Secukinumab: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Mechanism, Applications, and Biosimilar Advancements
Quick Facts About Secukinumab
What is Secukinumab
How Does Secukinumab Work?
What Are the Clinical Applications of Secukinumab?
What Are the Side Effects of Secukinumab?
1.) Understanding Secukinumab
Secukinumab (brand name Cosentyx) is a fully human monoclonal antibody developed by Novartis, specifically designed to target interleukin-17A (IL-17A), a key pro-inflammatory cytokine involved in several chronic autoimmune diseases. As an IL-17A inhibitor, Secukinumab provides a more targeted approach to immune modulation compared to traditional systemic immunosuppressants, which often have broader effects on the immune system and higher risks of adverse events. IL-17A plays a crucial role in driving inflammation in diseases such as plaque psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis. By selectively inhibiting IL-17A, Secukinumab helps reduce excessive immune activation, thereby alleviating symptoms and improving patient outcomes.
The development of Secukinumab represents a significant advancement in immunotherapy, particularly in dermatology and rheumatology. Since its approval by regulatory agencies such as the FDA and EMA, Secukinumab has become a preferred treatment option due to its high efficacy, rapid onset of action, and favorable safety profile. Unlike older biologics targeting tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), IL-17A inhibition offers an alternative mechanism of action for patients who do not respond adequately to TNF inhibitors. Clinical trials have consistently demonstrated its ability to provide long-term symptom relief, making it a valuable therapeutic option.
Additionally, ongoing research continues to explore new indications for Secukinumab beyond its established uses. Studies suggest its potential efficacy in conditions such as hidradenitis suppurativa, an inflammatory skin disease, and non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis, an early stage of ankylosing spondylitis. These expanding applications highlight the versatility of IL-17A blockade in managing immune-mediated disorders. As biologic therapies evolve, Secukinumab remains at the forefront of targeted treatments, offering improved quality of life for patients with chronic inflammatory diseases.
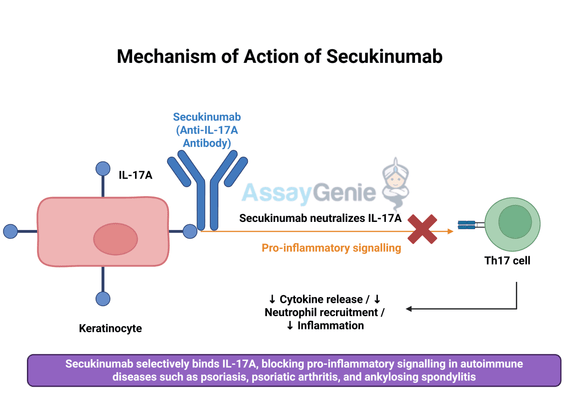
2.) Mechanism of Action of Secukinumab
Secukinumab exerts its therapeutic effects by selectively binding to and neutralizing interleukin-17A (IL-17A), a pro-inflammatory cytokine that plays a central role in autoimmune diseases. IL-17A is produced primarily by T-helper 17 (Th17) cells and acts as a key driver of inflammation by promoting the release of other pro-inflammatory mediators, recruiting neutrophils, and stimulating keratinocyte proliferation. This cascade of immune activation contributes to tissue damage and chronic inflammation in diseases like psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis.
By inhibiting IL-17A, Secukinumab disrupts this inflammatory signaling pathway, reducing immune cell recruitment and cytokine release. This results in decreased inflammation, alleviation of symptoms, and long-term disease control. Unlike broad-spectrum immunosuppressants that suppress multiple aspects of the immune system, Secukinumab offers a more targeted approach, minimizing the risk of systemic side effects while effectively managing disease activity. The specificity of Secukinumab for IL-17A allows it to act precisely at the source of inflammation without significantly impairing overall immune function.
The clinical benefits of IL-17A inhibition extend beyond immediate symptom relief. Studies have shown that Secukinumab leads to sustained reductions in disease severity, with many patients achieving complete or near-complete remission of symptoms. Additionally, its targeted action allows for better long-term disease management without the complications associated with corticosteroids or traditional immunosuppressive therapies. Importantly, Secukinumab has demonstrated a favorable safety profile, with the most common side effects being mild infections, such as upper respiratory tract infections, rather than severe immunosuppression-related complications. As research continues, further insights into IL-17A’s role in autoimmune diseases may expand the potential applications of Secukinumab in additional inflammatory conditions.
