Enavatuzumab: Revolutionizing Cancer Research Through Novel Therapeutics
Quick Facts About Enavatuzumab
What is Enavatuzumab?
Enavatuzumab is a monoclonal antibody targeting the TWEAK receptor (Fn14), pivotal in tumor growth and immune regulation.
What is the mechanism of action for Enavatuzumab?
Enavatuzumab binds to Fn14, inhibiting signaling pathways that promote tumor cell proliferation and survival while enhancing immune response.
What are the clinical applications of Enavatuzumab?
It is under investigation for treating solid tumors and hematologic malignancies due to its dual action of direct tumor cell targeting and immune system modulation.
Is Enavatuzumab safe?
Emerging studies indicate a manageable safety profile, though further trials are crucial for confirming long-term efficacy and safety.
1.) Understanding Enavatuzumab
Enavatuzumab is an innovative therapeutic antibody that selectively targets the TWEAK receptor (Fn14), which is overexpressed in a variety of cancers, including breast, lung, and pancreatic cancer. The TWEAK receptor plays a key role in tumor progression, immune modulation, and cell survival, making it an ideal target for therapeutic intervention. Enavatuzumab's dual mechanism of action sets it apart from traditional therapies: it not only inhibits tumor cell growth but also enhances the immune system’s ability to recognize and destroy malignant cells.
This dual action is achieved through the direct suppression of cancer cell proliferation and by modulating immune responses, such as increasing the activation of natural killer (NK) cells and promoting macrophage-mediated phagocytosis of tumor cells. By targeting Fn14, Enavatuzumab disrupts the signaling pathways that drive tumor growth and immune evasion, providing a more targeted approach to cancer treatment.
Early preclinical studies have shown promising results, indicating that Enavatuzumab may be especially effective when combined with other cancer therapies, particularly immunotherapies. This synergistic potential could enhance the overall effectiveness of treatment regimens, offering a promising strategy for tackling cancers that are difficult to treat with conventional therapies. As research continues, Enavatuzumab's potential in oncology grows, offering a precision medicine approach that minimizes collateral damage to healthy tissues.
2.) Mechanism of Action of Enavatuzumab
Enavatuzumab exerts its therapeutic effects through a multi-faceted mechanism centered on targeting the Fn14 receptor, which is overexpressed in several aggressive cancers. The TWEAK/Fn14 signaling axis plays a critical role in tumor progression by promoting cell survival, angiogenesis, and immune evasion. By binding to Fn14, Enavatuzumab disrupts this signaling pathway, directly inhibiting tumor growth and survival. The binding of Enavatuzumab to the Fn14 receptor triggers multiple cellular responses, including apoptosis, or programmed cell death, within the cancerous cells, preventing their continued proliferation.
In addition to directly killing tumor cells, Enavatuzumab enhances the body's immune response through antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC). In this process, immune effector cells such as natural killer (NK) cells recognize and destroy antibody-bound tumor cells, amplifying the immune system's ability to target and eliminate cancer cells. This dual action of direct tumor cell targeting and immune system activation makes Enavatuzumab a powerful tool in precision oncology.
Recent studies suggest that Enavatuzumab may also modulate the tumor microenvironment by reducing inflammation and facilitating immune cell infiltration into tumors. This effect could improve the immune system's ability to recognize and fight cancer, especially in challenging cancers like triple-negative breast cancer and metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma. By reprogramming the tumor microenvironment, Enavatuzumab enhances the overall effectiveness of cancer immunotherapies, offering a promising strategy for hard-to-treat malignancies.
3.) Clinical Applications of Enavatuzumab
Enavatuzumab is a promising therapeutic monoclonal antibody that has been explored in multiple clinical settings, with a primary focus on solid tumors and hematological malignancies. This antibody is designed to selectively target Fn14, a receptor overexpressed in various cancers while sparing healthy tissues. Fn14 is commonly associated with tumor progression, invasion, and metastasis, making it an attractive target for precision oncology. Enavatuzumab’s specificity allows it to concentrate its effects on cancer cells, minimizing off-target toxicity and enhancing its safety profile. Early-phase clinical trials have shown encouraging results in cancers with high Fn14 expression, including glioblastoma, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), and ovarian cancer, demonstrating significant potential in addressing these challenging malignancies.
One of the most compelling aspects of Enavatuzumab is its utility in combination therapies. When paired with immune checkpoint inhibitors, such as anti-PD-1 or anti-CTLA-4 antibodies, it has demonstrated synergistic effects in preclinical models. This combination approach enhances tumor cell killing while reactivating the immune system to mount a sustained anti-tumor response. Such synergism could be crucial in overcoming resistance to conventional therapies, especially in advanced-stage or refractory cancers.
Although clinical data on Enavatuzumab are still evolving, its unique mechanism of action and adaptability to combination regimens underscore its potential in advancing oncology treatment strategies. Researchers are particularly optimistic about its role in cancers with limited treatment options, where its precision targeting and immune-boosting capabilities could fill significant unmet needs and improve patient outcomes.

4.) Exploring Biosimilars for Enavatuzumab
What is a Biosimilar?
A biosimilar is a biologic medical product that is highly similar to an already approved reference product. It offers equivalent efficacy and safety but often at a lower cost, making advanced therapies more accessible for research and clinical applications.
