine at Cellular Resolution
Spatial Transcriptomics: Mapping the Future of Medicine at Cellular Resolution
Imagine being able to create a detailed map of a city, not just showing the streets and buildings, but also revealing the activities and conversations happening inside each house, in real-time. For decades, biologists have faced a similar challenge in understanding the intricate workings of our tissues. While we could identify the different cell types present, we couldn't see how they were arranged or how they communicated with each other in their natural environment. This is now changing, thanks to a revolutionary technology called spatial transcriptomics, which provides a high-resolution map of gene expression
…
2nd Dec 2025
Rescuing Exhausted T Cells: A New Frontier in Cancer Immunotherapy
For decades, the fight against cancer has been a story of incremental gains. But what if we could fundamentally shift the battlefield, turning the body's own immune system into a precision-guided weapon against tumors? This question has driven a revolution in oncology, leading to the development of immunotherapies that have transformed patient outcomes. However, these powerful treatments often face a formidable adversary: T-cell exhaustion, a phenomenon where our immune defenders lose their ability to fight. Recent breakthroughs are now revealing how combining existing drugs can reinvigorate these exhausted T cells, opening a new chapter in cancer treatment.
Introduction
The development of
…
30th Nov 2025
Cellular Senescence in Cancer Immunotherapy: The Double-Edged Sword
Cellular Senescence in Cancer Immunotherapy: The Double-Edged Sword
In the intricate world of cancer biology, some of our body's most potent defense mechanisms can paradoxically turn against us. Cellular senescence, a process where cells stop dividing in response to stress, has long been hailed as a powerful tumor suppressor. However, recent discoveries have revealed a more complex and fascinating story. It appears that these same senescent cells, under certain conditions, can create a microenvironment that shields tumors from the immune system and even fuels their growth. This surprising twist has led scientists to explore a new frontier in cancer treatment: targeting senescent cells to un
…
29th Nov 2025
The Brain's Sentinels: How Microglia Shape Neuroinflammation in Disease
The Brain's Sentinels: How Microglia Shape Neuroinflammation in Disease
In the intricate landscape of the human brain, a silent, ever-watchful guardian stands ready to defend against injury and invasion. These sentinels, known as microglia, are the brain's resident immune cells, tirelessly working to maintain a healthy environment. But what happens when these protectors turn against the very neurons they are meant to shield? This paradoxical turn from friend to foe is a central theme in the story of neurodegenerative diseases, where chronic inflammation fueled by dysfunctional microglia can accelerate cognitive decline. Recent research has begun to unravel the complex signals that govern mi
…
28th Nov 2025
Unlocking the Next Wave of Cancer Treatment: The Promise and Progress of CAR-T Cell Therapy
Imagine a living drug, engineered from a patient's own immune system, that can hunt down and destroy cancer cells with remarkable precision. This isn't science fiction; it's the reality of Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR)-T cell therapy, a revolutionary approach that has already transformed the treatment of blood cancers. For some patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell malignancies, this therapy has led to complete and lasting remissions, a feat once considered impossible. A landmark study has documented decade-long remissions in leukemia patients, underscoring the profound potential of this technology.
Introduction
Building on this success, the field of immunotherapy is buzzing with ex
…
27th Nov 2025
Unlocking the Next Wave of Cancer Treatment: The Rise of CAR-T Cell Therapy
A New Era in Oncology
Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR)-T cell therapy represents a paradigm shift in the fight against cancer, offering a personalized and powerful immunotherapy that trains a patient's own immune cells to recognize and destroy malignant cells. This revolutionary approach has already achieved remarkable success in treating various hematologic malignancies, and ongoing research is rapidly expanding its potential to tackle solid tumors and even autoimmune diseases. In this post, we will explore the latest breakthroughs in CAR-T cell therapy, from innovative engineering strategies to novel clinical applications, and discuss the challenges and future directions of this transform
…
25th Nov 2025
The Next Leap in Cancer Treatment: CAR-T Cell Therapy's Journey to Mainstream Medicine
For decades, the fight against cancer has been a grueling battle of attrition, with treatments often as harsh as the disease itself. But a revolutionary approach, chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell therapy, is rewriting the rules. This living drug, made from a patient's own immune cells, has achieved remarkable success in treating hematologic malignancies, offering hope where there was none. A recent study highlights how universal CAR-T cells could offer an off-the-shelf solution, making this groundbreaking therapy more accessible to patients in need.
