Blog
CB6 Biosimilar: Targeting SARS-CoV-2 with Cost-Effective Monoclonal Antibody Therapy
CB6, also known as Etesevimab, is a monoclonal antibody that targets the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. It neutralizes the virus by preventing it from binding to the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor on human cells. CB6 has been studied in combination with other antibodies, such as Bamlanivimab, for treating mild to moderate COVID-19 and preventing disease progression. The biosimilar HDBS0011 replicates CB6’s efficacy and safety while providing a cost-effective option for broader global access.This article explores the mechanism of action, clinical applications, and potential benefits of HDBS0011 in addressing the COVID-19 pandemic.1
…
4th Dec 2024
Vorsetuzumab: Advancing Cancer Research with CD70 Targeting
What You Need to Know About VorsetuzumabWhat is Vorsetuzumab?Vorsetuzumab is a monoclonal antibody targeting CD70, a protein found in various cancers. It shows promise for advancing cancer immunotherapy due to its tumor-specific activity.What is Vorsetuzumab mafodotin?Vorsetuzumab mafodotin is an antibody-drug conjugate combining vorsetuzumab with a cytotoxic agent. This combination delivers targeted therapy, killing CD70-positive cancer cells.Why is Vorsetuzumab significant?Its high specificity for cancer cells and potential to enhance immune response make it a key focus in emerging oncology research.1.) Understanding VorsetuzumabVorsetuzumab is a targeted therapeutic age
…
27th Nov 2024
Talacotuzumab: Exploring CD123-Targeting Therapies in AML and MDS Research
Key Facts About TalacotuzumabWhat is Talacotuzumab?Talacotuzumab is a monoclonal antibody designed to target CD123, a protein commonly found on the surface of certain blood cancer cells.How does Talacotuzumab work?It binds to CD123, recruiting the body’s immune cells to destroy cancer cells, making it a targeted and innovative approach in cancer therapy.What are Talacotuzumab’s potential uses?Talacotuzumab has been studied for treating acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS), offering hope for patients with these challenging conditions.1.) Understanding TalacotuzumabTalacotuzumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody developed to target CD123, a key marker
…
27th Nov 2024
Magrolimab: Unveiling the Role of Anti-CD47 in Cancer Research and Beyond
What You Need to Know About MagrolimabWhat is Magrolimab?Magrolimab is an anti-CD47 monoclonal antibody that targets the "don't eat me" signal on cancer cells, promoting their destruction by the immune system.Is Magrolimab safe?Magrolimab has shown a manageable safety profile in clinical trials, though side effects such as anemia and infusion reactions have been reported.What is the mechanism of action for Magrolimab?Magrolimab works by blocking CD47, a protein that helps cancer cells evade immune attack, thereby enabling macrophages to target and eliminate these cells.1.) Understanding MagrolimabMagrolimab is a groundbreaking therapeutic antibody developed to target CD47, a pr
…
27th Nov 2024
Elotuzumab: Revolutionizing Multiple Myeloma Treatment and Research Applications
Quick Facts About ElotuzumabWhat is Elotuzumab?Elotuzumab is a monoclonal antibody designed to enhance the immune system's ability to detect and destroy multiple myeloma cells. It targets the SLAMF7 protein, which is present on both myeloma and immune natural killer (NK) cells.How does Elotuzumab work?Elotuzumab activates NK cells by binding to SLAMF7, boosting their ability to attack cancer cells. It also directly marks myeloma cells for immune system destruction, making it a dual-action therapy.What is Elotuzumab used for?Primarily, Elotuzumab is used in combination therapies for relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. These include pairings with drugs like lenalidomide, pom
…
26th Nov 2024
Pembrolizumab: Unveiling Its Mechanism and Research Applications with Biosimilars
Key Facts: PembrolizumabIs Pembrolizumab Safe?Pembrolizumab is widely recognized as safe for most patients, with side effects ranging from mild to severe. Commonly reported side effects include fatigue, rash, and immune-related complications such as colitis or pneumonitis.What is the Mechanism of Action for Pembrolizumab?Pembrolizumab functions by inhibiting the PD-1 pathway, a mechanism that tumors often exploit to evade immune detection. By blocking this pathway, Pembrolizumab enhances the immune system’s ability to identify and destroy cancer cells.Does Pembrolizumab Lower IgG4 Levels?Research has shown that Pembrolizumab can reduce IgG4 levels, which may influence immune mo
