Description
Recombinant Mouse Neuropilin-1/NRP1/VEGF165R/CD304 Protein
The Recombinant Mouse Neuropilin-1/NRP1/VEGF165R/CD304 Protein is a high-quality recombinant protein designed for murine biological research applications. This protein serves as an essential reagent in mouse model studies, comparative immunology research, and preclinical therapeutic evaluations, enabling scientists to investigate Neuropilin-1/NRP1/VEGF165R/CD304 biology and its relevance to human disease mechanisms through translational research approaches.
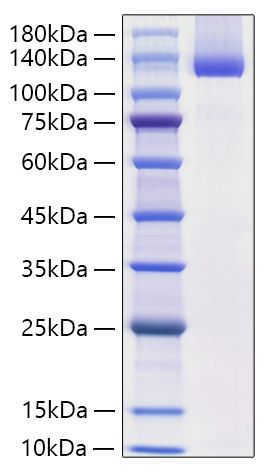
This product (SKU: RPCB1387) is produced using HEK293 cells and features a C-His tag for convenient detection and purification. The protein exhibits a calculated molecular weight of 94.51 kDa with an observed molecular weight of 120-140 kDa under denaturing conditions, achieving ≥ 90% as determined by SDS-PAGE., ensuring exceptional quality and consistency for research applications.
Key Features
| High Purity by Affinity Chromatography | |
| Mammalian & Bacterial Expression Systems | |
| High lot-to-lot consistency via strict QC |
| Product Name: | Recombinant Mouse Neuropilin-1/NRP1/VEGF165R/CD304 Protein |
| SKU: | RPCB1387 |
| Size: | 10 μg , 20 μg , 50 μg , 100 μg |
| Reactivity: | Mouse |
| Synonyms: | BDCA4, BDCA-4, CD304 antigen, CD304, DKFZp686A03134, DKFZp781F1414, neuropilin 1, Neuropilin1, Neuropilin-1, NP1, NRP, NRP1, transmembrane receptor, Vascular endothelial cell growth factor 165 receptor, VEGF165R |
| Tag: | C-His |
| Expression Host: | HEK293 cells |
| Calculated MW: | 94.51 kDa |
| Observed MW: | 120-140 kDa |
| Gene ID: | 18186 |
| Protein Description: | High quality, high purity and low endotoxin recombinant Recombinant Mouse Neuropilin-1/NRP1/VEGF165R/CD304 Protein (RPCB1387), tested reactivity in HEK293 cells and has been validated in SDS-PAGE.100% guaranteed. |
| Endotoxin: | < 0.1 EU/μg of the protein by LAL method. |
| Purity: | ≥ 90% as determined by SDS-PAGE. |
| Formulation: | Lyophilized from a 0.22 μm filtered solution of PBS, pH 7.4. |
| Reconstitution: | Centrifuge the vial before opening. Reconstitute to a concentration of 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile distilled water. Avoid vortex or vigorously pipetting the protein. For long term storage, it is recommended to add a carrier protein or stablizer (e.g. 0.1% BSA, 5% HSA, 10% FBS or 5% Trehalose), and aliquot the reconstituted protein solution to minimize free-thaw cycles. |
| Storage: | Store at -20℃.Store the lyophilized protein at -20℃ to -80 ℃ up to 1 year from the date of receipt. After reconstitution, the protein solution is stable at -20℃ for 3 months, at 2-8℃ for up to 1 week. |
Neuropilin-1 (Npn-1, previously neuropilin; also CD304 or BDCA4 in humans) is a 130 140 kDa type I transmembrane (TM) glycoprotein that regulates axon guidance and angiogenesis. The full-length 923 amino acid (aa) mouse Npn-1 contains a 623 aa extracellular domain (ECD) that shares 98% aa identity with rat and 93% aa identity with human, equine, bovine and canine Npn-1. The ECD contains two N-terminal CUB domains (termed a1a2), two domains with homology to coagulation factors V and VIII (b1b2) and a MAM (meprin) domain (c). At least one splice variant that diverges at aa 587 and lacks the TM domain has been sequenced. This form is potentially a soluble antagonist, based on results from human Npn-1 splice variants. The sema domains of Class III secreted semaphorins such as Sema3A bind Npn-1 a1a2. Heparin, the heparin-binding forms of VEGF (VEGF165, VEGF-B and VEGF-E), PlGF (PlGF2), and the C terminus of Sema3 bind the b1b2 region. Npn-1 and Npn-2 share 48% aa identity within the ECD and can form homo- and hetero-oligomers via interaction of their MAM domains. Neuropilins show partially overlapping expression in neuronal and endothelial cells during development. Both Neuropilins act as co-receptors with plexins, mainly plexin A3 and A4, to bind class III semaphorins that mediate axon repulsion. However, only Npn-1 binds Sema3A, and only Npn-2 binds Sema3F. Both are co receptors with VEGF R2 (also called KDR or Flk-1) for VEGF165 binding. Sema3A signaling can be blocked by VEGF165, which has higher affinity for Npn-1. Npn-1 is preferentially expressed in developing or remodeling arteries. Npn-1 is also expressed on dendritic cells and mediates DC-induced T cell proliferation.