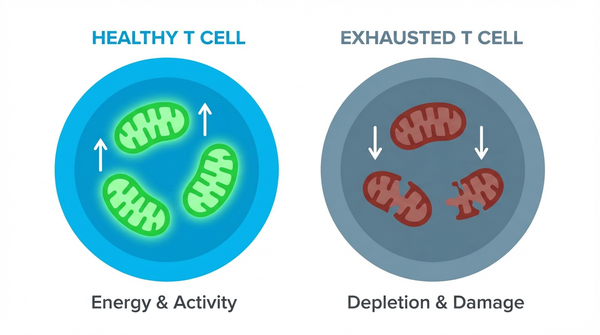
The Powerhouse of Immunity: How Mitochondrial Fitness Fuels the Fight Against Cancer
Why do powerful cancer immunotherapies work wonders for some patients but fail for others? The answer may lie not just in the cancer cells themselves, but in the energy levels of our own immune warriors. T cells, the elite soldiers of our immune system, often run out of steam in the hostile environment of a tumor, a phenomenon known as 'exhaustion.' But what if we could recharge their batteries? Emerging research reveals that the metabolic fitness of T cells—specifically the health of their mitochondria—is a critical battleground in the war on cancer, and scientists are now learning how to turn the tide.
Introduction
Our immune system is constantly on patrol, with CD8+ T cells acting as specialized assassins that identify and destroy cancerous cells. For decades, the goal of immunotherapy has been to unleash these cells to do their job more effectively.
However, the tumor microenvironment is a grueling battlefield. It's low on nutrients and oxygen, forcing T cells into a state of metabolic crisis. This, combined with constant stimulation from cancer antigens, leads to T cell exhaustion, where they lose their ability to fight and proliferate.
This is where the field of immunometabolism comes in. It explores the profound connection between a T cell's metabolic state and its function. Scientists are discovering that by targeting metabolism, we can make T cells more resilient, effective, and long-lasting, opening a new chapter in cancer treatment.
Study Summary
Building on decades of work, researchers have made significant progress. Scientists discovered that mitochondrial transfer via nanotubes enhances T cell fitness played a central role in their investigation.
Key Findings
The research uncovered several important discoveries that advance our understanding of this biological system.
- Finding 1: In the harsh, low-oxygen tumor environment, persistent T cell activation leads to severe mitochondrial stress. This metabolic crisis results in the accumulation of damaging reactive oxygen species (ROS) and a failure of the T cell's energy-producing powerhouses. Studies have shown that this leads to the accumulation of depolarized mitochondria that induce epigenetic reprogramming toward exhaustion, locking the T cells in a dysfunctional state. This isn't just a side effect; it's a primary mechanism that paralyzes our immune response.
- Finding 2: The good news is that this exhaustion isn't always permanent. Scientists are finding that providing the right kind of metabolic fuel can dramatically improve T cell function. For instance, research shows that linoleic acid improves mitochondrial fitness by enhancing the crucial connection between the ER and mitochondria, preventing exhaustion. In another exciting discovery, the metabolite succinate promotes T cell stemness via mitophagy, a quality-control process that removes damaged mitochondria and preserves the T cell's long-term potential.
- Finding 3: Perhaps the most futuristic finding is that T cells can receive mitochondrial donations. Groundbreaking research has revealed that mitochondrial transfer via nanotubes enhances T cell fitness. In this process, healthy stromal cells in the bone marrow form tiny tubes to physically deliver fresh, functional mitochondria to T cells. These 'supercharged' T cells show superior expansion, tumor infiltration, and killing ability, demonstrating a natural process of metabolic rescue that we could one day harness therapeutically.
Biological Mechanisms
To understand why these findings matter mechanistically, we need to examine the underlying processes. The journey from an energetic, cancer-fighting effector T cell to a dysfunctional, exhausted one is a story of metabolic collapse. Healthy effector T cells rely on glycolysis for quick energy to fuel their rapid expansion and cytotoxic activity. However, for long-term survival and memory, they must switch to mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS)—a much more efficient energy source. Exhausted T cells fail to make this switch, crippled by damaged mitochondria. The study reveals that IDH2 inhibitor enhances memory CAR T cell formation plays a crucial regulatory role in the observed system.
Molecular Pathways
This failure is orchestrated at the molecular level. Chronic stimulation and hypoxia repress key metabolic regulators like PGC-1α, which is essential for building new mitochondria. At the same time, quality control pathways like mitophagy—the process of clearing out damaged mitochondria—are impaired. This leads to a buildup of dysfunctional mitochondria that spew ROS, which not only damages the cell but also triggers signaling pathways that reinforce the exhausted state. Interventions like providing succinate can reboot this system by promoting BNIP3-mediated mitophagy, effectively taking out the mitochondrial trash and restoring cellular health. Research shows that depolarized mitochondria induce epigenetic reprogramming toward exhaustion in this pathway.