…
26th Nov 2024
Daratumumab: Advancing Research in Multiple Myeloma and Beyond
Key Facts About DaratumumabWhat is Daratumumab?Daratumumab is a monoclonal antibody that targets CD38, a protein highly expressed on the surface of multiple myeloma cells.How does Daratumumab work?It binds to CD38, triggering immune-mediated destruction of cancer cells through mechanisms like complement-dependent cytotoxicity and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity.What are the clinical applications of Daratumumab?Daratumumab is primarily used in the treatment of multiple myeloma, both as a monotherapy and in combination with other therapies. Research is also exploring its potential in other hematologic cancers.1.) Understanding DaratumumabDaratumumab is a groundbreaking t
…
26th Nov 2024
MHC Class I vs MHC Class II: Key Differences and Functions
Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) molecules are essential for immune recognition and response. They are specialized glycoproteins that present antigens to T cells, allowing the immune system to identify and eliminate pathogens or abnormal cells. MHC molecules are classified into Class I and Class II, each with distinct structures, functions, and roles in immune defense.This article explores the differences between MHC class I and MHC class II, highlighting their unique features and immune significance.Assay Genie · MHC Class I vs MHC Class II_ Key Differences and Functions1. Overview of MHC MoleculesMHC molecules play a crucial role in antigen presentation, enabling the ada
…
22nd Nov 2024
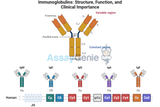
Immunoglobulins: Structure, Function, and Clinical Importance
Immunoglobulins (Igs), also known as antibodies, are glycoproteins produced by B cells and plasma cells. They play a central role in the immune system by identifying and neutralizing pathogens such as bacteria and viruses. These versatile molecules are essential for immune defense, and their alterations can signal immunodeficiencies, infections, or autoimmune conditions.Assay Genie · Immunoglobulins_ Structure, Function, and Clinical Importance1. Structure of ImmunoglobulinsBasic Antibody StructureImmunoglobulins are composed of:Four Polypeptide Chains:Two Heavy Chains (H-chains): Determine the antibody class (e.g., IgG, IgA).Two Light Chains (L-chains): Either kappa (κ) or lamb
…
20th Nov 2024
TREM2: Exploring Its Role in Tumor-Associated Macrophages and Cancer Immunotherapy
Introduction to TREM2 and Tumor-Associated Macrophages in CancerTREM2 (triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2) is an immunoregulatory receptor primarily expressed on macrophages, microglia, monocytes, and dendritic cells. In the context of cancer, TREM2 is highly expressed on tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), a major immune cell population in the tumor microenvironment (TME) that supports tumor growth and immune evasion. TREM2 signaling in TAMs promotes immunosuppressive functions, limiting the ability of the immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells.Research has shown that blocking TREM2 can shift TAMs from an immunosuppressive state to a more pro-inflamm
…
31st Oct 2024
FoxP3: Understanding Regulatory T Cell Control in Tumor Immunity
Introduction to FoxP3 and Regulatory T Cells in CancerFoxP3 (forkhead box P3) is a transcription factor critical for the development and function of regulatory T cells (Tregs), a specialized subset of CD4+ T cells responsible for maintaining immune tolerance and preventing autoimmune reactions. Tregs play a key role in regulating the immune response, preventing excessive immune activation that can damage normal tissues. However, in the context of cancer, Tregs, marked by high FoxP3 expression, often accumulate in the tumor microenvironment (TME) and suppress anti-tumor immune responses, creating an environment that enables tumors to evade immune surveillance.The presence of FoxP
…
30th Oct 2024
CD155: Breaking Immune Suppression in Tumor Environments
Introduction to CD155 in Cancer ImmunotherapyCD155, also known as Poliovirus Receptor (PVR), is a transmembrane protein that plays a pivotal role in tumor immune evasion. While CD155 is normally involved in cell adhesion and migration, its overexpression on tumor cells creates an immunosuppressive environment by engaging inhibitory receptors on natural killer (NK) cells and T cells. Through these interactions, CD155 contributes to the suppression of the body's natural immune responses, helping tumors evade detection and destruction.Targeting CD155 has emerged as a promising strategy to break immune suppression in the tumor microenvironment, allowing immune cells to regain their
