Description
Recombinant Human IFNAR2 Protein
The Recombinant Human IFNAR2 Protein is a biologically active recombinant protein that plays a significant role in various cellular processes and signaling pathways in human biology. This protein is widely employed in immunological research, cell biology studies, protein-protein interaction analyses, and therapeutic development, providing researchers with a reliable tool for investigating IFNAR2 function and its implications in health and disease.
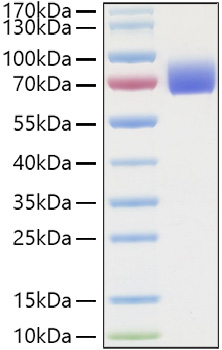
This product (SKU: RPCB1111) is produced using HEK293 cells and features a C-hFc&His tag for convenient detection and purification. The protein exhibits a calculated molecular weight of 51.54 kDa with an observed molecular weight of 66-90 kDa under denaturing conditions, achieving ≥ 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE.. Functional bioactivity has been validated through rigorous quality control assays, confirming its suitability for demanding research applications.
Key Features
| High Purity by Affinity Chromatography | |
| Mammalian & Bacterial Expression Systems | |
| High lot-to-lot consistency via strict QC |
| Product Name: | Recombinant Human IFNAR2 Protein |
| SKU: | RPCB1111 |
| Size: | 10 μg , 20 μg , 50 μg , 100 μg |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Synonyms: | IFNAR2, IFN-R, IFN-alpha-REC, IFNABR, IFNARB, IMD45, interferon alpha/beta receptor 2, IFN-R, IFN-alpha-REC, IFNABR, IFNARB, IMD45 |
| Tag: | C-hFc&His |
| Expression Host: | HEK293 cells |
| Calculated MW: | 51.54 kDa |
| Observed MW: | 66-90 kDa |
| Gene ID: | 3455 |
| Protein Description: | High quality, high purity and low endotoxin recombinant Recombinant Human IFNAR2 Protein (RPCB1111), tested reactivity in HEK293 cells and has been validated in SDS-PAGE.100% guaranteed. |
| Endotoxin: | < 0.1 EU/μg of the protein by LAL method. |
| Purity: | ≥ 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE. |
| Formulation: | Lyophilized from a 0.22 μm filtered solution of PBS, pH 7.4. |
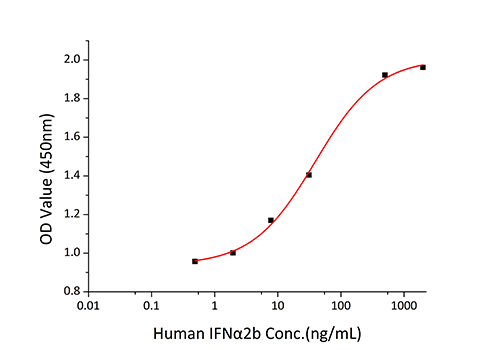
| Bio-Activity: | Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. Immobilized Human IFNAR2 at 2 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Mouse IFNAR2 with a linear range of 0.49-39.20 ng/mL. |
| Reconstitution: | Centrifuge the vial before opening. Reconstitute to a concentration of 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile distilled water. Avoid vortex or vigorously pipetting the protein. For long term storage, it is recommended to add a carrier protein or stablizer (e.g. 0.1% BSA, 5% HSA, 10% FBS or 5% Trehalose), and aliquot the reconstituted protein solution to minimize free-thaw cycles. |
| Storage: | Store at -20℃.Store the lyophilized protein at -20℃ to -80 ℃ up to 1 year from the date of receipt. After reconstitution, the protein solution is stable at -20℃ for 3 months, at 2-8℃ for up to 1 week. |
Interferon alpha/beta receptor 2 (IFNAR2) is also known as IFN-alpha binding protein, IFN-alpha/beta receptor 2, Type I interferon receptor 2, IFNABR and IFNARB, which is a single-pass type I membrane protein and belongs to the type II cytokine receptor family.Binding and activation of the receptor stimulate Janus protein kinases, which in turn phosphorylate several proteins, including STAT1 and STAT2. Initial cell-surface IFNAR2 expression at diagnosis assessed by flow cytometry was widely distributed but showed overall significantly higher expression in CML patients when compared with normal controls. In 15 fresh patients who subsequently received IFNα therapy, IFNAR2 expression at diagnosis was significantly higher in cytogenetic good responders than in poor responders. Down-regulation of IFNAR2 expression during IFNα therapy was observed only in good responders but not in poor responders. The encoded protein also functions as an antiviral factor. IFNAR2 may associate with IFNAR1 to form the type I interferon receptor. This protein serves as a receptor for interferons alpha and beta. IFNAR2 is also involved in IFN-mediated STAT1, STAT2, and STAT3 activation. Isoform 1 and isoform 2 are directly involved in signal transduction due to their association with the TYR kinase, JAK1. Isoform 3 is a potent inhibitor of type I IFN receptor activity. Following binding of IFNα2, IFNAR2 is internalized, but, instead of being routed towards degradation as it is when complexed to IFNβ, it recycles back to the cell surface.