Description
Recombinant Human Fibronectin/CIG/FN1 Protein
The Recombinant Human Fibronectin/CIG/FN1 Protein is a biologically active recombinant protein that plays a significant role in various cellular processes and signaling pathways in human biology. This protein is widely employed in immunological research, cell biology studies, protein-protein interaction analyses, and therapeutic development, providing researchers with a reliable tool for investigating Fibronectin/CIG/FN1 function and its implications in health and disease.
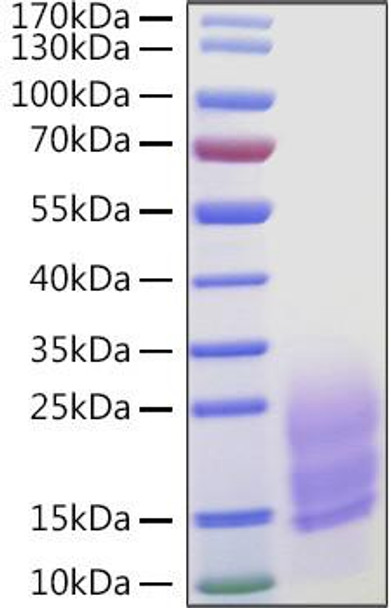
This product (SKU: RPCB0990) is produced using HEK293 cells and features a C-His tag for convenient detection and purification. The protein exhibits a calculated molecular weight of 10.70 kDa with an observed molecular weight of 15-30 kDa under denaturing conditions, achieving ≥ 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE.. Functional bioactivity has been validated through rigorous quality control assays, confirming its suitability for demanding research applications.
Key Features
| High Purity by Affinity Chromatography | |
| Mammalian & Bacterial Expression Systems | |
| High lot-to-lot consistency via strict QC |
| Product Name: | Recombinant Human Fibronectin/CIG/FN1 Protein |
| SKU: | RPCB0990 |
| Size: | 20 μg , 50 μg , 100 μg |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Synonyms: | FN1, CIG, ED-B, FINC, FN, FNZ, GFND, GFND2, LETS, MSF, fibronectin |
| Tag: | C-His |
| Expression Host: | HEK293 cells |
| Calculated MW: | 10.70 kDa |
| Observed MW: | 15-30 kDa |
| Gene ID: | 2335 |
| Protein Description: | High quality, high purity and low endotoxin recombinant Recombinant Human Fibronectin/CIG/FN1 Protein (RPCB0990), tested reactivity in HEK293 cells and has been validated in SDS-PAGE.100% guaranteed. |
| Endotoxin: | Please contact us for more information. |
| Purity: | ≥ 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE. |
| Formulation: | Lyophilized from a 0.22 μm filtered solution of PBS, pH 7.4. |
| Bio-Activity: | Measured by the ability of the immobilized protein to support the adhesion of NIH-3T3 mouse embryonic fibroblast cells.When cells are added to Fibronectin coated plates (2.5 μg/mL and 100 μL/well), approximately 30%-40% cells will adhere specifically after 30 minutes at 37℃. |
| Reconstitution: | Centrifuge the vial before opening. Reconstitute to a concentration of 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile distilled water. Avoid vortex or vigorously pipetting the protein. For long term storage, it is recommended to add a carrier protein or stablizer (e.g. 0.1% BSA, 5% HSA, 10% FBS or 5% Trehalose), and aliquot the reconstituted protein solution to minimize free-thaw cycles. |
| Storage: | Store at -20℃.Store the lyophilized protein at -20℃ to -80 ℃ up to 1 year from the date of receipt. After reconstitution, the protein solution is stable at -20℃ for 3 months, at 2-8℃ for up to 1 week. |
Fibronectin (FN) is a glycoprotein component of the extracellular matrix of the extracellular matrix (ECM) with roles in embryogenesis, development, and wound healing. More recently, FN has emerged as player in platelet thrombus formation and diseases associated with thrombosis including vascular remodeling, atherosclerosis, and cardiac repair following a myocardial infarct. Each monomer of FN consists of three types of homologous repeating units, that is 12 type I repeats, two type II repeats and 15-17 type III repeats. The occurrence of multiple isoforms results from alternative mRNA splicing of the ED-A, ED-B and III-CS regions, and subsequent post-translational modification. As an ECM component and one of the primary cell adhesion molecules, Fibronectin can be a ligand for fibrin, heparin, chondroitin sulfate, collagen/gelatin, as well as many integrin receptors through which FN mediates the variety of cellular signaling pathways. The study of solid human tumors showed among the early signs of malignant transformation the fragmentation of pericellular FN, concommitent with the increase of its production by the peritumoral stroma. These results should encourage further investigations concerning the potential importance of Fn production and breakdown during cancer progression. FN1 expression has been described to increase significantly from the morula towards the early blastocyst stage, suggesting that FN1 may also be involved in early blastocyst formation. The fragment 2 of FN comprises the first 7 FN type III repeats and is suggested to be important for self association during fibril growth via the key module III2.