Relevance to Human Health
Beyond the molecular picture, the implications for human health are substantial. These findings are incredibly relevant for patients. T cell exhaustion is a primary reason why promising treatments like PD-1 checkpoint inhibitors and CAR-T cell therapies have limited success in many patients, especially those with solid tumors. An exhausted T cell simply won't respond to signals that are supposed to activate it. Understanding the metabolic roots of this problem gives us a completely new set of targets to overcome this resistance. This study shows that linoleic acid improves mitochondrial fitness preventing exhaustion could benefit patients or shape future diagnostic or therapeutic strategies.
Therapeutic Applications
- Metabolic Drugs as Immunotherapy Boosters: We can now envision using FDA-approved drugs to reprogram T cell metabolism. For example, studies show that an IDH2 inhibitor enhances memory CAR T cell formation, making these engineered cells more durable and effective. This opens the door to combining metabolic modulators with existing immunotherapies.
- Nutritional Supplementation: The findings on linoleic acid and succinate suggest that specific dietary interventions or supplements could be used to improve T cell fitness before or during cancer treatment, offering a simple and powerful way to support the immune system.
- Next-Generation Cell Therapies: The discovery of mitochondrial transfer inspires a new generation of cell therapies. Future CAR-T cells could be pre-conditioned with metabolic enhancers or even 'supercharged' with healthy mitochondria in the lab before being infused into a patient, creating a more resilient and potent living drug.
Future Directions
Despite these advances, key questions remain. The road ahead is exciting. The next critical step is to translate these preclinical findings into human trials. Researchers will need to determine the best dosage, timing, and delivery methods for metabolic interventions in combination with immunotherapy. There is also a push to develop non-invasive biomarkers—perhaps by measuring metabolites in the blood—that can predict which patients are most likely to suffer from T cell exhaustion and would benefit most from metabolic support. The ultimate goal is to create personalized immunotherapy regimens that are tailored to the unique metabolic landscape of each patient's tumor and immune system. Scientists are now investigating succinate promotes T cell stemness via mitophagy to expand the field's understanding and address remaining challenges.
Conclusion
The fight against cancer is increasingly being understood as a metabolic war, not just a genetic one. The health of our T cells' mitochondria has emerged as a linchpin for successful immunotherapy. By learning the metabolic rules that govern T cell exhaustion, we are no longer limited to just cutting the brakes on the immune system; we can now actively get in the engine and refuel it. These discoveries are paving the way for a new wave of therapies that promise to make our own immune systems stronger, more resilient, and ultimately more successful in the fight against cancer.
References
- Scharping NE, Rivadeneira DB, Menk AV, Vignali PDA, Ford BR, Rittenhouse NL, Peralta R, Wang Y, Wang Y, DePeaux K, Poholek AC, Delgoffe GM (2021). Mitochondrial stress induced by continuous stimulation under hypoxia rapidly drives T cell exhaustion. Nat Immunol. 22(2):205-215. PMID: 33398183
- Baldwin JG, Heuser-Loy C, Saha T, et al. (2024). Intercellular nanotube-mediated mitochondrial transfer enhances T cell metabolic fitness and antitumor efficacy. Cell. 187(23):6614-6630.e21. PMID: 39276774
- Si X, Shao M, Teng X, et al. (2024). Mitochondrial isocitrate dehydrogenase impedes CAR T cell function by restraining antioxidant metabolism and histone acetylation. Cell Metab. 36(1):176-192.e10. PMID: 38171332
- Yu YR, Imrichova H, Wang H, et al. (2020). Disturbed mitochondrial dynamics in CD8+ TILs reinforce T cell exhaustion. Nat Immunol. 21(12):1540-1551. PMID: 33020660
- Nava Lauson CB, Tiberti S, Corsetto PA, et al. (2023). Linoleic acid potentiates CD8+ T cell metabolic fitness and antitumor immunity. Cell Metab. 35(4):633-650.e9. PMID: 36898381
- Ma K, Cheng H, Wang L, et al. (2025). Succinate preserves CD8+ T cell fitness to augment antitumor immunity. Immunity. 58(10):2505-2523.e8. PMID: 40816269
Recent Posts
-
IgG1 Plasma Cells: The Emerging Biomarker for Predicting Cancer Immunotherapy Success
In the relentless fight against cancer, immunotherapy has emerged as a beacon of hope, harnessing t …24th Feb 2026 -
The Rise of Cancer Neuroscience: How Neural Circuits Drive Tumor Progression
For decades, we viewed cancer as a rogue army of cells, a biological glitch driven solely by geneti …23rd Feb 2026 -
CRISPR-Powered Light Sensors: A New Frontier in Ultra-Sensitive Cancer Detection
Cancer detection often relies on advanced imaging or invasive procedures, frequently catching the d …20th Feb 2026