Glenzocimab: A Novel Antiplatelet Therapy for Stroke Prevention
Quick Facts About Glenzocimab
What is Glenzocimab?
How does Glenzocimab work?
What are the clinical applications of Glenzocimab?
1.) Understanding Glenzocimab
Glenzocimab is a first-in-class monoclonal antibody designed to offer a safer and more targeted alternative to traditional antiplatelet therapies. Unlike widely used agents such as aspirin and clopidogrel, which broadly inhibit platelet activation and aggregation, Glenzocimab selectively targets glycoprotein VI (GPVI), a key receptor involved in pathological thrombus formation. This precision-driven mechanism provides an innovative approach to stroke prevention and thrombotic disease management by reducing clot formation while preserving essential hemostatic functions.
The development of Glenzocimab addresses a critical challenge in cardiovascular medicine: balancing effective stroke prevention with minimizing bleeding risks. Traditional antiplatelets, though effective at preventing thrombotic events, also impair normal platelet function, increasing the likelihood of spontaneous or excessive bleeding. This is particularly problematic for patients requiring long-term therapy, such as those with atrial fibrillation or a history of ischemic stroke. Glenzocimab’s selective inhibition of GPVI offers a potential breakthrough by reducing the risk of arterial thrombosis while maintaining the body's ability to form necessary clots for wound healing.
With stroke remaining a leading cause of disability and mortality worldwide, novel therapeutic options are essential. Glenzocimab has demonstrated promising results in clinical trials, showing potential not only in acute ischemic stroke treatment but also in secondary stroke prevention and broader cardiovascular applications. Ongoing studies continue to explore its efficacy in various high-risk conditions, including atrial fibrillation, myocardial infarction, and peripheral artery disease. As research progresses, Glenzocimab could emerge as a key advancement in neurovascular and cardiovascular medicine, offering a safer and more effective alternative to conventional antiplatelet therapies.
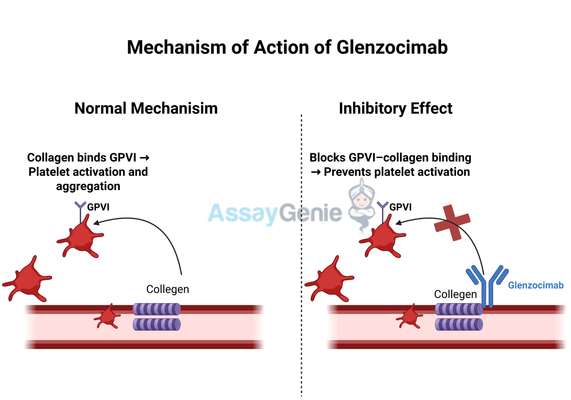
2.) Mechanism of Action of Glenzocimab
Glenzocimab exerts its effects by inhibiting GPVI, a collagen-binding glycoprotein found on the surface of platelets. GPVI plays a crucial role in platelet adhesion, activation, and aggregation in response to vascular injury. This receptor is particularly important in forming arterial thrombi, as it mediates platelet interactions with exposed collagen in damaged blood vessels. However, excessive GPVI activation can lead to pathological thrombus formation, increasing the risk of ischemic stroke and other thrombotic disorders.
By selectively blocking GPVI, Glenzocimab prevents the formation of occlusive blood clots while allowing normal platelet function necessary for physiological hemostasis. This selective inhibition is a major advantage over conventional antiplatelet drugs, such as P2Y12 inhibitors and aspirin, which inhibit broader pathways involved in platelet activation, often leading to systemic bleeding complications. In contrast, Glenzocimab’s targeted approach reduces the likelihood of hemorrhagic side effects, making it a particularly attractive option for high-risk patients.
A key feature of Glenzocimab’s mechanism is its reversibility. Studies suggest that once treatment is stopped, platelet function gradually recovers, providing an additional safety advantage. This characteristic is particularly beneficial in acute settings, such as ischemic stroke, where controlled thrombus reduction is essential without compromising overall hemostatic integrity. Research into Glenzocimab’s pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics continues to refine its optimal therapeutic window, ensuring its safety and efficacy across different patient populations.
With its unique mechanism, Glenzocimab holds significant potential not only for acute stroke management but also for long-term prevention of thrombotic events in cardiovascular conditions. Ongoing clinical investigations are assessing its role in various thromboembolic disorders, positioning it as a potential breakthrough in targeted antiplatelet therapy.
