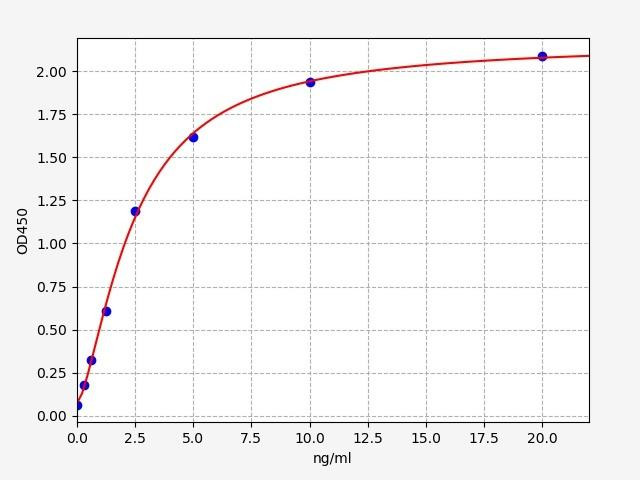
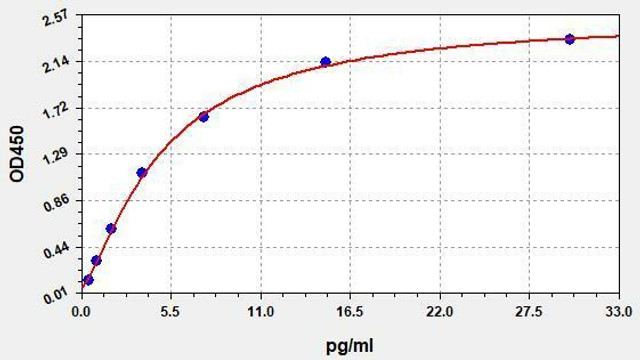
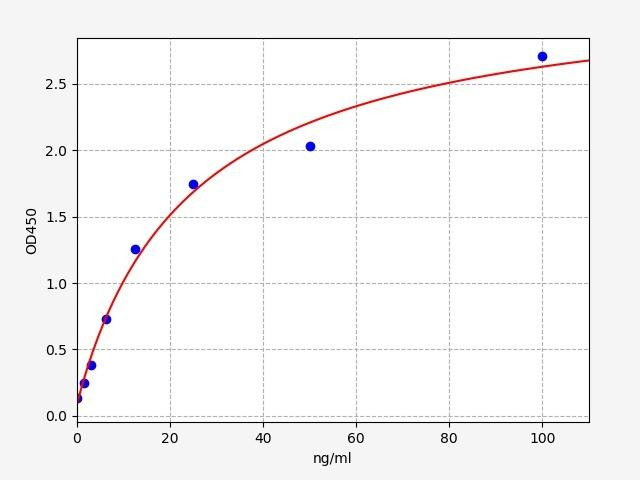
Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) are very large molecules that are composed of sugars and lipids. They are a major component of the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria and can trigger strong immune responses. LPS has been implicated in a variety of diseases, including sepsis, arthritis and atherosclerosis. LPS is often used as a biomarker for bacterial infection, with LPS ELISA Kits typically used in the research of immune responses. LPS ELISA kits can also be used to study pneumothroax (collapsed lung).
The Assay Genie LPS ELISA Kit allows for the quantitative determination of LPS in serum, blood, plasma, cell culture supernatant and other related supernatants and tissue samples.