…
29th Oct 2024
TNFRSF9: Enhancing Immune Cell Activity Against Tumors
Introduction to TNFRSF9 and Its Role in Immune ActivationTNFRSF9, also known as 4-1BB or CD137, is a co-stimulatory receptor expressed on the surface of T cells, natural killer (NK) cells, and dendritic cells. It belongs to the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily (TNFRSF), which plays critical roles in regulating immune responses. Activation of TNFRSF9 boosts the activity and survival of T cells and NK cells, making it a powerful target in cancer immunotherapy where enhanced anti-tumor immunity is essential for effective treatment.When TNFRSF9 binds to its ligand, 4-1BBL, expressed on antigen-presenting cells (APCs), it delivers a robust co-stimulatory signal that promote
…
29th Oct 2024
Dual PD-1/PD-L2 Blockade: Expanding the Horizons of Cancer Immunotherapy
Introduction to PD-1, PD-L1, and PD-L2 in Cancer ImmunotherapyThe PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint pathway has been instrumental in cancer immunotherapy, with PD-1 (programmed death-1) inhibitors showing success across various cancers by restoring T cell function and enhancing immune responses. PD-1, a receptor on T cells, interacts with its ligand PD-L1, which is commonly expressed on tumor cells and tumor-associated immune cells. This binding suppresses T cell activity, allowing tumors to evade immune destruction. However, PD-L1 is not the only ligand for PD-1—PD-L2 also binds to PD-1 and can significantly contribute to immune evasion in certain tumors.While most current therapies
…
29th Oct 2024
CD86: Enhancing T Cell Activation in Immunotherapy
Introduction to CD86 and Its Role in Immune Activation CD86 is a crucial co-stimulatory molecule that plays an essential role in T cell activation, driving the immune system’s ability to recognize and destroy infected or cancerous cells. Expressed primarily on antigen-presenting cells (APCs) such as dendritic cells, macrophages, and B cells, CD86 binds to receptors on T cells to regulate their activity. CD86 interacts with CD28 to provide a critical co-stimulatory signal necessary for full T cell activation, promoting proliferation, cytokine production, and effector functions in immune responses.In the context of cancer immunotherapy, harnessing CD86's co-stimulatory functi
…
23rd Oct 2024
CD80: Amplifying Immune Activation Through Co-Stimulatory Pathways
Introduction to CD80 and Its Role in Immune Activation CD80 is a critical immune checkpoint molecule that plays an essential role in T cell activation through co-stimulatory pathways. Expressed primarily on antigen-presenting cells (APCs) such as dendritic cells, B cells, and macrophages, CD80 interacts with receptors on T cells to regulate immune responses. Specifically, CD80 engages CD28 to provide a crucial co-stimulatory signal necessary for full T cell activation, proliferation, and differentiation. This co-stimulation amplifies the immune system's ability to recognize and attack pathogens, as well as cancer cells.In addition to its role in immune activation, CD80 can
…
23rd Oct 2024
TLR4: Unraveling the Role of Inflammation in Cancer Progression
Introduction to TLR4 and Cancer Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) is a key component of the innate immune system, primarily responsible for detecting infections and initiating inflammatory responses. This receptor recognizes pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs), such as lipopolysaccharides (LPS) from bacteria, and damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) from injured or stressed cells. Once activated, TLR4 triggers the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which are crucial for defending the body against infections.However, the role of TLR4 in cancer is more complex. While TLR4-mediated inflammation is essential for immune protection, chronic inflammation driven by
…
22nd Oct 2024
CD73: Combating Tumor Immunosuppression by Targeting Adenosine
Introduction to CD73 and Tumor Immunosuppression CD73, also known as ecto-5'-nucleotidase, is an enzyme found on the surface of various cells, including tumor cells and immune cells. It plays a central role in producing adenosine, a molecule with potent immunosuppressive effects, particularly in the tumor microenvironment. By breaking down extracellular ATP (a danger signal) into adenosine, CD73 contributes to creating an environment that dampens immune responses, allowing tumors to evade immune surveillance and grow unchecked.The adenosine pathway has emerged as a critical target in cancer immunotherapy, as elevated adenosine levels within tumors lead to the suppression of
