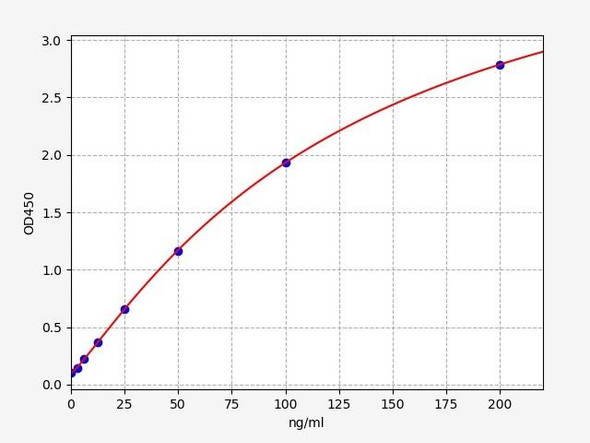
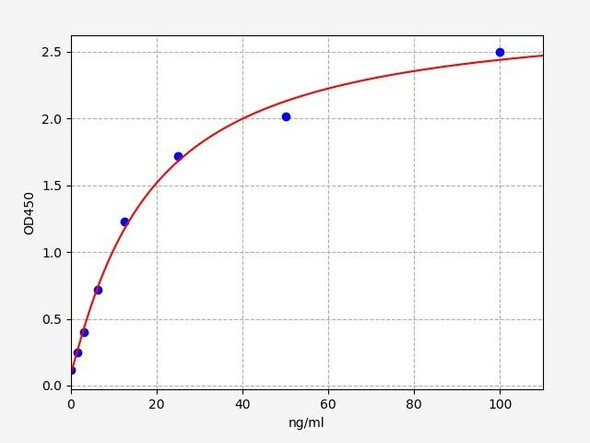
| Synonyms: | KCNJ6, BIR1, GIRK-2, GIRK2, KATP-2, KATP2, KCNJ7, KIR3.2, KPLBS, hiGIRK2 |
| Background: | This gene encodes a member of the G protein-coupled inwardly-rectifying potassium channel family of inward rectifier potassium channels. This type of potassium channel allows a greater flow of potassium into the cell than out of it. These proteins modulate many physiological processes, including heart rate in cardiac cells and circuit activity in neuronal cells, through G-protein coupled receptor stimulation. Mutations in this gene are associated with Keppen-Lubinsky Syndrome, a rare condition characterized by severe developmental delay, facial dysmorphism, and intellectual disability. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | This potassium channel may be involved in the regulation of insulin secretion by glucose and/or neurotransmitters acting through G-protein-coupled receptors. Inward rectifier potassium channels are characterized by a greater tendency to allow potassium to flow into the cell rather than out of it. Their voltage dependence is regulated by the concentration of extracellular potassium; as external potassium is raised, the voltage range of the channel opening shifts to more positive voltages. The inward rectification is mainly due to the blockage of outward current by internal magnesium. |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a member of the G protein-coupled inwardly-rectifying potassium channel family of inward rectifier potassium channels. This type of potassium channel allows a greater flow of potassium into the cell than out of it. These proteins modulate many physiological processes, including heart rate in cardiac cells and circuit activity in neuronal cells, through G-protein coupled receptor stimulation. Mutations in this gene are associated with Keppen-Lubinsky Syndrome, a rare condition characterized by severe developmental delay, facial dysmorphism, and intellectual disability. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2015] |
| UniProt Code: | P48051 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 4504843 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 3763 |
| NCBI Accession: | NP_002231.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P48051,Q3MJ74, Q53WW6, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P48051 |
| Molecular Weight: | 46 |
| NCBI Full Name: | G protein-activated inward rectifier potassium channel 2 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily J member 6 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | KCNJ6 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | BIR1; GIRK2; KATP2; KCNJ7; KPLBS; GIRK-2; KATP-2; KIR3.2; hiGIRK2 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | G protein-activated inward rectifier potassium channel 2 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | G protein-activated inward rectifier potassium channel 2 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | BIR1; Inward rectifier K(+) channel Kir3.2; KATP-2; Potassium channel, inwardly rectifying subfamily J member 6 |
| UniProt Gene Name: | KCNJ6 |