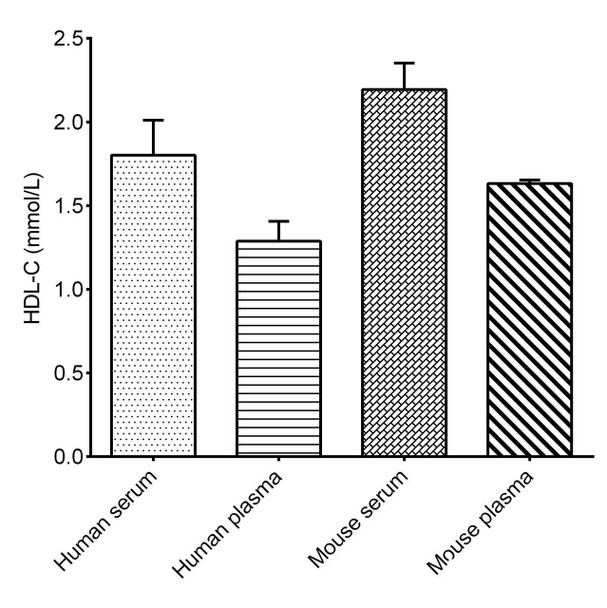
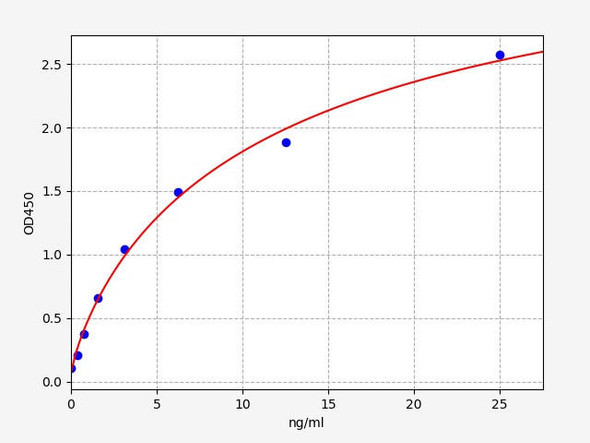
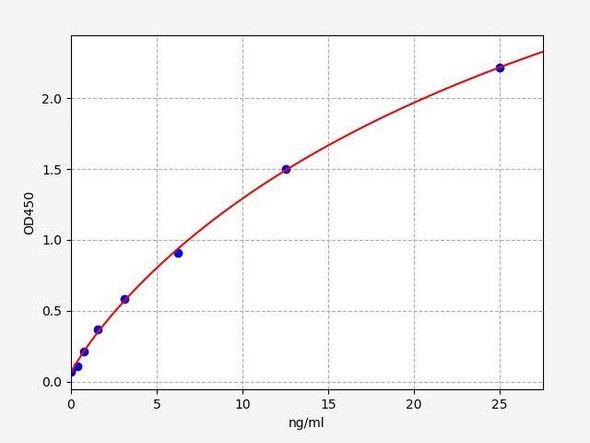
High-density lipoprotein cholesterol is mainly synthesized in the liver. It is an anti- atherosclerotic lipoprotein that can transport cholesterol from extrahepatic tissues to the liver for metabolism and excretion of bile from the body. Its plasma level is negatively correlated with the risk of cardiovascular disease. High-density lipoprotein can take cholesterol from the cell membrane, catalyzed by lecithin cholesterol acyltransferase to form cholesterol ester, and then transfer the carried cholesterol ester to very low density lipoprotein and low density lipoprotein. High-density lipoprotein cholesterol content is relatively fixed, containing about 20% to 30% of the total body cholesterol.