Description
Recombinant Rat IL-1Ra/IL-1F3/IL-1RN Protein
The Recombinant Rat IL-1Ra/IL-1F3/IL-1RN Protein is a high-quality recombinant protein produced for advanced research applications in molecular biology and biotechnology. This protein serves as a critical reagent in various experimental contexts, including functional studies, binding assays, and therapeutic development programs, providing researchers with a standardized and reliable tool for investigating protein function and interactions.
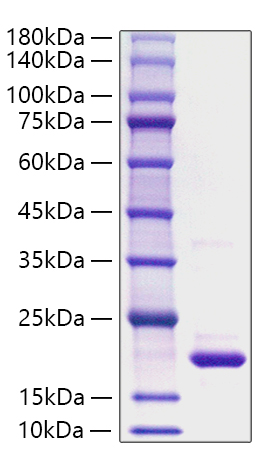
This product (SKU: RPCB1823) is produced using E. coli and features a NO-tag tag for convenient detection and purification. The protein exhibits a calculated molecular weight of 17.38 kDa with an observed molecular weight of 15-25 kDa under denaturing conditions, achieving ≥ 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE.. Functional bioactivity has been validated through rigorous quality control assays, confirming its suitability for demanding research applications.
Key Features
| High Purity by Affinity Chromatography | |
| Mammalian & Bacterial Expression Systems | |
| High lot-to-lot consistency via strict QC |
| Product Name: | Recombinant Rat IL-1Ra/IL-1F3/IL-1RN Protein |
| SKU: | RPCB1823 |
| Size: | 10 μg , 20 μg , 50 μg , 100 μg |
| Reactivity: | Rat |
| Synonyms: | IL-1ra, il1ra, il-1ra, IL1RA |
| Tag: | NO-tag |
| Expression Host: | E. coli |
| Calculated MW: | 17.38 kDa |
| Observed MW: | 15-25 kDa |
| Gene ID: | 60582 |
| Protein Description: | High quality, high purity and low endotoxin recombinant Recombinant Rat IL-1Ra/IL-1F3/IL-1RN Protein (RPCB1823), tested reactivity in E. coli and has been validated in SDS-PAGE.100% guaranteed. |
| Endotoxin: | < 1 EU/μg of the protein by LAL method. |
| Purity: | ≥ 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE. |
| Formulation: | Lyophilized from a 0.22 μm filtered solution of PBS, pH 7.4. |
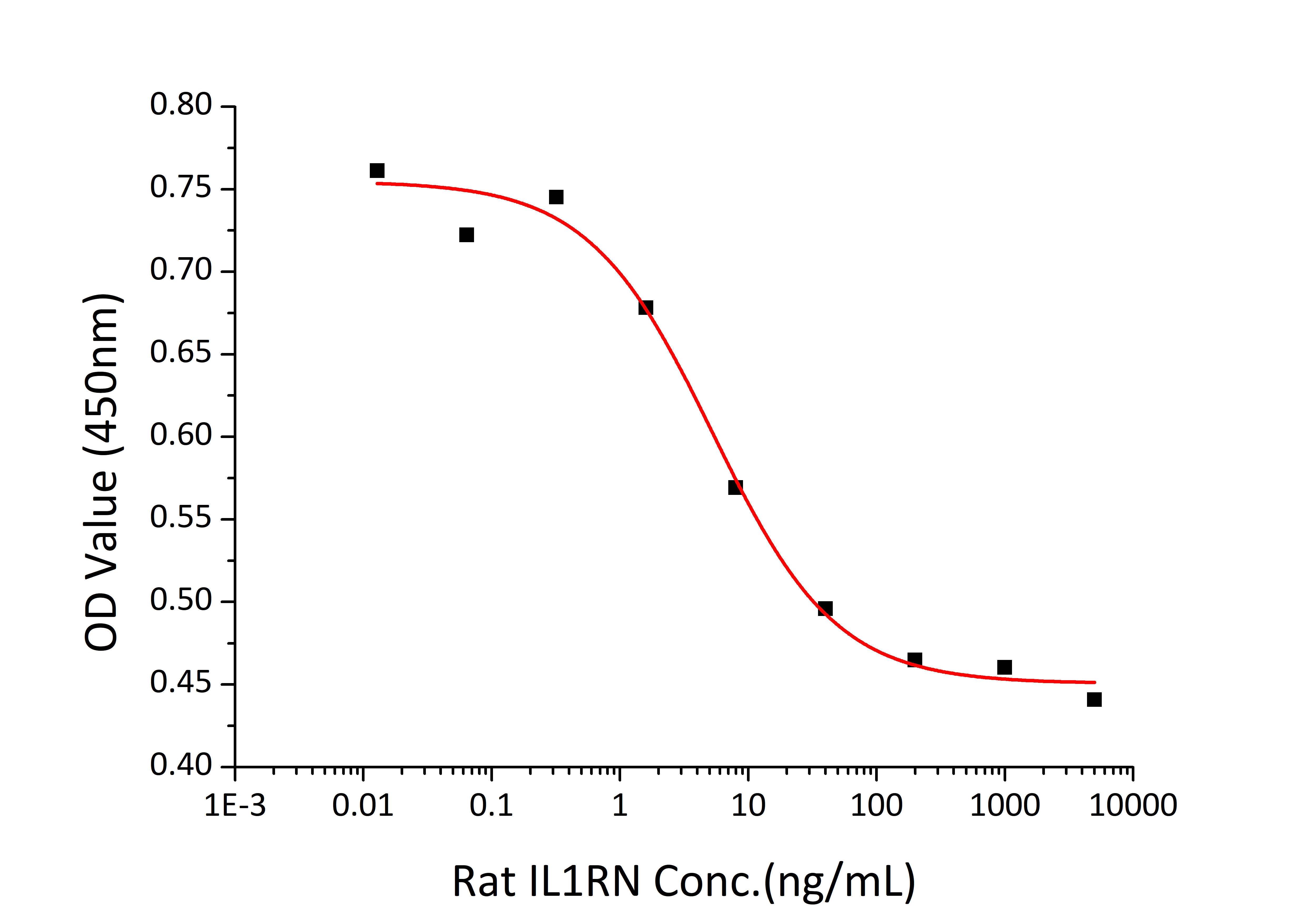
| Bio-Activity: | Measured by its ability to inhibit IL-1 alpha-dependent proliferation in D10.G4.1 mouse helper T cells. The ED 50 for this effect is 2.62-10.48 ng/mL in the presence of 50 pg/mL of rrIL-1 alpha(RPCB1186), corresponding to a specific activity of 9.54×10 4 ~3.82×10 5 units/mg. |
