Vopratelimab: Unlocking the Potential of ICOS in Cancer Research
What You Need to Know About Vopratelimab
What is Vopratelimab?
Vopratelimab is an experimental monoclonal antibody that targets the Inducible T-cell CO-Stimulator (ICOS) protein, playing a pivotal role in enhancing immune system activity against cancer.
What is the mechanism of action for Vopratelimab?
Vopratelimab activates ICOS on T-cells, boosting their proliferation and effector functions, which are crucial for mounting an effective anti-tumor immune response.
What are the clinical applications of Vopratelimab?
Emerging studies suggest that Vopratelimab holds promise in cancer immunotherapy, particularly for solid tumors like non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC).
1.) Understanding Vopratelimab
Vopratelimab is a monoclonal antibody developed to target the inducible T-cell co-stimulator (ICOS) protein, a co-stimulatory receptor found on activated T-cells. ICOS is a key regulator in the immune response, playing a vital role in enhancing T-cell activation and proliferation. Once T-cells are stimulated through their T-cell receptor (TCR), ICOS further amplifies the immune response by promoting the production of cytokines, which are crucial for sustaining immune activity. This co-stimulation increases the cytotoxic potential of T-cells, particularly in their ability to recognize and destroy tumor cells.
In the context of cancer, ICOS is important because it facilitates the immune system’s ability to mount a strong and sustained anti-tumor response. By targeting ICOS, Vopratelimab aims to boost the immune system’s efficacy in fighting cancer, particularly by enhancing the proliferation and activation of tumor-specific T-cells. This mechanism holds great potential in cancers where immune evasion is a significant challenge, such as in solid tumors.
Vopratelimab is part of a growing class of immunotherapies known as co-stimulatory checkpoint inhibitors, which are designed to enhance the immune system's natural ability to combat cancer. By targeting pathways that enhance immune activation rather than inhibit it, Vopratelimab offers a new avenue for boosting immune responses, making it a promising candidate in the expanding field of immuno-oncology.
Prefer to Listen? Check out the Vopratelimab Podcast Episode
2.) Mechanism of Action of Vopratelimab
Vopratelimab works by specifically binding to the inducible T-cell co-stimulator (ICOS) receptor on activated T-cells. ICOS is a key co-stimulatory receptor that plays a pivotal role in amplifying T-cell responses during immune activation. When Vopratelimab binds to ICOS, it enhances T-cell activation and proliferation, leading to an increased number of highly active T-cells capable of mounting an effective anti-tumor response. This binding also stimulates the production of cytokines, such as interleukin-2 (IL-2), which further activates immune cells and promotes a more robust immune response.
By targeting ICOS, Vopratelimab directly enhances T-cell-mediated immunity, improving the immune system’s ability to recognize and eliminate tumor cells. This amplification of T-cell activity is particularly critical in cancers where immune evasion mechanisms prevent effective immune surveillance, such as in solid tumors with immune-suppressive microenvironments.
Vopratelimab’s mechanism of action has shown significant promise in combination therapies, especially when paired with immune checkpoint inhibitors like anti-PD-1 antibodies (e.g., pembrolizumab). While PD-1 inhibitors work by blocking the inhibitory signals that dampen T-cell responses, Vopratelimab complements this by boosting T-cell activation through the ICOS pathway. This dual approach creates a synergistic effect that amplifies immune system activity on multiple fronts, enhancing overall efficacy and potentially overcoming resistance mechanisms that tumors may use to evade immune responses. As a result, the combination of Vopratelimab with checkpoint inhibitors offers a compelling strategy for improving treatment outcomes in cancers that are difficult to treat with monotherapies.

3.) Clinical Applications of Vopratelimab
Vopratelimab is a promising investigational therapy under clinical evaluation for its potential in treating a variety of solid tumors. Its mechanism involves targeting the inducible T-cell co-stimulator (ICOS) pathway, which plays a crucial role in regulating immune responses. This approach has opened new avenues for enhancing antitumor immunity, particularly in cancers known for their complex immunosuppressive microenvironments.
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC):
Clinical trials have demonstrated the potential of Vopratelimab, particularly when combined with other immunotherapies like anti-PD-1 inhibitors, in treating NSCLC. These studies highlight its ability to promote immune activation by enhancing ICOS signaling, which boosts T-cell proliferation and function. Patients with NSCLC often experience significant immune evasion by tumors, and Vopratelimab's synergistic effects with existing therapies offer hope for overcoming these barriers.
Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC):
In early-phase clinical trials, Vopratelimab has shown encouraging results in improving outcomes for patients with HNSCC. By targeting the ICOS pathway, it potentially enhances the tumor-specific immune response, particularly in combination regimens. While additional studies are required, preliminary data suggest improved progression-free survival and tumor control in a subset of patients
While some trials have faced challenges, including patient recruitment and study design adjustments, the insights gained have significantly advanced the understanding of ICOS-targeted therapies.
4.) Advancing Research on Vopratelimab
What is a Biosimilar?
A biosimilar is a biologic medical product highly similar to an already approved reference product. Biosimilars offer a cost-effective and accessible alternative, facilitating research and innovation in various fields, including cancer immunotherapy.
