Iscalimab: Advancing Research in Autoimmune Diseases and Transplantation
What You Need to Know About Iscalimab
What is Iscalimab?
Iscalimab (CFZ533) is a monoclonal antibody targeting CD40, a key protein involved in immune system regulation.
What is the mechanism of action for Iscalimab?
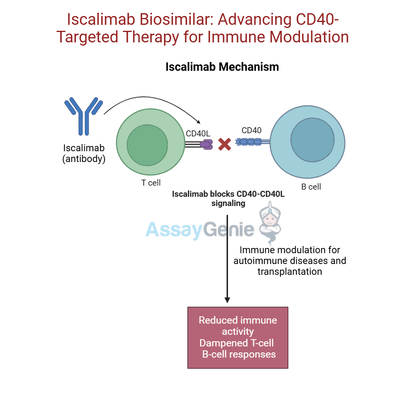
Iscalimab blocks the CD40-CD40L pathway, preventing the activation of T cells and B cells, which are central to autoimmune responses and transplant rejection.
What are the clinical applications of Iscalimab?
Iscalimab is under investigation for treating autoimmune diseases like Sjögren's syndrome, lupus nephritis, and for improving outcomes in organ transplantation.
1.) Understanding Iscalimab
Iscalimab (CFZ533) is an innovative monoclonal antibody developed by Novartis to target CD40, a pivotal costimulatory protein in immune cell activation. CD40 is primarily expressed on antigen-presenting cells (APCs), such as dendritic cells, macrophages, and B cells, and interacts with its ligand, CD40L (CD154), found on T cells. This interaction is essential for initiating and amplifying immune responses, including the activation of T cells, B cell maturation, and the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines.
By inhibiting the CD40-CD40L pathway, Iscalimab aims to suppress overactive immune responses that contribute to the pathology of various diseases. This mechanism is particularly relevant in autoimmune disorders, where excessive immune activation leads to tissue damage. In preclinical and clinical studies, Iscalimab has demonstrated the ability to reduce inflammatory markers and attenuate disease progression in conditions such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and rheumatoid arthritis.
Iscalimab’s potential extends beyond autoimmune diseases to applications in organ transplantation. The CD40-CD40L axis is a key player in allograft rejection, where immune cells attack transplanted organs. By modulating this pathway, Iscalimab reduces the likelihood of rejection while minimizing the need for traditional immunosuppressants, which often have significant side effects.
Additionally, Iscalimab has shown promise in chronic inflammatory conditions like Sjögren’s syndrome and in certain cancers where the CD40 pathway contributes to tumor-associated inflammation. Its targeted mechanism and broad applicability highlight Iscalimab as a versatile therapeutic agent with the potential to improve outcomes in diverse clinical settings.
Prefer to Listen? Check out the Iscalimab Podcast Episode
2.) Mechanism of Action of Iscalimab
Iscalimab’s mechanism of action is rooted in its ability to selectively block the interaction between CD40, a costimulatory receptor expressed on antigen-presenting cells (APCs), and its ligand CD40L (CD154), found on activated T cells. The CD40-CD40L interaction plays a critical role in immune system activation, driving processes such as T-cell activation, B-cell proliferation, antibody production, and cytokine release. This pathway is central to both adaptive and innate immunity and is often dysregulated in autoimmune diseases, chronic inflammation, and transplant rejection.
By binding to CD40 and preventing its engagement with CD40L, Iscalimab interrupts the signaling cascade that leads to T-cell and B-cell activation. This disruption inhibits the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), and interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), which are commonly elevated in autoimmune and inflammatory conditions. Additionally, Iscalimab curtails germinal center formation and plasma cell differentiation, thereby reducing autoantibody production—a hallmark of diseases like systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
A key advantage of Iscalimab is its selective modulation of the immune response. Unlike traditional immunosuppressive therapies that broadly deplete immune cells or dampen immune activity, Iscalimab specifically targets the CD40-CD40L pathway without compromising the overall immune cell population. This precision reduces the risk of infections and other side effects commonly associated with generalized immunosuppression.