Introduction
The concept of harnessing the immune system to fight cancer is not new, but CAR-T cell therapy represents a significant lea
…
24th Nov 2025
The Double-Edged Sword: How Neutrophil Traps Can Both Help and Hinder Cancer's Spread
The Double-Edged Sword: How Neutrophil Traps Can Both Help and Hinder Cancer's Spread
In the intricate battlefield of the human body, the immune system’s foot soldiers, neutrophils, have long been recognized for their heroic role in fighting off infections. But what if these same soldiers, in their attempt to protect, inadvertently create pathways for an even greater enemy to advance? Recent research has uncovered a fascinating and complex story about neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs)—web-like structures neutrophils release to ensnare pathogens—and their paradoxical role in cancer metastasis. While these traps can sometimes help the immune system fight tumors, studies are revealing that
…
21st Nov 2025
Tumor-Associated Macrophages: Double Agents in the Cancer Battlefield
Tumor-Associated Macrophages: Double Agents in the Cancer Battlefield
In the intricate theater of the human body, the immune system acts as a vigilant guardian, dispatching cellular soldiers to seek and destroy invaders like cancer. But what happens when some of these soldiers turn traitor? This is the complex reality of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), which often act as double agents within the tumor microenvironment (TME). While they possess the ability to eliminate malignant cells, they are frequently co-opted by tumors to support their growth and shield them from attack. Recent research has begun to unravel this dual nature, revealing that TAMs represent the predominant immune cell
…
20th Nov 2025
Liquid Biopsy and ctDNA: The New Frontier in Cancer Detection
Imagine a future where a simple blood test could detect cancer in its earliest stages, long before symptoms appear. This isn't science fiction; it's the rapidly advancing reality of liquid biopsy, a revolutionary diagnostic approach poised to transform oncology. For decades, tissue biopsies have been the gold standard for cancer diagnosis, but their invasive nature, cost, and inability to capture the full picture of a patient's disease have created significant limitations. Now, researchers are harnessing the power of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) to create non-invasive, real-time monitoring tools that promise to usher in a new era of precision medicine. A recent surge in publications through
…
20th Nov 2025
Exosomes: Tiny Messengers Revolutionizing Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy
In the intricate world of cancer biology, a silent conversation is constantly unfolding between tumor cells and their environment. For decades, we viewed this dialogue as a one-way street, with cancer cells dictating terms. But what if the body’s own cellular messaging system could be harnessed to fight back? Recent breakthroughs have illuminated the role of exosomes—tiny vesicles once dismissed as cellular debris—as critical mediators in this conversation, capable of both driving and suppressing cancer. A groundbreaking study now reveals that engineering these exosomes can dramatically enhance immunotherapy outcomes, turning a tumor's own weapon against it.
