Durvalumab: Advancing Immunotherapy in Cancer Treatment
Quick Facts About Durvalumab
What is Durvalumab?
How does Durvalumab work?
What are the clinical applications of Durvalumab?
What are the side effects of Durvalumab?
1.) Understanding Durvalumab
Durvalumab is a monoclonal antibody designed to target programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1), a crucial immune checkpoint protein that allows cancer cells to evade immune detection. Under normal conditions, PD-L1 binds to programmed death-1 (PD-1) receptors on T cells, suppressing their activity and preventing an overactive immune response. However, many tumors exploit this pathway by overexpressing PD-L1, effectively “hiding” from the immune system. By inhibiting PD-L1, Durvalumab blocks this immune escape mechanism, restoring T-cell function and enhancing the body’s ability to recognize and eliminate cancer cells.
Developed by AstraZeneca, Durvalumab has been a major advancement in immuno-oncology, gaining regulatory approval for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and extensive-stage small cell lung cancer (SCLC), particularly as a consolidation therapy following chemotherapy. The approval of Durvalumab has transformed the standard of care, improving progression-free and overall survival for patients with these aggressive malignancies.
Beyond its established indications, ongoing research is exploring the efficacy of Durvalumab in a variety of other cancers, including head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, gastroesophageal carcinoma, and bladder cancer. Investigators are particularly interested in its role in combination therapies, such as its pairing with the CTLA-4 inhibitor Tremelimumab, which may produce a more robust and durable anti-tumor immune response. Additionally, studies are evaluating the benefits of combining Durvalumab with chemotherapy and targeted therapies to improve patient outcomes across multiple tumor types. As research progresses, Durvalumab continues to be a cornerstone of immune checkpoint blockade strategies, offering new therapeutic options for patients with difficult-to-treat malignancies.
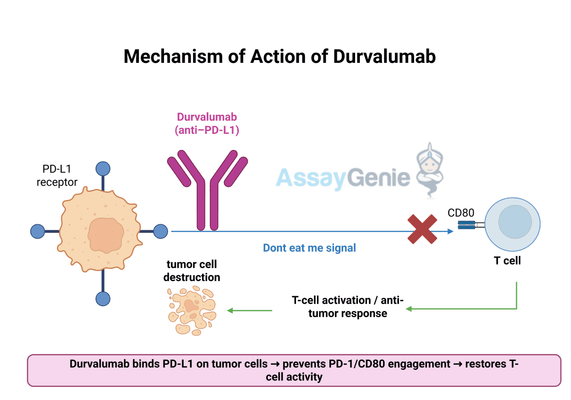
2.) Mechanism of Action of Durvalumab
Durvalumab functions as an immune checkpoint inhibitor, selectively binding to PD-L1 to prevent its interaction with PD-1 and CD80 receptors on T cells. This blockade effectively disrupts the tumor’s ability to evade immune surveillance, restoring T-cell activity and allowing the immune system to mount a more effective anti-tumor response. The inhibition of PD-L1 not only enhances direct tumor recognition by T cells but also contributes to a broader immune-stimulating effect within the tumor microenvironment.
- PD-L1 Inhibition: By directly binding to PD-L1, Durvalumab prevents the suppression of T-cell activation, allowing immune cells to function at full capacity in targeting cancer cells. This mechanism is particularly important in tumors with high PD-L1 expression, where immune evasion is a primary driver of disease progression.
- Enhanced Immune Surveillance: By blocking PD-L1 signaling, Durvalumab helps reinvigorate exhausted T cells, improving their ability to recognize and attack tumors. This immune restoration effect has been shown to enhance long-term tumor control and delay disease progression in lung cancer and other malignancies.
- Combination Therapy Potential: Preclinical and clinical studies suggest that Durvalumab is even more effective when used alongside other immune-modulating agents. For example, when combined with Tremelimumab, a CTLA-4 inhibitor, Durvalumab enhances the immune response by promoting both T-cell activation and memory formation, leading to a more sustained anti-tumor effect. Additionally, chemotherapy combinations with Durvalumab can promote tumor antigen release, further boosting immune recognition.
Durvalumab’s targeted mechanism makes it an essential therapy for patients with PD-L1-expressing tumors, particularly those with lung cancer. Ongoing research aims to refine its clinical use by identifying biomarkers that predict response and exploring novel drug combinations to maximize therapeutic benefits while minimizing toxicity.
3.) Clinical Applications of Durvalumab
Durvalumab is a key immunotherapy in oncology, particularly for lung and biliary tract cancers. As a PD-L1 inhibitor, it restores T-cell activity, enhancing the immune response against tumors. Its approvals are based on strong clinical trial data demonstrating improved survival and disease control.
- Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): Durvalumab is the standard consolidation therapy for unresectable stage III NSCLC after chemoradiotherapy. The PACIFIC trial showed significantly longer progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS), making it a key advancement in NSCLC treatment.
- Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC): Approved as first-line therapy with chemotherapy for extensive-stage SCLC, Durvalumab significantly improves OS, as demonstrated in the CASPIAN trial. This has reshaped SCLC treatment by integrating immunotherapy into frontline care.
- Biliary Tract Cancer (BTC): Durvalumab, combined with chemotherapy, has been approved for advanced BTC, addressing an aggressive disease with limited treatment options.
Emerging Research & Combination Therapies:
Durvalumab’s potential is expanding through combination approaches:
- Tremelimumab (CTLA-4 Inhibitor): Enhances tumor suppression in liver, bladder, and head and neck cancers.
- Chemotherapy Combinations: Evaluated in gastric, esophageal, and bladder cancers to boost immune responses.
- Neoadjuvant/Adjuvant Therapy: Studied in NSCLC and triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) to reduce recurrence.
With ongoing trials refining its use, Durvalumab remains a cornerstone of modern immuno-oncology, offering new hope for patients with aggressive cancers.
Key Clinical Applications:Emerging Research & Combination Therapies:
4.) Exploring Biosimilars for Durvalumab
What is a Biosimilar?
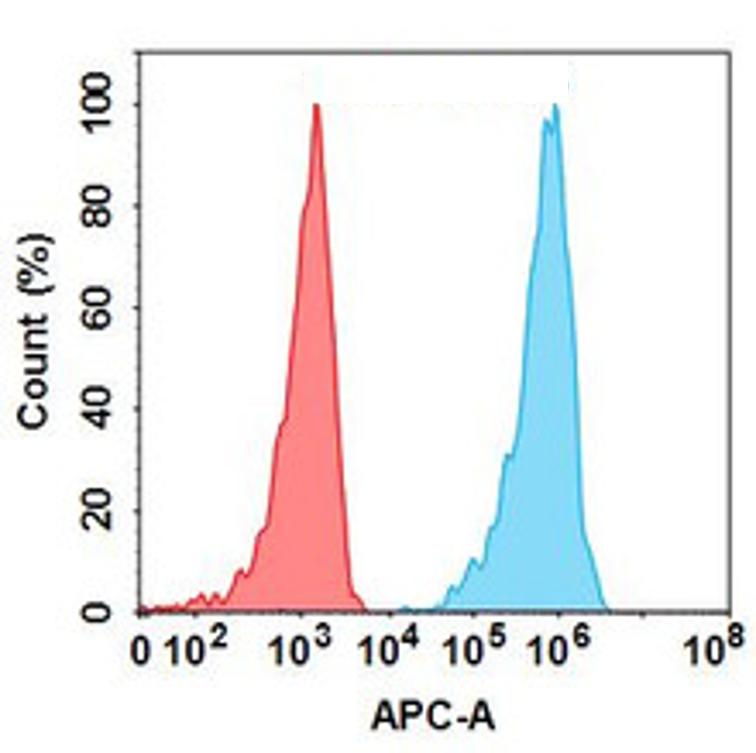
| Durvalumab (Anti-PDL1) Biosimilar Antibody | |
|---|---|
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Protein: | PD-L1 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
Durvalumab Biosimilar vs. Durvalumab
Intended Use: Durvalumab is used in clinical settings, while the biosimilar is designated for research use only.
Availability: The biosimilar is broadly available for laboratory studies, enabling researchers to explore PD-L1 inhibition mechanisms.
Cost Efficiency: Biosimilars provide a cost-effective alternative for preclinical research, advancing immuno-oncology discoveries.
Advancing Research with Durvalumab Biosimilars
Research Use Only Disclaimer:
Discover Our Biosimilar Range
At Assay Genie, we specialize in providing high-quality biosimilars for research use! Check out our full biosimilar range to learn more.

By David Lee, PhD
Recent Posts
-
IgG1 Plasma Cells: The Emerging Biomarker for Predicting Cancer Immunotherapy Success
In the relentless fight against cancer, immunotherapy has emerged as a beacon of hope, harnessing t …24th Feb 2026 -
The Rise of Cancer Neuroscience: How Neural Circuits Drive Tumor Progression
For decades, we viewed cancer as a rogue army of cells, a biological glitch driven solely by geneti …23rd Feb 2026 -
CRISPR-Powered Light Sensors: A New Frontier in Ultra-Sensitive Cancer Detection
Cancer detection often relies on advanced imaging or invasive procedures, frequently catching the d …20th Feb 2026