The targeted nature of Iscalimab’s action positions it as a promising therapeutic agent in managing autoimmune diseases, chronic inflammation, and preventing organ transplant rejection.

3.) Clinical Applications of Iscalimab
Iscalimab, a monoclonal antibody targeting CD40, has emerged as a promising therapeutic agent with diverse clinical applications, ranging from autoimmune diseases to transplantation medicine. By modulating immune responses, Iscalimab offers a targeted approach to managing complex conditions, reducing the need for broad immunosuppression and its associated side effects.
Iscalimab has demonstrated significant potential in treating autoimmune conditions such as Sjögren’s syndrome, lupus nephritis, and hidradenitis suppurativa. These diseases often result from dysregulated immune responses, leading to chronic inflammation and tissue damage. By inhibiting CD40 signaling, Iscalimab effectively reduces immune activation, alleviating symptoms and slowing disease progression. For example, in lupus nephritis, it may help preserve kidney function by mitigating the autoimmune attack on renal tissues, offering hope for improved long-term outcomes in affected patients.
In the context of organ transplantation, Iscalimab is being investigated as a novel strategy to prevent graft rejection. Traditional immunosuppressants, while effective, often carry significant risks, including infections and malignancies. Iscalimab’s targeted mechanism allows for precise immune modulation, potentially reducing these complications. Kidney transplant trials have shown encouraging results, suggesting it could improve graft survival while minimizing the adverse effects of conventional therapies.
Beyond its current applications, ongoing research is exploring Iscalimab’s role in conditions like diabetes and myasthenia gravis. These studies highlight its versatility as a therapeutic tool and its potential to address a broader spectrum of immune-mediated diseases. With its targeted approach and expanding clinical scope, Iscalimab continues to garner attention as a valuable asset in immunotherapy.
4.) Advancing Research on Iscalimab
What is a Biosimilar?
