Rituximab: Mechanism, Applications, and Research Potential
Quick Facts About Rituximab
What is Rituximab?
Rituximab is a monoclonal antibody targeting CD20, a protein found on the surface of B cells. It plays a crucial role in treating autoimmune diseases and certain cancers, such as non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.
What is the mechanism of action for Rituximab?
Rituximab works by binding to CD20, leading to B cell destruction through immune-mediated processes such as complement activation and apoptosis.
What are the clinical applications of Rituximab?
Rituximab is used to treat conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. It’s also being explored for multiple sclerosis (MS) and lupus.
What are the clinical applications of Rituximab?
Rituximab is used to treat conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. It’s also being explored for multiple sclerosis (MS) and lupus.
Is Rituximab safe?
While effective, Rituximab has side effects such as infusion reactions and increased risk of infections. Patients should consult healthcare providers for personalized advice.
How does Rituximab impact the immune system?
Rituximab reduces the number of B cells, which are involved in autoimmune responses and certain cancers. This temporary immunosuppression can help control disease activity.
1.) Understanding Rituximab
Rituximab, a revolutionary monoclonal antibody, has significantly reshaped the field of immunotherapy since its FDA approval in 1997. By targeting CD20, a transmembrane molecule found on the surface of B cells, Rituximab induces selective B-cell depletion, which is a critical mechanism in managing both malignant and autoimmune conditions. Its precision and efficacy have established it as a cornerstone in the treatment of hematological cancers such as non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, as well as autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus.
What distinguishes Rituximab from traditional chemotherapies is its ability to provide highly targeted treatment, resulting in fewer off-target effects. This specificity minimizes collateral damage to healthy tissues, improving patient outcomes and reducing treatment-related toxicity. Consequently, Rituximab has become a model for the development of other monoclonal antibody therapies, spurring advancements across various medical disciplines.
Moreover, ongoing research continues to expand Rituximab's therapeutic potential, particularly in neurology. Studies investigating its efficacy in neuroinflammatory disorders such as multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica have yielded promising results. These conditions often involve immune-mediated damage to the central nervous system, and Rituximab’s ability to modulate aberrant immune responses offers a novel avenue for disease management. As a result, it is being explored not only as a treatment for established diseases but also for off-label applications in refractory or rare neurological conditions.
The legacy of Rituximab extends beyond its immediate clinical applications, as it continues to inspire innovative approaches in antibody-based therapies, reinforcing its role as a pioneer in modern medicine.
2.) Mechanism of Action of Rituximab
The efficacy of Rituximab is rooted in its precise and multifaceted mechanism of action, which selectively targets B cells expressing the CD20 protein. CD20 is a transmembrane protein found on the surface of pre-B and mature B lymphocytes but is absent on stem cells and plasma cells. This selective targeting ensures that essential immune functions, such as antibody production by plasma cells, remain unaffected, while aberrant or malignant B cells are efficiently eliminated.
Rituximab’s mechanism of action involves three primary pathways:
1. Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity (ADCC): Once Rituximab binds to CD20, it marks B cells for destruction. Effector cells of the immune system, such as natural killer (NK) cells and macrophages, recognize the Fc region of the antibody and engage with the tagged B cells, leading to their elimination through cytotoxic activity.
2. Complement-Dependent Cytotoxicity (CDC): Rituximab activates the complement system upon binding to CD20. The complement cascade culminates in the formation of the membrane attack complex (MAC), which creates pores in the B cell membrane, resulting in cell lysis. This pathway amplifies the immune response, ensuring rapid clearance of targeted cells.
3. Direct Apoptosis Induction: Beyond immune-mediated destruction, Rituximab directly interacts with CD20 to trigger intracellular signaling pathways that lead to programmed cell death (apoptosis) in B cells. This intrinsic mechanism is crucial for eliminating B cells in environments where immune system engagement may be limited.
The combined action of these pathways ensures the efficient and selective depletion of CD20-expressing cells, making Rituximab particularly effective in conditions driven by abnormal B cell activity, such as non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and autoimmune diseases. This targeted approach not only maximizes therapeutic efficacy but also minimizes damage to other immune cells, underpinning its success and widespread application in modern medicine.

3.) Clinical Applications of Rituximab
Rituximab has revolutionized the treatment landscape for both malignant and autoimmune diseases, solidifying its position as a cornerstone therapy in modern medicine.