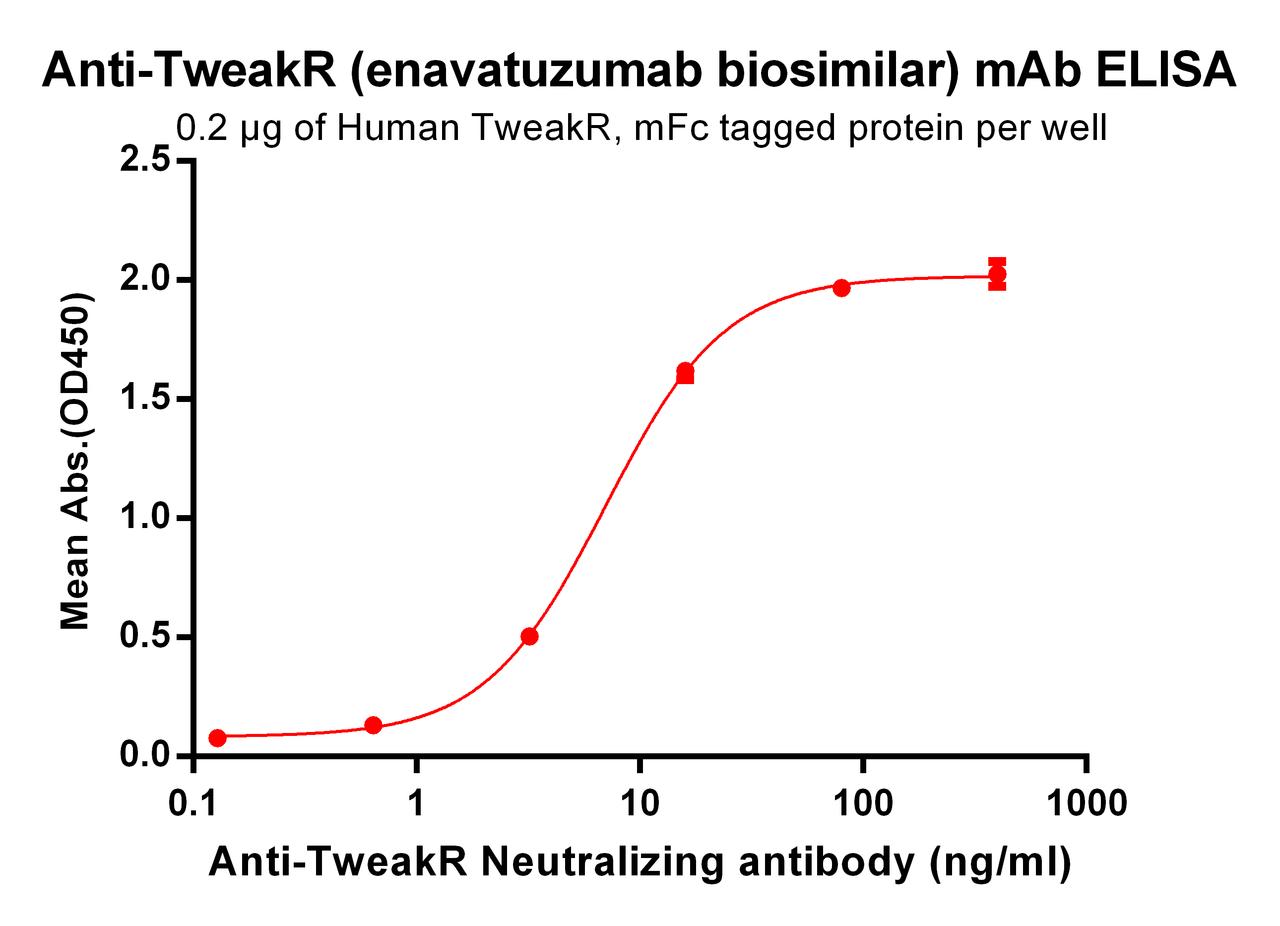
| Enavatuzumab (Anti-TweakR) Biosimilar Antibody | |
|---|---|
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Protein: | TweakR |
| Reactivity: | Human |
How Does the Enavatuzumab Biosimilar Compare to Enavatuzumab?
Our Enavatuzumab biosimilar is designed for research use only, closely mimicking the structure and function of the original antibody. It retains the ability to bind Fn14 and trigger similar biological responses, making it a valuable tool for preclinical studies and drug development.
Benefits of the Enavatuzumab Biosimilar
2. Reliability: Offers consistent performance in experimental settings.
3. Advancing Discoveries: Facilitates exploration of new therapeutic combinations and mechanisms.
Research Use Only Disclaimer
The Enavatuzumab biosimilar is strictly for research use and not intended for clinical applications. This distinction ensures compliance with regulatory standards while supporting innovation in laboratory settings.
Discover Our Biosimilar Range
At Assay Genie, we specialize in providing high-quality biosimilars for research use! Check out our full biosimilar range to learn more.

By Marina Alberto, PhD
Marina Alberto, PhD, holds a robust academic background in Biotechnology, earning her Bachelor’s Degree and PhD in Science and Technology from Quilmes National University. Her research spans cancer immunotherapy, glycan profiling, and vaccine development, including innovative projects on pediatric leukemia diagnosis and cancer-associated carbohydrate-mimetic vaccines. She currently serves as a Technical Support and Sales Specialist at Assay Genie.
Recent Posts
-
IgG1 Plasma Cells: The Emerging Biomarker for Predicting Cancer Immunotherapy Success
In the relentless fight against cancer, immunotherapy has emerged as a beacon of hope, harnessing t …24th Feb 2026 -
The Rise of Cancer Neuroscience: How Neural Circuits Drive Tumor Progression
For decades, we viewed cancer as a rogue army of cells, a biological glitch driven solely by geneti …23rd Feb 2026 -
CRISPR-Powered Light Sensors: A New Frontier in Ultra-Sensitive Cancer Detection
Cancer detection often relies on advanced imaging or invasive procedures, frequently catching the d …20th Feb 2026




