Tomaralimab: Unveiling the Role of Anti-CD47 in Cancer Research
Quick Facts About Tomaralimab
What is Tomaralimab?
Tomaralimab is an anti-CD47 monoclonal antibody designed to enhance immune system recognition of cancer cells by blocking the "don't eat me" signal.
What is the mechanism of action for Tomaralimab?
Tomaralimab inhibits CD47, a protein that allows cancer cells to evade macrophage-mediated phagocytosis. By blocking CD47, it promotes immune clearance of tumors.
What are the clinical applications of Tomaralimab?
It has been investigated in hematologic malignancies and solid tumors, with ongoing research into its potential combination therapies.
1.) Understanding Tomaralimab
Tomaralimab represents a significant advancement in immuno-oncology, particularly in overcoming immune evasion strategies employed by cancer cells. CD47, often referred to as the "don’t eat me" signal, is an immune checkpoint widely expressed on tumor cells. This molecule interacts with its receptor, signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPα), on macrophages, effectively preventing phagocytosis and allowing cancer cells to evade immune destruction. By exploiting this mechanism, tumor cells gain a survival advantage, contributing to disease progression and resistance to conventional therapies.
As a monoclonal antibody, Tomaralimab is designed to block CD47, thereby disrupting its interaction with SIRPα. This blockade restores immune surveillance by enhancing macrophage-mediated phagocytosis and stimulating antigen presentation to T cells, ultimately leading to a more robust anti-tumor immune response. Preclinical and clinical studies have demonstrated that Tomaralimab not only promotes macrophage activity but may also enhance the efficacy of other immunotherapeutic strategies.
Recent research suggests that Tomaralimab may work synergistically with other treatments, including immune checkpoint inhibitors such as anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies and chemotherapeutic agents. By combining these modalities, the immune system’s ability to recognize and destroy cancer cells is further amplified. Additionally, emerging evidence indicates that targeting CD47 could have broader implications beyond macrophage activation, potentially influencing dendritic cell function and adaptive immunity.
Due to its promising mechanism of action, Tomaralimab is being investigated in clinical trials for various malignancies, including solid tumors and hematologic cancers. Its ability to reverse immune suppression and enhance tumor clearance positions it as a key player in the evolving landscape of cancer immunotherapy.
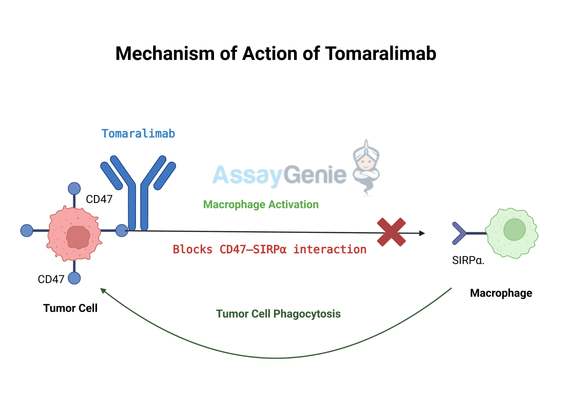
2.) Mechanism of Action of Tomaralimab
Tomaralimab exerts its therapeutic effect by targeting CD47, a crucial immune checkpoint that cancer cells exploit to evade destruction. CD47 interacts with signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPα) on macrophages, delivering a "don’t eat me" signal that inhibits phagocytosis and allows malignant cells to persist unchecked. By binding to CD47, Tomaralimab effectively blocks this interaction, preventing tumor cells from escaping immune surveillance and enhancing the body's ability to mount an effective anti-cancer response.
The mechanism of action of Tomaralimab involves multiple immune-modulating processes:
CD47 Blockade: Tomaralimab directly binds to CD47 on tumor cells, preventing its interaction with SIRPα on macrophages. This removes the inhibitory signal that suppresses macrophage activity, allowing immune cells to recognize and target cancer cells more effectively.
Macrophage Activation: With the suppression lifted, macrophages are activated to engulf and destroy tumor cells through phagocytosis. This process not only reduces tumor burden but also leads to the release of tumor-derived antigens, which can further stimulate the immune response.
Adaptive Immune Stimulation: The phagocytosis of tumor cells by macrophages facilitates antigen presentation to dendritic cells, which subsequently activate T cells. This cascade strengthens the adaptive immune response, ensuring a sustained and more robust attack on cancer cells.
