Galegenimab: Unlocking the Potential of Anti-CD47 in Cancer Research
Quick Facts About Galegenimab
What is Galegenimab?
How Does Galegenimab Work?
What Are the Clinical Applications of Galegenimab?
Galegenimab is being investigated for its potential in treating hematologic malignancies and solid tumors, particularly in combination with other immunotherapies.
1.) Understanding Galegenimab
Galegenimab represents a significant advancement in immuno-oncology by targeting CD47, an immune checkpoint that plays a crucial role in cancer cell evasion. CD47 is a transmembrane protein highly expressed on various tumor cells, where it interacts with signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPα) on macrophages, transmitting a “don’t eat me” signal. This mechanism allows malignant cells to escape immune surveillance and persist in the body despite an active immune system. Galegenimab functions as an anti-CD47 monoclonal antibody that disrupts this interaction, thereby reactivating macrophages and enabling them to engulf and destroy tumor cells efficiently.
Unlike traditional chemotherapy and radiation therapy, which directly target cancer cells but often result in significant toxicity, anti-CD47 therapies offer a more targeted approach to immune activation. By leveraging the innate immune system’s ability to recognize and clear malignant cells, Galegenimab has the potential to be an effective therapy for a range of cancers, including hematologic malignancies such as acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS), as well as solid tumors like ovarian, breast, and lung cancers.
Current research focuses on optimizing Galegenimab’s efficacy while minimizing side effects. Because CD47 is also present on healthy cells, particularly red blood cells, early studies have explored different dosing regimens and combination strategies to reduce potential off-target effects, such as anemia. Additionally, researchers are investigating how Galegenimab may work synergistically with existing immunotherapies, such as PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors, to enhance overall treatment efficacy. As ongoing trials continue to refine its clinical application, Galegenimab stands at the forefront of innovative cancer therapies, offering new hope for patients with treatment-resistant malignancies.
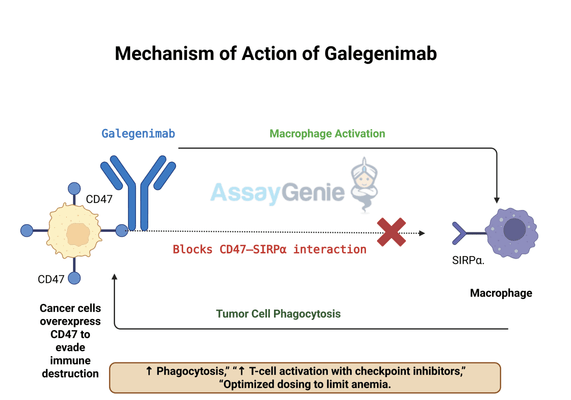
2.) Mechanism of Action of Galegenimab
Galegenimab works by selectively binding to CD47 on cancer cells, thereby preventing its interaction with SIRPα, a key receptor on macrophages and dendritic cells. Under normal physiological conditions, this CD47-SIRPα signaling pathway helps distinguish self from non-self, preventing the immune system from attacking healthy cells. However, in cancer, CD47 is often overexpressed, enabling tumor cells to evade immune destruction. Galegenimab effectively blocks this “don’t eat me” signal, restoring macrophage-mediated phagocytosis and allowing the immune system to recognize and eliminate cancerous cells.
- Phagocytosis Enhancement: By disrupting the CD47-SIRPα interaction, Galegenimab removes the immune suppression barrier, enabling macrophages to engulf and digest tumor cells more efficiently. This mechanism is particularly relevant in hematologic cancers, where immune evasion is a significant challenge.
- Synergistic Immunotherapy Potential: Research indicates that Galegenimab’s effects are amplified when used in combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors such as anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies. These therapies work by further boosting T-cell activation, creating a dual approach that enhances immune responses against tumors.
- Selective Targeting Strategies: Since CD47 is also expressed on normal cells, particularly red blood cells, careful dosing strategies are required to minimize potential hematologic side effects such as anemia. Ongoing studies are exploring ways to optimize treatment regimens, including intermittent dosing and combination therapies, to enhance safety while maintaining efficacy.
Emerging research is also investigating biomarkers that could help predict patient response to Galegenimab, ensuring that the treatment is tailored to individuals most likely to benefit. By refining patient selection criteria and optimizing administration strategies, Galegenimab holds the potential to become a cornerstone therapy in both hematologic and solid tumor oncology.
Key Mechanisms at Play:3.) Clinical Applications of Galegenimab
Galegenimab has demonstrated significant potential in treating a range of cancers, particularly hematologic malignancies such as AML and MDS. These cancers are often associated with high CD47 expression, making them ideal candidates for CD47-targeting therapies. Preclinical and early clinical studies have shown that blocking CD47 with Galegenimab enhances immune cell-mediated clearance of malignant cells, leading to improved patient outcomes. Additionally, research suggests that Galegenimab can enhance the efficacy of standard cancer treatments such as chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and immune checkpoint inhibitors.