Introduction
The tumor microenvi
…
20th Nov 2025
Tertiary Lymphoid Structures: The Body's Hidden Arsenals in the Fight Against Cancer
Tertiary Lymphoid Structures: The Body's Hidden Arsenals in the Fight Against Cancer
Imagine a battlefield within the body, where the immune system stands as the last line of defense against the relentless advance of cancer. For decades, scientists have focused on the well-known lymphoid organs like the spleen and lymph nodes as the primary training grounds for cancer-fighting immune cells. However, a series of groundbreaking discoveries has revealed the existence of hidden immune arsenals, known as tertiary lymphoid structures (TLS), that form directly within tumors. These structures are now emerging as a critical factor in determining a patient's response to immunotherapy, and their manip
…
20th Nov 2025
Ferroptosis: A New Frontier in Cancer Therapy
For decades, the primary strategy in cancer treatment has been to trigger apoptosis, a form of programmed cell death, in malignant cells. However, many cancers develop resistance to apoptosis-inducing therapies, leading to treatment failure and relapse. This clinical challenge has spurred a search for alternative ways to eliminate cancer cells. Now, a groundbreaking area of research is focused on a different form of cell death called ferroptosis, an iron-dependent process that overcomes resistance to existing cancer therapies and offers a powerful new strategy in the fight against cancer.
Introduction
Ferroptosis is a unique form of regulated cell death characterized by the iron-dependen
…
20th Nov 2025
Unlocking a New Immune Checkpoint: The CD47-Thrombospondin-1 Pathway in Cancer
Cancer immunotherapy has revolutionized oncology, offering powerful new ways to treat various malignancies by harnessing the body's own immune system. Central to this success are immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), which release the brakes on T cells, allowing them to attack and destroy cancer cells. For years, the PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 pathways have been the primary targets for these therapies. However, a significant portion of patients do not respond to these treatments, and many who initially respond eventually develop resistance. This has driven researchers to explore new mechanisms of immune evasion. A groundbreaking study recently published in Nature Immunology has unveiled a novel im
…
20th Nov 2025
CAR-NK Cell Therapy: The Next Frontier in Cancer Immunotherapy
For decades, the fight against cancer has been a relentless battle of incremental gains. While immunotherapies like CAR-T cell therapy have offered revolutionary hope, their personalized nature, high cost, and severe side effects have limited their reach. But what if there was a readily available, “off-the-shelf” solution that could overcome these hurdles? Recent breakthroughs in cellular immunotherapy are pointing to a powerful new contender: Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR)-Natural Killer (NK) cells. These engineered immune cells are demonstrating the ability to effectively target and destroy cancer cells with a safety profile that could make cutting-edge treatments accessible to more pati
…
20th Nov 2025
Mitochondrial Transfer: A Novel Immune Evasion Mechanism in Cancer
In the intricate dance between the immune system and cancer, tumors often deploy cunning strategies to evade destruction. A groundbreaking 2025 study in Nature has unveiled a startling new tactic: cancer cells transfer their damaged mitochondria to immune cells, effectively sabotaging their ability to fight back. This discovery opens a new frontier in our understanding of immune evasion and presents exciting possibilities for the next generation of cancer immunotherapies.
Introduction
The tumor microenvironment (TME) is a complex battlefield where cancer cells and immune cells vie for dominance. A key player in this struggle is the tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte (TIL), a type of T cell that
…
20th Nov 2025
2025 Nobel Prize in Medicine: Regulatory T Cells and Peripheral Immune Tolerance
The 2025 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine has been awarded to a trio of scientists for their groundbreaking work on peripheral immune tolerance, a mechanism that prevents our immune system from attacking our own body. Their discoveries of regulatory T cells (Tregs) and the critical role of the FOXP3 gene have revolutionized our understanding of immune regulation, with one study showing that Tregs are essential for maintaining peripheral tolerance and preventing autoimmune diseases.
Introduction
For decades, scientists believed that immune tolerance was primarily established in the thymus through a process called central tolerance. However, the work of Mary E. Brunkow, Fred Ramsdell, an
…
20th Nov 2025
Breakthrough Discovery: Epstein-Barr Virus Identified as Primary Trigger for Lupus
Breakthrough Discovery: Epstein-Barr Virus Identified as Primary Trigger for Lupus
A groundbreaking study published in November 2025 has provided the most definitive evidence to date that the common Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is a primary trigger for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), a complex and debilitating autoimmune disease. The research, led by a team at Stanford University, uncovers the precise cellular mechanisms by which this nearly ubiquitous virus can cause the immune system to turn against the body's own tissues, a finding that could revolutionize the diagnosis and treatment of lupus and other autoimmune disorders.