| Reconstitution: | Centrifμge the vial before opening. Reconstitute to a concentration of 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile distilled water. Avoid vortex or vigorously pipetting the protein. For long term storage, it is recommended to add a carrier protein or stablizer (e.g. 0.1% BSA, 5% HSA, 10% FBS or 5% Trehalose), and aliquot the reconstituted protein solution to minimize free-thaw cycles. |
| Storage: | Store at -20℃.Store the lyophilized protein at -20℃ to -80 ℃ up to 1 year from the date of receipt. After reconstitution, the protein solution is stable at -20℃ for 3 months, at 2-8℃ for up to 1 week. |
Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1RA) also known as IL1RN is a member of the interleukin 1 cytokine family. This protein inhibits the activities of interleukin 1, alpha (IL1A), and interleukin 1, beta (IL1B), and modulates a variety of interleukin 1 related immune and inflammatory responses. A polymorphism of this protein-encoding gene is reported to be associated with an increased risk of osteoporotic fractures and gastric cancer. IL-1RA/IL1RN may inhibit the activity of IL-1 by binding to its receptor and it has no IL-1 like activity. Genetic variation in IL-1RA/IL1RN is associated with susceptibility to microvascular complications of diabetes type 4 (MVCD4). These are pathological conditions that develop in numerous tissues and organs as a consequence of diabetes mellitus. They include diabetic retinopathy, diabetic nephropathy leading to end-stage renal disease, and diabetic neuropathy. Diabetic retinopathy remains the major cause of new-onset blindness among diabetic adults. It is characterized by vascular permeability and increased tissue ischemia and angiogenesis. Defects in IL-1RA/IL1RN are the cause of interleukin 1 receptor antagonist deficiency (DIRA) which is also known as deficiency of interleukin 1 receptor antagonist. Autoinflammatory diseases manifest inflammation without evidence of infection, high-titer autoantibodies, or autoreactive T-cells. DIRA is a rare, autosomal recessive, genetic autoinflammatory disease that results in sterile multifocal osteomyelitis, and pustulosis from birth.