3.) Clinical Applications of Glenzocimab
Acute Ischemic Stroke (AIS)
One of Glenzocimab’s most promising applications is in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke (AIS), where rapid intervention is critical to restoring blood flow to the brain. Current stroke management relies heavily on thrombolytic therapy, particularly tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), and mechanical thrombectomy in eligible patients. However, these interventions are often limited by the risk of hemorrhagic transformation, a serious complication that occurs when weakened blood vessels rupture due to aggressive clot dissolution.
Clinical trials have explored Glenzocimab as an adjunct therapy to thrombolytics, with the goal of enhancing clot breakdown while minimizing bleeding risks. By targeting GPVI, Glenzocimab helps prevent excessive platelet activation and secondary thrombus formation without impairing normal hemostasis. Preliminary data suggest that this approach may improve overall stroke outcomes, potentially reducing infarct size and enhancing neurological recovery.
Secondary Stroke Prevention
Patients who have experienced an ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA) are at significant risk of recurrence, often necessitating long-term antiplatelet therapy. However, many individuals struggle with the bleeding risks associated with conventional antiplatelet agents, particularly those with underlying conditions such as gastrointestinal ulcers or cerebral microbleeds.
Glenzocimab is being investigated as a potential long-term therapeutic option for secondary stroke prevention, particularly in patients who cannot tolerate traditional antiplatelets. By selectively targeting GPVI, it offers a means of reducing thrombotic risk while preserving normal clotting function, potentially lowering the likelihood of spontaneous bleeding events.
Cardiovascular and Thrombotic Conditions
Beyond stroke management, Glenzocimab’s unique mechanism suggests potential applications in various cardiovascular and thrombotic conditions. In diseases such as atrial fibrillation, myocardial infarction, and peripheral artery disease, arterial thrombosis plays a major role in disease progression and adverse outcomes. Traditional anticoagulants and antiplatelet drugs remain the standard of care, but their bleeding risks often necessitate careful patient selection and monitoring.
Glenzocimab’s targeted GPVI inhibition could offer an alternative approach, reducing thrombotic risk in high-risk patients while preserving necessary platelet function. Preliminary studies suggest that it may have a role in preventing arterial thrombosis in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary interventions (PCI) or those with chronic vascular disease.

4.) Exploring Biosimilars for Glenzocimab
What is a Biosimilar?
| Glenzocimab (Anti-GP6) Biosimilar Antibody | |
|---|---|
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Protein: | GP6 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
How Glenzocimab Biosimilar Compares to Glenzocimab
Biosimilars of Glenzocimab are designed to replicate its mechanism of action while providing a cost-effective option for scientific exploration. They facilitate drug discovery by allowing researchers to investigate GPVI inhibition in various disease models without relying on limited clinical supplies of the original biologic.
Benefits of Glenzocimab Biosimilar for Research
Cost-Effective Studies: Enables extensive research without the high costs associated with proprietary biologics.
Accessibility: Provides wider access to GPVI-targeting agents for laboratories studying thrombotic diseases.
Regulatory Flexibility: Facilitates preclinical testing in conditions where clinical-grade Glenzocimab may not be available.
Research Use Only Disclaimer:
Discover Our Biosimilar Range
At Assay Genie, we specialize in providing high-quality biosimilars for research use! Check out our full biosimilar range to learn more.

By Chris McNally, PhD
Chris McNally, PhD, has a strong foundation in Biomedical Science, completing a PhD scholarship in collaboration with Randox Laboratories and Ulster University. Chris has published extensively in prostate cancer research, focusing on biomarker discovery, cancer risk stratification, and molecular mechanisms such as hypoxia-induced regulation. He currently serves as a Business Development Manager at Assay Genie.
Recent Posts
-
IgG1 Plasma Cells: The Emerging Biomarker for Predicting Cancer Immunotherapy Success
In the relentless fight against cancer, immunotherapy has emerged as a beacon of hope, harnessing t …24th Feb 2026 -
The Rise of Cancer Neuroscience: How Neural Circuits Drive Tumor Progression
For decades, we viewed cancer as a rogue army of cells, a biological glitch driven solely by geneti …23rd Feb 2026 -
CRISPR-Powered Light Sensors: A New Frontier in Ultra-Sensitive Cancer Detection
Cancer detection often relies on advanced imaging or invasive procedures, frequently catching the d …20th Feb 2026