A biosimilar is a biologic product highly similar to an original (reference) biologic, with no clinically meaningful differences in terms of safety, purity, and potency. Biosimilars offer a cost-effective alternative, accelerating research and discovery in various fields.
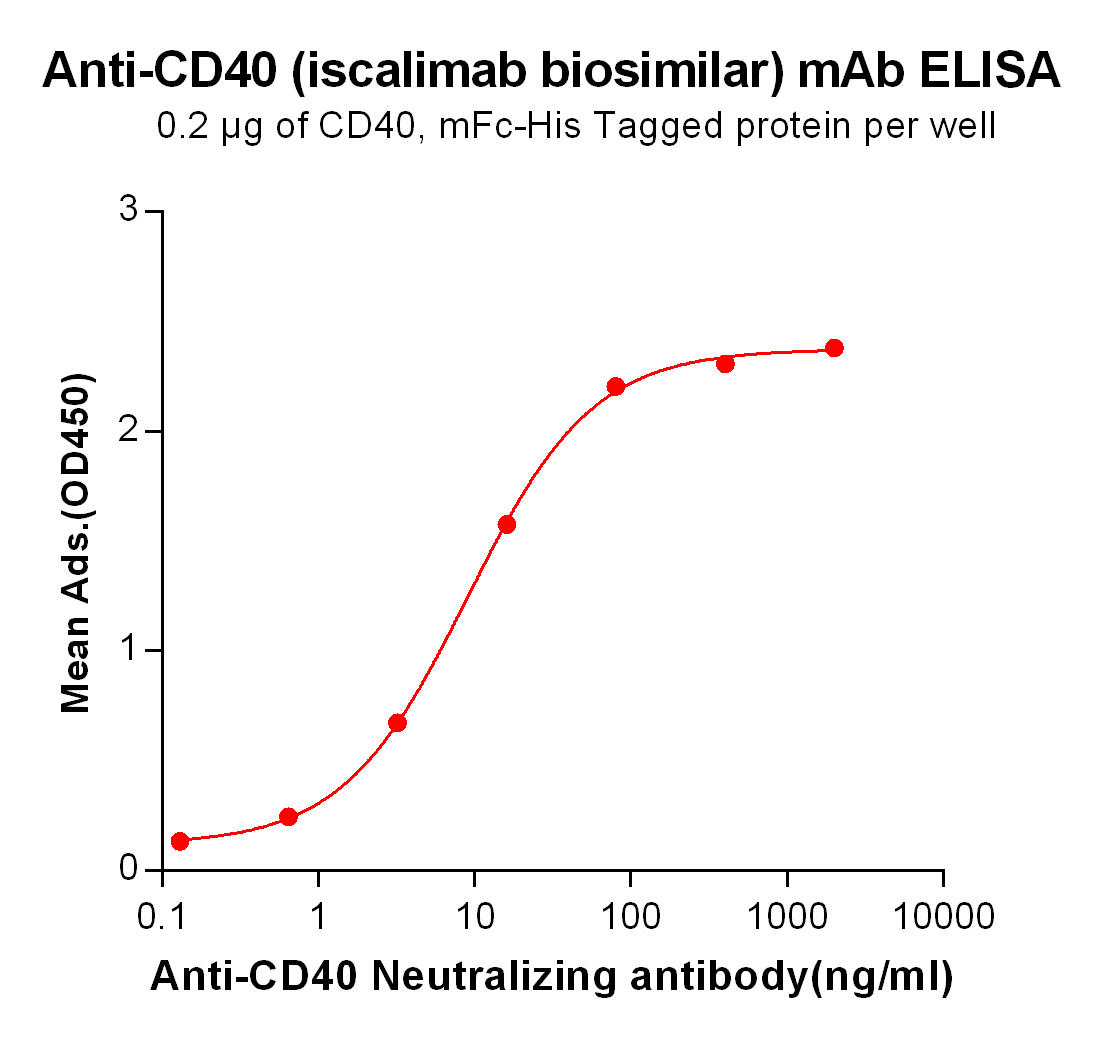
| Iscalimab (Anti-CD40) Biosimilar Antibody | |
|---|---|
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Protein: | CD40 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
Exploring Biosimilars for Iscalimab
Our Iscalimab biosimilar provides researchers with a valuable tool to investigate the CD40 pathway. It enables in-depth exploration of Iscalimab’s mechanisms and potential applications in autoimmune diseases and transplantation.
Benefits of Using the Iscalimab Biosimilar
- Supports advanced research in immune modulation.
- Provides a cost-effective option for preclinical studies.
- Enables researchers to explore emerging applications of CD40-targeted therapies.
Note: This product is for research use only and is not intended for clinical or patient use.
Discover Our Biosimilar Range
At Assay Genie, we specialize in providing high-quality biosimilars for research use! Check out our full biosimilar range to learn more.

By Chris McNally, PhD
Chris McNally, PhD, has a strong foundation in Biomedical Science, completing a PhD scholarship in collaboration with Randox Laboratories and Ulster University. Chris has published extensively in prostate cancer research, focusing on biomarker discovery, cancer risk stratification, and molecular mechanisms such as hypoxia-induced regulation. He currently serves as a Business Development Manager at Assay Genie.
Recent Posts
-
IgG1 Plasma Cells: The Emerging Biomarker for Predicting Cancer Immunotherapy Success
In the relentless fight against cancer, immunotherapy has emerged as a beacon of hope, harnessing t …24th Feb 2026 -
The Rise of Cancer Neuroscience: How Neural Circuits Drive Tumor Progression
For decades, we viewed cancer as a rogue army of cells, a biological glitch driven solely by geneti …23rd Feb 2026 -
CRISPR-Powered Light Sensors: A New Frontier in Ultra-Sensitive Cancer Detection
Cancer detection often relies on advanced imaging or invasive procedures, frequently catching the d …20th Feb 2026