3.) Clinical Applications of Secukinumab
Secukinumab is currently approved for multiple autoimmune diseases, where IL-17A plays a critical role in disease pathogenesis. Its primary indications include psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis, though ongoing research is exploring its efficacy in additional conditions such as hidradenitis suppurativa and non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis.
- Psoriasis: Secukinumab is particularly effective in treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis, a chronic autoimmune skin disorder characterized by red, scaly plaques. Clinical trials have demonstrated that Secukinumab provides rapid and sustained skin clearance, with many patients achieving PASI 75 (75% reduction in Psoriasis Area and Severity Index) within 12 weeks. Unlike traditional therapies such as methotrexate or cyclosporine, which have broad immunosuppressive effects, Secukinumab specifically targets the IL-17A pathway, reducing systemic side effects while improving skin symptoms.
- Psoriatic Arthritis: In psoriatic arthritis, an inflammatory joint condition associated with psoriasis, Secukinumab reduces joint pain, stiffness, and swelling by inhibiting IL-17A-driven inflammation. This leads to improved joint function and prevents long-term joint damage. Studies have shown that Secukinumab significantly reduces the progression of structural joint damage, making it a valuable treatment option for patients who do not respond to TNF inhibitors or other disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs).
- Ankylosing Spondylitis: Secukinumab has shown strong efficacy in ankylosing spondylitis (AS), a chronic inflammatory disease affecting the spine and sacroiliac joints. By blocking IL-17A, Secukinumab reduces spinal inflammation, improves mobility, and alleviates pain, particularly in patients who have not responded adequately to TNF inhibitors. Clinical studies have demonstrated significant reductions in disease activity scores, confirming its role as an effective long-term therapy for AS.
- Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS): Although not yet an officially approved indication, emerging data suggest that Secukinumab may be beneficial in treating hidradenitis suppurativa, a debilitating chronic inflammatory skin disease characterized by painful nodules and abscesses. IL-17A is believed to contribute to the excessive inflammation seen in HS, and early clinical trials indicate that IL-17A inhibition with Secukinumab can help reduce lesion count and disease severity.
As further research and clinical trials expand our understanding of IL-17A’s role in inflammatory diseases, the therapeutic applications of Secukinumab may continue to grow, offering new hope to patients with chronic immune-mediated conditions.

4.) Exploring Biosimilars for Secukinumab
What is a Biosimilar?
| Secukinumab (Anti-IL17A) Biosimilar Antibody | |
|---|---|
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Protein: | IL-17A |
| Reactivity: | Human |
How Secukinumab Biosimilar Compares to Secukinumab
The biosimilar version of Secukinumab is designed to mirror the original in structure and function. While regulatory pathways ensure its similarity, biosimilars are typically used in research settings to explore novel therapeutic strategies.
Advantages of Secukinumab Biosimilars in Research
- Cost-Effective Alternative: Enables broader access for preclinical and translational studies.
- Facilitates Comparative Studies: Helps in evaluating long-term efficacy and safety.
- Supports Innovation: Provides insights into new therapeutic applications and combination strategies.
Research Use Only Disclaimer:
Discover Our Biosimilar Range
At Assay Genie, we specialize in providing high-quality biosimilars for research use! Check out our full biosimilar range to learn more.

By Miren Ruiz de Eguilaz, PhD
Miren Ruiz de Eguilaz, PhD, has an extensive academic background, earning a BSc in Biology from UPV/EHU, an MSc in Biotechnology from the University of Oviedo, and a PhD in Chemistry from Dublin City University (DCU). Miren’s expertise lies in biosensor technology and bacterial diagnostics. She currently serves as a Product Manager at Assay Genie.
Recent Posts
-
IgG1 Plasma Cells: The Emerging Biomarker for Predicting Cancer Immunotherapy Success
In the relentless fight against cancer, immunotherapy has emerged as a beacon of hope, harnessing t …24th Feb 2026 -
The Rise of Cancer Neuroscience: How Neural Circuits Drive Tumor Progression
For decades, we viewed cancer as a rogue army of cells, a biological glitch driven solely by geneti …23rd Feb 2026 -
CRISPR-Powered Light Sensors: A New Frontier in Ultra-Sensitive Cancer Detection
Cancer detection often relies on advanced imaging or invasive procedures, frequently catching the d …20th Feb 2026