- Hematologic Cancers: In AML and MDS, Galegenimab enhances the phagocytic activity of macrophages, helping to clear cancer cells that would otherwise evade immune detection. Given the aggressive nature of these diseases, CD47-targeting strategies could provide an important new avenue for treatment, particularly in patients who are resistant to standard therapies.
- Solid Tumors: While much of the initial focus has been on blood cancers, ongoing research is exploring Galegenimab’s effectiveness in treating solid tumors, including breast, lung, and ovarian cancers. Early data suggest that CD47 blockade may enhance immune infiltration into tumors, making them more susceptible to immune-mediated destruction.
- Combination Therapies: One of the most promising aspects of Galegenimab is its potential to work synergistically with existing cancer treatments. Studies indicate that combining CD47 blockade with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors may amplify immune activation, leading to a more robust and sustained anti-tumor response. Additionally, preclinical models suggest that Galegenimab may improve responses to chemotherapy and radiation therapy by enhancing immune-mediated tumor clearance.
Despite these promising findings, further research is needed to optimize treatment strategies and ensure long-term safety. Ongoing clinical trials aim to refine dosing regimens, assess potential side effects, and identify biomarkers that can help predict which patients are most likely to benefit from CD47-targeted therapy. As these studies progress, Galegenimab represents a promising new approach to cancer immunotherapy, offering hope for patients with aggressive or treatment-resistant malignancies.
Current Research Focus:
4.) Exploring Biosimilars for Galegenimab
What is a Biosimilar?
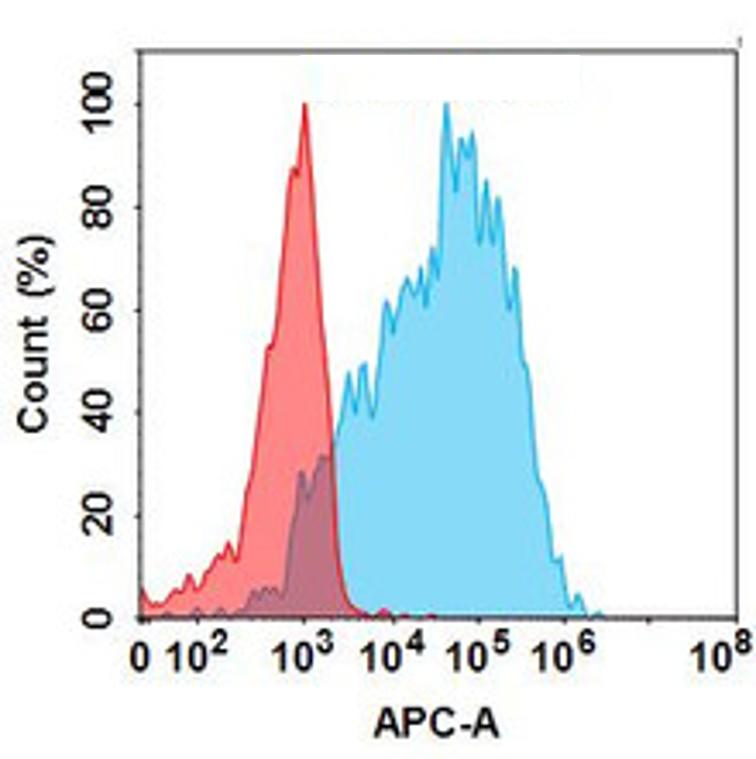
| Galegenimab (Anti-HTRA1) Biosimilar Antibody | |
|---|---|
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Protein: | HTRA1 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
How Galegenimab Biosimilar Advances Research
Our Galegenimab biosimilar (Product Link) enables researchers to explore CD47-targeting strategies without the high costs associated with original biologics. Key benefits include:
- Reliable Performance: Maintains similar binding affinity and functional activity as the original molecule.
- Cost-Effective Research Solutions: Allows broader preclinical studies and combination therapy exploration.
- Scalability for Experimental Models: Supports in vitro and in vivo research without supply limitations.
Key Differences Between Galegenimab and Its Biosimilar
Research Use Only Disclaimer:
Discover Our Biosimilar Range
At Assay Genie, we specialize in providing high-quality biosimilars for research use! Check out our full biosimilar range to learn more.

By David Lee, PhD
Recent Posts
-
IgG1 Plasma Cells: The Emerging Biomarker for Predicting Cancer Immunotherapy Success
In the relentless fight against cancer, immunotherapy has emerged as a beacon of hope, harnessing t …24th Feb 2026 -
The Rise of Cancer Neuroscience: How Neural Circuits Drive Tumor Progression
For decades, we viewed cancer as a rogue army of cells, a biological glitch driven solely by geneti …23rd Feb 2026 -
CRISPR-Powered Light Sensors: A New Frontier in Ultra-Sensitive Cancer Detection
Cancer detection often relies on advanced imaging or invasive procedures, frequently catching the d …20th Feb 2026