For decades, scientists have suspected a link between EBV and lu
…
19th Nov 2025
Reprogramming Regulatory T Cells: A Breakthrough in Cancer Immunotherapy
A New Dawn in Cancer Treatment: Reprogramming the Immune System's Own Soldiers
For decades, the fight against cancer has been a relentless battle of attrition, with treatments like chemotherapy and radiation often causing significant collateral damage to the patient's body. However, a new era of cancer therapy is dawning, one that harnesses the power of our own immune system to fight back. This field, known as cancer immunotherapy, has seen remarkable progress, and a recent breakthrough from scientists at Indiana University School of Medicine is poised to revolutionize how we approach some of the most aggressive forms of the disease.
The Double-Edged Sword: Regulatory T Cells
Our immune s
…
19th Nov 2025
Alemtuzumab: Mechanism, Applications, and Biosimilar Advancements
Quick Facts About AlemtuzumabWhat is Alemtuzumab?Alemtuzumab is a monoclonal antibody targeting CD52, primarily used in the treatment of multiple sclerosis (MS) and certain cancers like chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).What is the mechanism of action for Alemtuzumab?Alemtuzumab binds to CD52 on lymphocytes, leading to their depletion via immune-mediated cytotoxicity, resetting the immune system in diseases like MS.What are the clinical applications of Alemtuzumab?Alemtuzumab is FDA-approved for relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS) and is used off-label for various hematologic conditions.What are Alemtuzumab’s common side effects?Side effects include infusion-related
…
26th May 2025
Enavatuzumab: Revolutionizing Cancer Research Through Novel Therapeutics
Quick Facts About EnavatuzumabWhat is Enavatuzumab?Enavatuzumab is a monoclonal antibody targeting the TWEAK receptor (Fn14), pivotal in tumor growth and immune regulation.What is the mechanism of action for Enavatuzumab?Enavatuzumab binds to Fn14, inhibiting signaling pathways that promote tumor cell proliferation and survival while enhancing immune response.What are the clinical applications of Enavatuzumab?It is under investigation for treating solid tumors and hematologic malignancies due to its dual action of direct tumor cell targeting and immune system modulation.Is Enavatuzumab safe?Emerging studies indicate a manageable safety profile, though further trials are crucial
…
26th May 2025
Praluzatamab: Unveiling the Promise of CD47-Targeted Therapy in Cancer Research
Quick Facts About PraluzatamabWhat is Praluzatamab?Praluzatamab is an experimental monoclonal antibody that targets CD47, a “don’t eat me” signal used by cancer cells to evade immune destruction.What role does Praluzatamab play in targeting CD47?It blocks CD47–SIRPα signaling, promoting phagocytosis of tumor cells and enhancing antitumor immune responses.Is Praluzatamab safe?Initial studies reported tolerable safety profiles, but further trials were needed to fully assess its risks and hematologic side effects.What are the clinical applications of Praluzatamab?Praluzatamab has been investigated for treating myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS), acute myeloid leukemia (AML), and soli
…
13th May 2025
Polatuzumab: Redefining Targeted Therapies in B-Cell Lymphoma
What You Need to Know About PolatuzumabWhat is Polatuzumab??Polatuzumab vedotin is an antibody-drug conjugate targeting CD79b, a component of the B-cell receptor, used primarily in B-cell lymphomas like DLBCL.What is the mechanism of action for Polatuzumab?It delivers a cytotoxic payload directly to B cells by binding to CD79b, leading to selective cell death with reduced off-target effects.What are the clinical applications of Polatuzumab?Polatuzumab is used in combination therapies for relapsed/refractory DLBCL and is being explored for front-line treatment.Is Polatuzumab safe?It has a manageable safety profile, with common side effects including neutropenia, peripheral neuro
…
9th May 2025