Ulviprubart: A Breakthrough in Autoimmune Disease Treatment
Quick Facts About Ulviprubart
What is Ulviprubart?
Ulviprubart is an experimental complement inhibitor designed to modulate immune responses in autoimmune diseases.
What is the mechanism of action for Ulviprubart?
Ulviprubart targets the complement system, reducing excessive immune activation and preventing tissue damage.
What are the clinical applications of Ulviprubart?
Research is evaluating Ulviprubart’s potential in treating autoimmune diseases such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome.
1.) Understanding Ulviprubart
Ulviprubart represents a significant advancement in immunotherapy, particularly for autoimmune diseases where excessive complement system activation contributes to disease progression. The complement system, an essential component of the innate immune response, plays a vital role in inflammation, pathogen clearance, and immune surveillance. However, its dysregulation in autoimmune conditions can lead to chronic inflammation, tissue damage, and disease exacerbation. This is evident in disorders such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS), and paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH), where uncontrolled complement activation damages host tissues.
Unlike traditional immunosuppressants that broadly suppress immune function, Ulviprubart is designed to selectively inhibit specific complement cascade components, preventing excessive activation while maintaining essential immune defenses. By precisely targeting key mediators in the complement pathway, Ulviprubart reduces the risk of infections and other complications associated with generalized immunosuppression. Additionally, its targeted mechanism helps preserve beneficial immune responses, ensuring that the body can still fight infections and maintain immunological balance.
This precision-based approach represents a paradigm shift in autoimmune disease treatment, potentially improving patient outcomes with fewer side effects than conventional therapies. Ongoing clinical trials and research continue to explore its therapeutic potential across multiple complement-mediated disorders, highlighting its promise as a next-generation immunotherapeutic agent.
2.) Mechanism of Action of Ulviprubart
Ulviprubart functions by selectively inhibiting key proteins within the complement system, effectively preventing the formation of the membrane attack complex (MAC). The MAC is a critical terminal component of the complement cascade, responsible for directly lysing target cells by forming pores in their membranes. While this process is essential for eliminating pathogens, excessive activation in autoimmune diseases can lead to chronic inflammation, tissue destruction, and disease progression. By blocking complement activation at a crucial step, Ulviprubart reduces pathological immune responses while preserving essential immune functions.
Selective Complement Inhibition – Ulviprubart specifically targets complement pathways involved in disease progression, preventing excessive activation without completely suppressing the immune response. This selectivity is particularly beneficial in conditions such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS), and other complement-mediated disorders.
Reduction of Inflammatory Mediators – By modulating complement activation, Ulviprubart lowers the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6, TNF-α, and C5a, which are key drivers of immune system overactivation and chronic inflammation. This mechanism helps mitigate tissue damage while reducing the severity of autoimmune responses.
Preservation of Immune Surveillance – Unlike broad-spectrum immunosuppressants, which indiscriminately dampen immune function and increase susceptibility to infections, Ulviprubart allows normal immune responses against pathogens while minimizing autoimmunity-related tissue damage. This targeted approach helps maintain the body's natural defense mechanisms without the severe immunosuppressive side effects of conventional therapies.
By precisely modulating complement system activity, Ulviprubart represents a safer and more effective alternative to traditional immunosuppressants, offering improved outcomes for patients with complement-driven autoimmune diseases.
3.) Clinical Applications of Ulviprubart
Emerging research highlights Ulviprubart’s potential as a targeted immunotherapeutic agent for managing autoimmune diseases by selectively modulating complement system activity. Unlike traditional immunosuppressants, which broadly suppress immune responses and increase infection risks, Ulviprubart provides a more precise therapeutic approach, reducing excessive inflammation while preserving immune function. Key areas of investigation include its role in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS), where complement dysregulation contributes significantly to disease pathogenesis.
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) – SLE is a chronic autoimmune disorder where complement activation plays a crucial role in lupus nephritis, a severe complication leading to kidney inflammation and potential failure. Uncontrolled complement-mediated inflammation exacerbates tissue damage. By inhibiting key complement components, Ulviprubart may help reduce renal inflammation, prevent further tissue damage, and improve long-term kidney function.
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) – Complement overactivation is implicated in joint inflammation and synovial damage in RA. Persistent immune responses lead to cartilage destruction and loss of joint function. Ulviprubart’s selective inhibition of the complement cascade may reduce inflammation, alleviate pain, and preserve joint integrity without broad immunosuppressive effects.
Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome (aHUS) – aHUS is a rare but life-threatening disorder characterized by uncontrolled complement activation, leading to red blood cell destruction, blood clot formation, and acute kidney failure. Current treatment options are limited, and Ulviprubart represents a promising therapeutic strategy to control disease progression, prevent severe complications, and improve patient outcomes.
Ongoing clinical trials and real-world studies continue to evaluate Ulviprubart’s safety, efficacy, and long-term benefits across multiple complement-mediated conditions, ensuring its viability as a next-generation therapy for autoimmune and inflammatory diseases.
4.) Exploring Biosimilars for Ulviprubart
As research progresses, biosimilars of Ulviprubart provide valuable tools for further investigation and preclinical studies.
What is a Biosimilar?
Biosimilars are biologic drugs designed to closely resemble an original biologic in structure and function. These alternatives offer cost-effective solutions for research and therapeutic advancements.
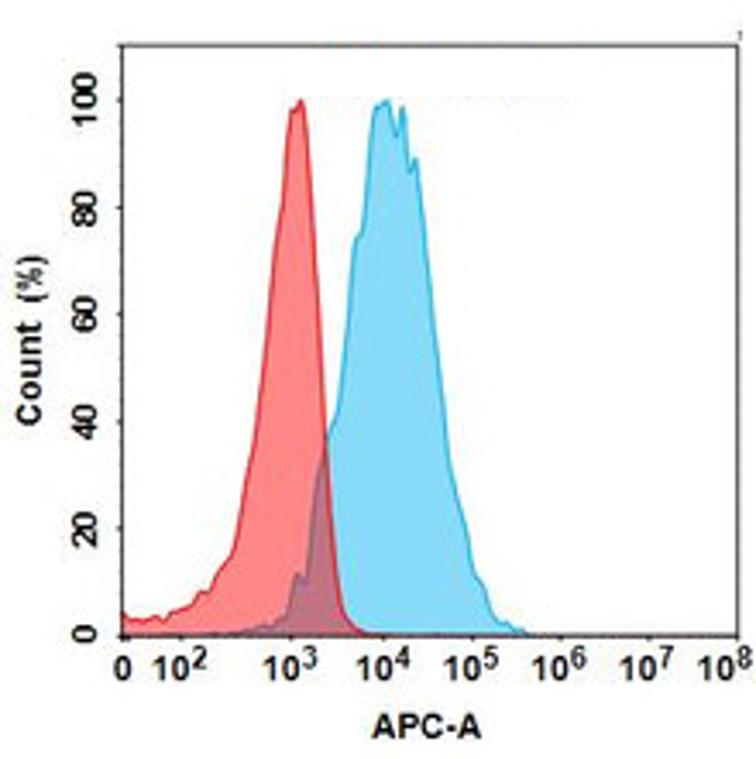
| Ulviprubart (Anti-KLRG1) Biosimilar Antibody | |
|---|---|
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Protein: | KLRG1 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
How Ulviprubart Biosimilar Compares to Ulviprubart
Advancing Research on Ulviprubart
Research Use Only Disclaimer:
Ulviprubart biosimilar is intended solely for research purposes and is not approved for clinical use.
Discover Our Biosimilar Range
At Assay Genie, we specialize in providing high-quality biosimilars for research use! Check out our full biosimilar range to learn more.

By Marina Alberto, PhD
Marina Alberto, PhD, holds a robust academic background in Biotechnology, earning her Bachelor’s Degree and PhD in Science and Technology from Quilmes National University. Her research spans cancer immunotherapy, glycan profiling, and vaccine development, including innovative projects on pediatric leukemia diagnosis and cancer-associated carbohydrate-mimetic vaccines. She currently serves as a Technical Support and Sales Specialist at Assay Genie.
Recent Posts
-
Metabolic Exhaustion: How Mitochondrial Dysfunction Sabotages CAR-T Cell Therapy in Solid Tumors
Imagine engineering a patient's own immune cells into precision-guided missiles against cancer—cells …8th Dec 2025 -
The Powerhouse of Immunity: How Mitochondrial Fitness Fuels the Fight Against Cancer
Why do powerful cancer immunotherapies work wonders for some patients but fail for others? The answe …5th Dec 2025 -
How Cancer Cells Hijack Immune Defenses Through Mitochondrial Transfer
Imagine a battlefield where the enemy doesn't just hide from soldiers—it actively sabotages their we …5th Dec 2025