Cancer Therapy:
Rituximab is integral in managing B-cell malignancies, such as non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). By targeting CD20 on malignant B cells, it facilitates their efficient elimination while sparing other immune cells. It is commonly used in combination with chemotherapy regimens, such as CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone), to enhance treatment outcomes. Clinical trials have demonstrated that adding Rituximab significantly improves progression-free and overall survival rates in patients with NHL and CLL, cementing its role in hematological cancer therapy.
Autoimmune Diseases:
Rituximab’s ability to selectively deplete B cells has also made it a valuable treatment for autoimmune disorders, where abnormal B-cell activity drives disease pathology. It is approved for conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and vasculitis, particularly for patients who fail to respond to traditional immunosuppressive therapies. Its targeted mechanism reduces disease activity while minimizing systemic side effects, offering a lifeline to those with refractory autoimmune conditions.
Emerging Indications:
Ongoing research continues to expand Rituximab’s clinical utility. It shows promise in treating rare and refractory conditions, including neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder and IgG4-related diseases. Additionally, its role as a conditioning agent in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation is gaining recognition, with studies indicating its efficacy in reducing graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) and improving transplant outcomes.
Despite its transformative impact, optimizing Rituximab’s dosing regimens and mitigating side effects remain priorities for enhancing its safety and long-term efficacy. Its success has paved the way for innovative therapies, reinforcing its significance in medicine.
4.) Advancing Research on Rituximab: The Role of Biosimilars
What is a Biosimilar?
Biosimilars are highly similar to original biologic drugs, with no clinically meaningful differences in safety or efficacy. They provide cost-effective alternatives and broaden access to critical therapies.
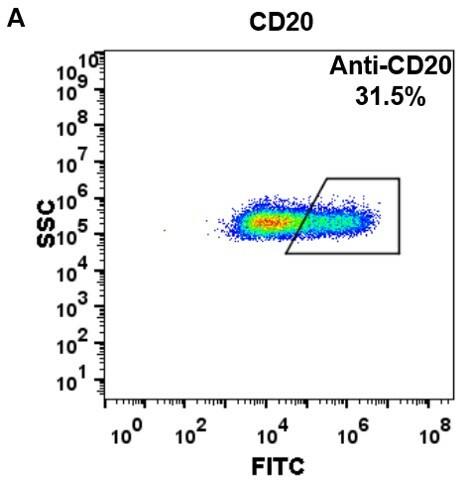
| Rituximab (Anti-CD20) Biosimilar Antibody | |
|---|---|
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Protein: | CD20 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
Exploring Biosimilars for Rituximab
Biosimilars of Rituximab, such as Amagen Rituximab, are instrumental in advancing research. These alternatives offer:
Enhanced Accessibility: Reduced costs make these therapies more widely available.
Facilitated Research: Biosimilars provide researchers with tools to explore new indications and combination therapies.
Comparable Efficacy: Rigorous testing ensures biosimilars match the original drug’s performance, maintaining therapeutic outcomes.
Research Use Only Disclaimer:
Biosimilars used in research are typically labeled for “research use only” and are not intended for clinical applications. This distinction is essential for ensuring ethical and regulatory compliance in studies.
Discover Our Biosimilar Range
At Assay Genie, we specialize in providing high-quality biosimilars for research use! Check out our full biosimilar range to learn more.

By Miren Ruiz de Eguilaz, PhD
Miren Ruiz de Eguilaz, PhD, has an extensive academic background, earning a BSc in Biology from UPV/EHU, an MSc in Biotechnology from the University of Oviedo, and a PhD in Chemistry from Dublin City University (DCU). Miren’s expertise lies in biosensor technology and bacterial diagnostics. She currently serves as a Product Manager at Assay Genie.
Recent Posts
-
IgG1 Plasma Cells: The Emerging Biomarker for Predicting Cancer Immunotherapy Success
In the relentless fight against cancer, immunotherapy has emerged as a beacon of hope, harnessing t …24th Feb 2026 -
The Rise of Cancer Neuroscience: How Neural Circuits Drive Tumor Progression
For decades, we viewed cancer as a rogue army of cells, a biological glitch driven solely by geneti …23rd Feb 2026 -
CRISPR-Powered Light Sensors: A New Frontier in Ultra-Sensitive Cancer Detection
Cancer detection often relies on advanced imaging or invasive procedures, frequently catching the d …20th Feb 2026