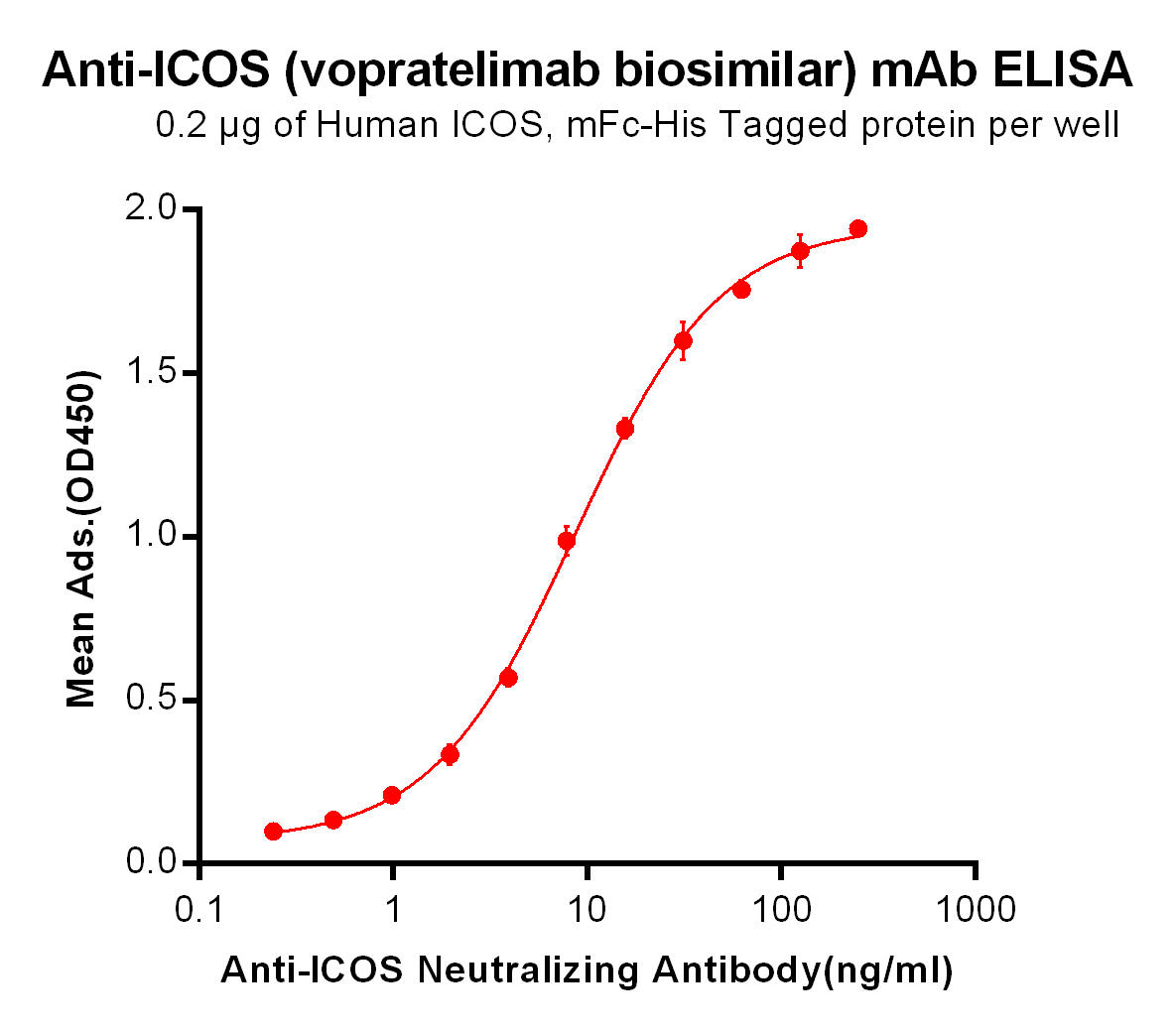
| Vopratelimab (Anti-ICOS) Biosimilar Antibody | |
|---|---|
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Protein: | ICOS |
| Reactivity: | Human |
How Does the Vopratelimab Biosimilar Compare?
Our Vopratelimab biosimilar provides a high-quality, research-use-only alternative to the original monoclonal antibody. It is engineered to match the structural and functional characteristics of Vopratelimab, ensuring reliable results in preclinical studies.
Benefits of the Vopratelimab Biosimilar
- Research Applications: Ideal for studying the ICOS pathway and its role in cancer immunotherapy.
- Cost-Effective: Provides a more accessible option for academic and industrial research.
- High Quality: Designed to meet rigorous standards for preclinical research.
Disclaimer:
The Vopratelimab biosimilar is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic or therapeutic applications.
Discover Our Biosimilar Range
At Assay Genie, we specialize in providing high-quality biosimilars for research use! Check out our full biosimilar range to learn more.

By Miren Ruiz de Eguilaz, PhD
Miren Ruiz de Eguilaz, PhD, has an extensive academic background, earning a BSc in Biology from UPV/EHU, an MSc in Biotechnology from the University of Oviedo, and a PhD in Chemistry from Dublin City University (DCU). Miren’s expertise lies in biosensor technology and bacterial diagnostics. She currently serves as a Product Manager at Assay Genie.
Recent Posts
-
IgG1 Plasma Cells: The Emerging Biomarker for Predicting Cancer Immunotherapy Success
In the relentless fight against cancer, immunotherapy has emerged as a beacon of hope, harnessing t …24th Feb 2026 -
The Rise of Cancer Neuroscience: How Neural Circuits Drive Tumor Progression
For decades, we viewed cancer as a rogue army of cells, a biological glitch driven solely by geneti …23rd Feb 2026 -
CRISPR-Powered Light Sensors: A New Frontier in Ultra-Sensitive Cancer Detection
Cancer detection often relies on advanced imaging or invasive procedures, frequently catching the d …20th Feb 2026