Preclinical and early clinical studies suggest that Tomaralimab significantly enhances tumor shrinkage and improves patient response rates, particularly when combined with other immunotherapies such as PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors and chemotherapy. By reprogramming the immune system to better recognize and eliminate cancer cells, Tomaralimab represents a promising advancement in the evolving landscape of cancer immunotherapy.
3.) Clinical Applications of Tomaralimab
Tomaralimab has emerged as a promising immunotherapy for a wide range of cancers, particularly those that exploit CD47-mediated immune evasion. By blocking the CD47-SIRPα interaction, Tomaralimab restores immune surveillance and facilitates the elimination of cancer cells. It has been extensively evaluated in both hematologic malignancies and solid tumors, demonstrating its potential to improve treatment outcomes, especially in combination with other immunotherapies.
Hematologic Malignancies
Tomaralimab has shown encouraging results in treating myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML)—two aggressive blood cancers with limited treatment options. In these malignancies, cancerous cells overexpress CD47 to avoid macrophage-mediated destruction, making them prime candidates for CD47 blockade therapy. Preclinical and early-phase clinical studies suggest that Tomaralimab can enhance macrophage phagocytosis and stimulate an adaptive immune response, leading to improved disease control. In combination with hypomethylating agents or chemotherapy, Tomaralimab has demonstrated increased efficacy in AML and MDS, making it a valuable addition to existing treatment regimens.
Solid Tumors
Tomaralimab is also being evaluated in various solid tumors, including non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and colorectal cancer (CRC). These cancers frequently exhibit immune resistance mechanisms, making checkpoint inhibitors like PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies less effective in some patients. Research suggests that combining Tomaralimab with anti-PD-1/PD-L1 agents can enhance immune activation, improving tumor response rates.
Despite some challenges, such as dose-limiting toxicities observed in early trials, ongoing research continues to refine CD47-targeting strategies. The potential of Tomaralimab in oncology remains strong, with ongoing trials exploring optimized dosing regimens and novel combination approaches to maximize therapeutic benefits.

4.) Exploring Biosimilars for Tomaralimab
Biosimilars play a crucial role in expanding access to critical research tools. A biosimilar to Tomaralimab provides researchers with a reliable alternative for studying CD47 blockade mechanisms in cancer.
What is a Biosimilar?
A biosimilar is a biologic product highly similar to an existing reference biologic, offering comparable safety and efficacy.
| Tomaralimab (Anti-TLR2) Biosimilar Antibody | |
|---|---|
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Protein: | TLR2 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
Comparison Between Tomaralimab and Its Biosimilar
Feature | Tomaralimab | Tomaralimab Biosimilar |
Target | CD47 | CD47 |
Research Use Only? | No | Yes |
Mechanism | Identical | Identical |
Advancing Research on Tomaralimab
Biosimilars allow for broader preclinical exploration of CD47-targeting therapies, helping researchers:
Investigate immune evasion mechanisms
Test combination strategies
Develop next-generation immunotherapies
Research Use Only Disclaimer:
The Tomaralimab biosimilar is intended for research purposes only and is not approved for clinical applications.
Discover Our Biosimilar Range
At Assay Genie, we specialize in providing high-quality biosimilars for research use! Check out our full biosimilar range to learn more.

By Marina Alberto, PhD
Marina Alberto, PhD, holds a robust academic background in Biotechnology, earning her Bachelor’s Degree and PhD in Science and Technology from Quilmes National University. Her research spans cancer immunotherapy, glycan profiling, and vaccine development, including innovative projects on pediatric leukemia diagnosis and cancer-associated carbohydrate-mimetic vaccines. She currently serves as a Technical Support and Sales Specialist at Assay Genie.
Recent Posts
-
The Rise of Cancer Neuroscience: How Neural Circuits Drive Tumor Progression
For decades, we viewed cancer as a rogue army of cells, a biological glitch driven solely by geneti …23rd Feb 2026 -
CRISPR-Powered Light Sensors: A New Frontier in Ultra-Sensitive Cancer Detection
Cancer detection often relies on advanced imaging or invasive procedures, frequently catching the d …20th Feb 2026 -
The Rise of Alpha-Emitting Radiopharmaceuticals: A New Era in Targeted Cancer Therapy
Imagine a microscopic sniper, capable of delivering a lethal blow to a single cancer cell while lea …19th Feb 2026