Avdoralimab: Exploring Its Role in Immunotherapy and Biosimilar Advancements
Quick Facts About Avdoralimab
What is Avdoralimab?
Avdoralimab is a monoclonal antibody targeting C5aR1, playing a crucial role in modulating immune response and inflammation.
What is the mechanism of action of Avdoralimab?
Avdoralimab blocks the C5a receptor (C5aR1), preventing excessive immune activation and reducing inflammatory damage in various conditions.
What are the clinical applications of Avdoralimab?
Avdoralimab has been investigated for treating inflammatory diseases, including bullous pemphigoid, and has potential applications in oncology and COVID-19-related complications.
1.) Understanding Avdoralimab
Avdoralimab has been investigated for its therapeutic potential in a range of immune-related and inflammatory conditions. One of the key diseases where its role has been explored is bullous pemphigoid, a chronic autoimmune blistering disorder characterized by autoantibodies targeting the basement membrane of the skin. This condition leads to severe blister formation and tissue damage, with complement activation playing a central role in disease progression. By blocking C5aR1, Avdoralimab reduces the recruitment and activation of immune cells, helping to control inflammation and limit tissue destruction, making it a promising therapeutic option for patients with this debilitating condition.
Beyond dermatological applications, Avdoralimab has also been studied in the context of COVID-19 complications, particularly in severe cases where hyperinflammation, often referred to as a “cytokine storm,” contributes to respiratory failure and organ damage. The complement system, including C5aR1 activation, has been implicated in the pathogenesis of severe COVID-19, driving excessive immune responses that lead to tissue injury. By inhibiting this pathway, Avdoralimab may help mitigate uncontrolled inflammation, reduce lung damage, and improve patient outcomes in severe COVID-19 cases.
Moreover, the potential of Avdoralimab extends to cancer therapy, where complement activation has been linked to tumor progression and immune evasion. Tumor cells can exploit the complement system to create an immunosuppressive microenvironment, preventing effective anti-tumor immune responses. Avdoralimab’s ability to block C5aR1-mediated signaling may enhance anti-cancer immunity, making it a potential adjunct therapy in oncology.
With its broad applications in inflammatory and immune-mediated diseases, Avdoralimab remains a promising candidate for further clinical research and development.
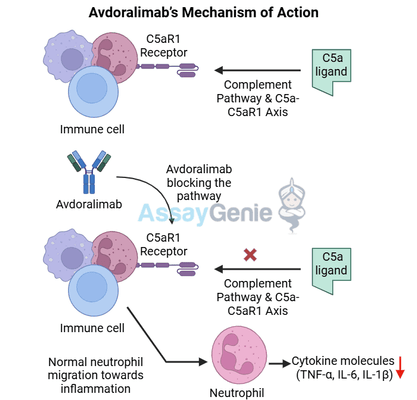
2.) Avdoralimab Mechanism of Action
Avdoralimab functions by selectively targeting C5aR1 (complement component 5a receptor 1) and inhibiting its interaction with C5a, a potent inflammatory mediator within the complement system. The C5a-C5aR1 axis plays a crucial role in immune modulation, as C5a is responsible for amplifying inflammatory responses, recruiting immune cells, and promoting cytokine release. By blocking this receptor, Avdoralimab effectively modulates immune activity and prevents excessive inflammation that can contribute to various disease pathologies.
Key Mechanisms of Action:
1. Reducing Neutrophil Recruitment:
Neutrophils are key effector cells in inflammation and immune responses, but their overactivation can lead to tissue damage and chronic inflammatory diseases. C5a is a strong neutrophil chemoattractant, drawing these cells to inflammation sites. Avdoralimab inhibits neutrophil migration by blocking C5aR1, thereby reducing tissue infiltration and minimizing inflammation-induced injury.
2. Limiting Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Release:
The activation of C5aR1 leads to the excessive release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β, which contribute to a hyperactive immune state. In diseases like severe infections, autoimmune disorders, and cancer, this cytokine surge exacerbates disease progression. Avdoralimab disrupts this signaling pathway, preventing harmful immune overactivation and restoring immune balance.
3. Preventing Tissue Damage in Chronic Inflammatory and Autoimmune Disorders:
Persistent activation of the complement system contributes to tissue damage in conditions like bullous pemphigoid, cancer, and respiratory diseases. By blocking C5aR1, Avdoralimab helps protect tissues from immune-mediated destruction, reducing disease severity and improving clinical outcomes.
By modulating the C5a-C5aR1 pathway, Avdoralimab holds therapeutic potential in conditions where immune dysregulation drives pathology, including oncology, dermatology, and respiratory diseases.
3.) Clinical Applications of Avdoralimab

