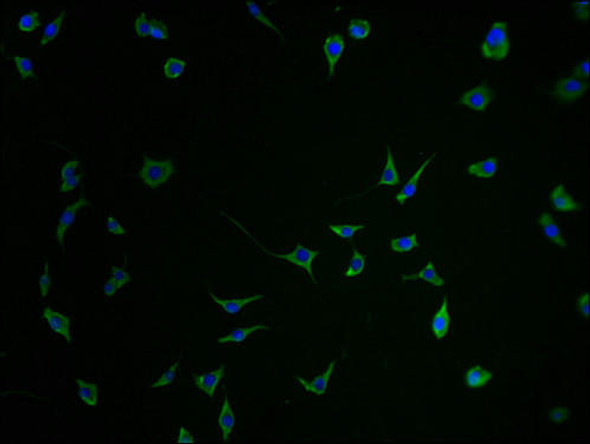
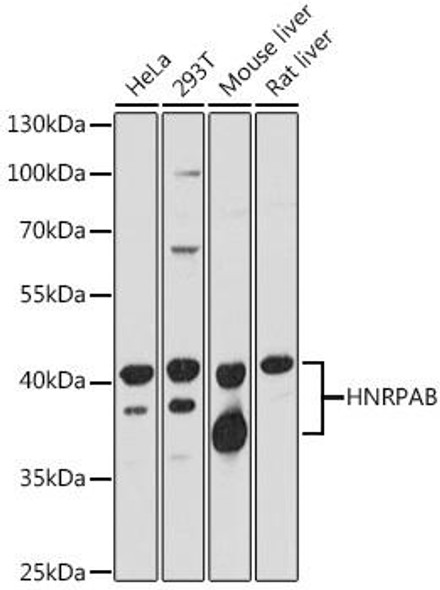
Description
MMAB Antibody (PACO10519)
The MMAB Polyclonal Antibody (PAC010519) is a valuable tool for researchers studying the MMAB protein, which plays a crucial role in the biosynthesis of adenosylcobalamin (AdoCbl), an essential cofactor for multiple enzymes involved in various metabolic pathways. This antibody, produced in rabbits, demonstrates high specificity and sensitivity for detecting MMAB in human samples, making it a reliable choice for Western blot applications.MMAB is a key enzyme involved in the conversion of cobalamin to AdoCbl, a process essential for the normal function of several enzymes responsible for amino acid and fatty acid metabolism. Dysregulation of MMAB activity can lead to disorders such as methylmalonic acidemia and homocystinuria, highlighting the importance of studying this protein in the context of metabolic diseases.
By utilizing the MMAB Polyclonal Antibody, researchers can gain insight into the expression and function of MMAB in different cell types and tissues, providing valuable information for understanding the role of this enzyme in health and disease. This antibody is a valuable tool for studies in biochemistry, metabolism, and metabolic disorders, offering a reliable means of investigating the complex pathways involving AdoCbl biosynthesis.
| Antibody Name: | MMAB Antibody (PACO10519) |
| Antibody SKU: | PACO10519 |
| Size: | 50ul |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Tested Applications: | ELISA, WB, IHC |
| Recommended Dilutions: | |
| Species Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen: | Human MMAB |
| Form: | Liquid |
| Storage Buffer: | PBS with 0.1% Sodium Azide, 50% Glycerol, pH 7.3. -20°C, Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. |
| Purification Method: | Antigen Affinity Purified |
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Conjugate: | Non-conjugated |
| Synonyms: | methylmalonic acid, ria (cobalamin deficiency) cblB type;MMAB;ATR;MGC20496;cblB ; |
| UniProt Protein Function: | MMAB: Defects in MMAB are the cause of methylmalonic aciduria type cblB (MMAB); also known as methylmalonic aciduria type B or vitamin B12-responsive methylmalonicaciduria of cblB complementation type. MMAB is a disorder of methylmalonate and cobalamin metabolism due to defective synthesis of adenosylcobalamin. Inheritance is autosomal recessive. Belongs to the Cob(I)alamin adenosyltransferase family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Motility/polarity/chemotaxis; EC 2.5.1.17; Transferase; Cofactor and Vitamin Metabolism - porphyrin and chlorophyll Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 12q24 Cellular Component: mitochondrial matrix Molecular Function:cob(I)yrinic acid a,c-diamide adenosyltransferase activity; ATP binding Biological Process: vitamin metabolic process; cobalamin biosynthetic process; cobalamin metabolic process; water-soluble vitamin metabolic process Disease: Methylmalonic Aciduria, Cblb Type |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a protein that catalyzes the final step in the conversion of vitamin B(12) into adenosylcobalamin (AdoCbl), a vitamin B12-containing coenzyme for methylmalonyl-CoA mutase. Mutations in the gene are the cause of vitamin B12-dependent methylmalonic aciduria linked to the cblB complementation group. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2011] |
| UniProt Code: | Q96EY8 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 38258221 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 326625 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q96EY8.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q96EY8,Q9D273, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q96EY8 |
| Molecular Weight: | 27388 |
| NCBI Full Name: | Corrinoid adenosyltransferase |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | metabolism of cobalamin associated B |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | MMAB |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | ATR; cob; cblB; CFAP23 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | corrinoid adenosyltransferase |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Cob(I)yrinic acid a,c-diamide adenosyltransferase, mitochondrial |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Cob(I)alamin adenosyltransferase; Methylmalonic aciduria type B protein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | MMAB |
| UniProt Entry Name: | MMAB_HUMAN |