…
21st Oct 2024
CD39: A Novel Target to Overcome Immunosuppression in Cancer
Introduction to CD39 and Cancer Immunosuppression CD39 is an ectonucleotidase enzyme that plays a crucial role in generating adenosine, a powerful immunosuppressive molecule within the tumor microenvironment. By converting extracellular ATP (a danger signal that activates the immune system) into AMP, CD39 initiates the adenosine production pathway, which is completed by CD73. Adenosine, in turn, suppresses immune cell activity, particularly that of T cells, natural killer (NK) cells, and dendritic cells, thus protecting tumor cells from immune destruction.Targeting CD39 with therapies like BU69, a monoclonal antibody that inhibits CD39 activity, is a promising strategy to r
…
21st Oct 2024
SLAMF7: Activating Natural Killer Cells for Potent Anti-Cancer Responses
Introduction to SLAMF7 in Cancer Immunotherapy SLAMF7, also known as Signaling Lymphocytic Activation Molecule F7, is a surface receptor found on natural killer (NK) cells, T cells, plasma cells, and certain immune-regulatory cells. This receptor plays a crucial role in modulating immune responses, particularly by enhancing the cytotoxic activity of NK cells, which are a critical part of the body’s first line of defense against tumors. The SLAMF7 receptor, also referred to as CD319, has garnered significant attention as a target for cancer immunotherapy due to its ability to activate NK cells and facilitate tumor destruction.In cancers such as multiple myeloma and solid tum
…
16th Oct 2024
BTLA: A Key Player in Immune Regulation and Cancer Therapy
Introduction to BTLA in Immune Regulation B and T lymphocyte attenuator (BTLA) is an immune checkpoint molecule that plays a critical role in regulating immune responses by suppressing T cell activity. Structurally similar to other inhibitory receptors like CTLA-4 and PD-1, BTLA functions as a negative regulator of immune activation, maintaining immune tolerance and preventing excessive inflammation. While this is essential for avoiding autoimmune diseases, it can also be exploited by tumors to escape immune surveillance. BTLA's role in immune regulation has made it a promising target for cancer immunotherapy, where blocking its inhibitory effects can restore T cell activit
…
16th Oct 2024
CD122: Fine-Tuning T Cell Responses in Immunotherapy
Introduction to CD122 in Immunotherapy CD122, also known as the interleukin-2 receptor beta chain (IL-2Rβ), is a critical component of the immune system's response to pathogens and malignancies. Its primary function is to mediate signaling through the IL-2 and IL-15 cytokine pathways, which are essential for T cell proliferation, survival, and differentiation. These T cells, particularly CD8+ T cells and natural killer (NK) cells, play a central role in the body’s immune defense against cancer and infections.In recent years, immunotherapy has become a transformative approach in cancer treatment. The ability to harness and modify the body's own immune system to fight tumors
…
15th Oct 2024
TNFR2: Taming Regulatory T Cells to Enhance Anti-Tumor Immunity
In recent years, cancer immunotherapy has become a powerful tool for treating various malignancies. One promising approach involves targeting the tumor microenvironment, particularly regulatory T cells (Tregs), which play a key role in suppressing the immune response against tumors. TNFR2 (Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor 2) is highly expressed on Tregs within the tumor, making it an attractive target for immunotherapy. Antibodies such as https://www.assaygenie.com/tnfr2-taming-regulatory-t-cells-to-enhance-anti-tumor-immunity/, which block TNFR2, have the potential to enhance anti-tumor immunity by reducing the suppressive function of Tregs and promoting a more robust immune resp
…
14th Oct 2024
CD27 Activation: Strengthening the Immune Army Against Cancer
Harnessing the immune system to fight cancer has become a pivotal strategy in modern oncology. A key component in this fight is CD27, a receptor that plays a crucial role in T-cell activation and immune memory. CD27 stimulation can enhance the immune system’s ability to detect and destroy cancer cells, making it an attractive target for immunotherapy. Antibodies such as AT124-5 are being developed to activate CD27, offering new hope for strengthening the immune response against cancer. What is CD27? CD27 is a member of the TNF receptor superfamily, expressed primarily on T cells and B cells. Its primary function is to enhance T-cell activation, support the formation of
…
14th Oct 2024