Bullous Pemphigoid
Bullous pemphigoid (BP) is a chronic autoimmune blistering disease affecting the skin, characterized by autoantibody-driven complement activation and excessive inflammation. C5a, a key inflammatory mediator, plays a crucial role in disease progression by recruiting neutrophils and promoting tissue damage. Avdoralimab, through selective C5aR1 inhibition, reduces the inflammatory response, thereby alleviating blister formation and improving overall disease control. Clinical studies suggest that targeting C5aR1 could provide a novel therapeutic approach for BP, offering an alternative to steroid-based treatments, which often carry significant side effects. By modulating the immune response, Avdoralimab may help manage BP more effectively and with fewer complications.
Oncology
In cancer, particularly in solid tumors, the complement system plays a dual role—it can support immune responses but also facilitate tumor progression by creating an immunosuppressive microenvironment. C5aR1 activation within tumors has been linked to increased recruitment of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) and regulatory T cells (Tregs), which dampen the body's ability to mount an effective anti-tumor immune response. Avdoralimab’s C5aR1 blockade aims to shift this balance by reducing immune suppression and enhancing anti-tumor immunity. Early research suggests that Avdoralimab may improve the efficacy of checkpoint inhibitors and other immunotherapies, making it a promising candidate in cancer treatment strategies.
COVID-19-Related Inflammation
During the COVID-19 pandemic, severe cases were often associated with hyperinflammatory states, driven by complement activation and cytokine storms. The C5a-C5aR1 axis was identified as a contributor to lung damage, multi-organ failure, and poor outcomes in critically ill COVID-19 patients. Avdoralimab was evaluated as a potential therapy to mitigate excessive immune responses and reduce lung inflammation. While clinical trials yielded mixed results, they highlighted Avdoralimab’s ability to modulate immune activation, reinforcing its potential in conditions involving complement overactivation beyond COVID-19.
With its broad applicability in autoimmune diseases, oncology, and inflammatory disorders, Avdoralimab remains an important candidate for further clinical research and therapeutic development.
4.) Exploring Biosimilars for Avdoralimab
What is a Biosimilar?
A biosimilar is a biologic product highly similar to an already approved reference biologic. Biosimilars offer comparable efficacy, safety, and immunogenicity while providing cost-effective research and therapeutic options.

| Avdoralimab (Anti-C5AR1) Biosimilar Antibody | |
|---|---|
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Protein: | C5AR1 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
How Avdoralimab Biosimilar Compares to Avdoralimab
Avdoralimab biosimilars replicate the original antibody’s mechanism, making them essential tools for preclinical and translational research.
Benefits of Avdoralimab Biosimilar in Research
- Cost-effective alternative for studying C5aR1 inhibition.
- Supports drug development by enabling large-scale experiments.
- Ensures consistent results in immunology and inflammation research.
Research Use Only Disclaimer:
Avdoralimab biosimilar is intended for research purposes only and is not approved for clinical use. Researchers can utilize it to explore complement system modulation and its therapeutic implications.
Discover Our Biosimilar Range
At Assay Genie, we specialize in providing high-quality biosimilars for research use! Check out our full biosimilar range to learn more.

By Chris McNally, PhD
Chris McNally, PhD, has a strong foundation in Biomedical Science, completing a PhD scholarship in collaboration with Randox Laboratories and Ulster University. Chris has published extensively in prostate cancer research, focusing on biomarker discovery, cancer risk stratification, and molecular mechanisms such as hypoxia-induced regulation. He currently serves as a Business Development Manager at Assay Genie.
Recent Posts
-
IgG1 Plasma Cells: The Emerging Biomarker for Predicting Cancer Immunotherapy Success
In the relentless fight against cancer, immunotherapy has emerged as a beacon of hope, harnessing t …24th Feb 2026 -
The Rise of Cancer Neuroscience: How Neural Circuits Drive Tumor Progression
For decades, we viewed cancer as a rogue army of cells, a biological glitch driven solely by geneti …23rd Feb 2026 -
CRISPR-Powered Light Sensors: A New Frontier in Ultra-Sensitive Cancer Detection
Cancer detection often relies on advanced imaging or invasive procedures, frequently catching the d …20th Feb 2026