Volagidemab: A Breakthrough in GLP-1 Receptor Agonists for Metabolic Disorders
Quick Facts About Volagidemab
What is Volagidemab?
How Does Volagidemab Work?
What Are the Clinical Applications of Volagidemab?
1.) Understanding Volagidemab
Volagidemab is a novel therapeutic agent targeting the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor, representing a unique approach in metabolic disease treatment. Unlike GLP-1 receptor agonists, which enhance insulin secretion and improve glucose metabolism, Volagidemab acts as a GLP-1 receptor antagonist, modulating the receptor’s activity in a distinct manner. This differentiation sets it apart from widely used GLP-1-based therapies for type 2 diabetes and obesity management.
The primary focus of Volagidemab research has been its potential in managing type 2 diabetes, particularly in patients who may not respond optimally to traditional GLP-1 receptor agonists. By modulating GLP-1 receptor activity, it aims to provide an alternative means of glycemic control, potentially offering benefits in cases where excessive GLP-1 stimulation is counterproductive. Additionally, emerging studies suggest that GLP-1 receptor modulation plays a role in appetite regulation and energy expenditure, making Volagidemab a candidate for obesity treatment.
As interest in metabolic therapies grows, Volagidemab has gained attention for its ability to provide new insights into the complex mechanisms of glucose homeostasis, insulin sensitivity, and metabolic adaptation. Researchers continue to investigate its broader implications, including its impact on pancreatic function and its potential role in treating metabolic syndrome. While the full therapeutic scope of Volagidemab is still being explored, its novel mechanism of action highlights the growing interest in alternative strategies for metabolic disease management. Future clinical studies will be crucial in determining its long-term efficacy and safety in various patient populations.
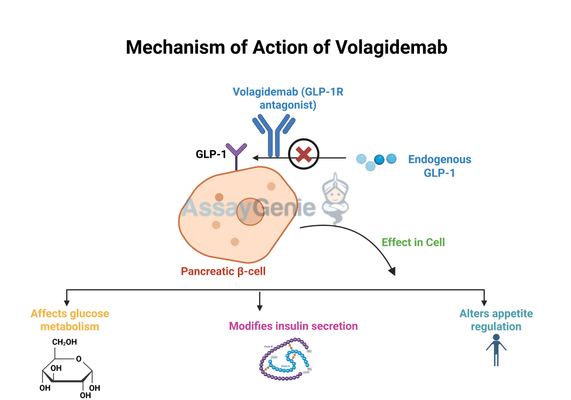
2.) Mechanism of Action of Volagidemab
Volagidemab functions as a GLP-1 receptor antagonist, inhibiting the receptor’s ability to bind to endogenous GLP-1. GLP-1 is a key incretin hormone involved in glucose metabolism, insulin secretion, and appetite regulation. Traditional GLP-1 receptor agonists enhance these effects to improve glycemic control, whereas Volagidemab takes an opposite approach by blocking receptor activity, leading to modified insulin secretion and metabolic responses.
The rationale behind GLP-1 receptor antagonism is based on the hypothesis that excessive or prolonged GLP-1 signaling may contribute to metabolic imbalances in certain individuals. By inhibiting the receptor, Volagidemab alters the balance of insulin and glucagon secretion, potentially offering a new therapeutic approach for metabolic disorders. Preclinical and clinical studies have suggested that this modulation may provide benefits beyond glucose control, such as influencing lipid metabolism, energy expenditure, and appetite regulation.
One area of ongoing research is Volagidemab’s long-term impact on pancreatic function. Since GLP-1 receptor activity is linked to beta-cell proliferation and survival, researchers are evaluating whether receptor antagonism affects pancreatic health over time. Additionally, studies are investigating whether Volagidemab can be effectively combined with other metabolic therapies to optimize patient outcomes. Given the increasing complexity of metabolic disorders, understanding how GLP-1 receptor antagonism fits into the broader landscape of metabolic disease treatment remains a key research priority.
3.) Clinical Applications of Volagidemab
Diabetes Management
Obesity and Metabolic Disorders
Future Directions
As research on Volagidemab progresses, scientists are particularly interested in its long-term effects on metabolic health. Ongoing clinical trials are examining how sustained GLP-1 receptor antagonism impacts glucose metabolism, pancreatic function, and energy expenditure. Additionally, combination therapies involving Volagidemab and other metabolic agents are being explored to determine whether a multi-target approach could enhance treatment efficacy.
While GLP-1 receptor agonists have dominated the landscape of metabolic disease treatment, Volagidemab introduces a novel strategy that challenges conventional therapeutic paradigms. Future studies will provide critical insights into its safety, efficacy, and broader applications, shaping its potential role in metabolic disease management.

4.) Exploring Biosimilars for Volagidemab
What is a Biosimilar?
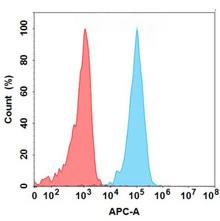
| Volagidemab (Anti-GCGR) Biosimilar Antibody | |
|---|---|
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Protein: | GCGR |
| Reactivity: | Human |
Volagidemab Biosimilar in Research
Benefits of Volagidemab Biosimilar
Cost-Effective Research: Enables broader accessibility for metabolic studies.
Mechanism Exploration: Supports in-depth analysis of GLP-1 receptor functions.
Expanding Therapeutic Understanding: Facilitates new discoveries in metabolic disease treatment.
Research Use Only Disclaimer:
Discover Our Biosimilar Range
At Assay Genie, we specialize in providing high-quality biosimilars for research use! Check out our full biosimilar range to learn more.

By Marina Alberto, PhD
Marina Alberto, PhD, holds a robust academic background in Biotechnology, earning her Bachelor’s Degree and PhD in Science and Technology from Quilmes National University. Her research spans cancer immunotherapy, glycan profiling, and vaccine development, including innovative projects on pediatric leukemia diagnosis and cancer-associated carbohydrate-mimetic vaccines. She currently serves as a Technical Support and Sales Specialist at Assay Genie.
Recent Posts
-
IgG1 Plasma Cells: The Emerging Biomarker for Predicting Cancer Immunotherapy Success
In the relentless fight against cancer, immunotherapy has emerged as a beacon of hope, harnessing t …24th Feb 2026 -
The Rise of Cancer Neuroscience: How Neural Circuits Drive Tumor Progression
For decades, we viewed cancer as a rogue army of cells, a biological glitch driven solely by geneti …23rd Feb 2026 -
CRISPR-Powered Light Sensors: A New Frontier in Ultra-Sensitive Cancer Detection
Cancer detection often relies on advanced imaging or invasive procedures, frequently catching the d …20th Feb 2026