Liquid Zinc Assay - Information
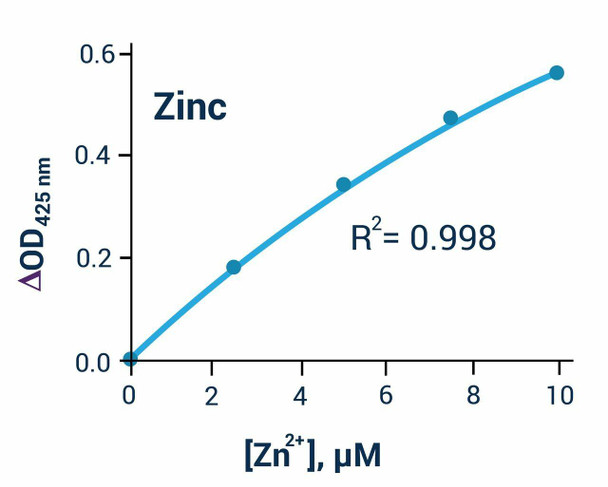
This liquid zinc assay kit is designed to measure zinc directly in biological samples without any pretreatment. The present method utilizes a chromogen that forms a colored complex specifically with zinc. The intensity of the color, measured at 425 nm, is directly proportional to the zinc concentration in the sample.
Applications
For quantitative determination of zinc ion Zn
2+and evaluation of drug effects on zinc metabolism.
Liquid Zinc Assay - Key Features
- Sensitive and accurate. Uses 50 samples. Linear detection range 0.12 (0.78 ug/dL) to 10 (65 ug/dL) zinc in 96-well assay format.
- Simple and high-throughput. The procedure involves addition of a single working reagent and incubation for 30 min. Can be readily automated as a high-throughput assay for thousands of samples per day.
- Improved reagent stability and versatility. The optimized formulation has greatly enhanced reagent and signal stability. Cuvette or 96-well plate assay formats possible.
- Low interference in biological samples. No pretreatments are needed.
Liquid Zinc Assay - Data Sheet | |
| Kit Includes | Reagent A: 50 mL Reagent B: 1 mL Reagent C: 1 mL EDTA: 1 mL 100 mM Zinc standard: 1 mL 50 mM |
| Kit Requires | Pipeting devices and accessories. Clear bottom 96-well plates and plate reader, or cuvettes and spectrophotometer for measuring OD 425nm |
| Method of Detection | OD425nm |
| Detection Limit | 0.78 ug/dL (0.12 ) |
| Samples | Serum, plasma, urine, saliva, food, beverage and environment |
| Species | All |
| Protocol Length | 30 min |
| Size | 250 tests |
| Storage | Store Reagents B and C at -20°C and other components at 4°C. |
| Shelf Life | 6 Months |
More Details
Zinc is an essential trace element and plays many key roles in metabolism. It is required for the activity of more than 300 enzymes, the structure of many proteins, and control of genetic expression. Zinc status affects basic processes of cell division, growth, differentiation, development, performance and aging through its requirement for synthesis and repair of DNA, RNA and protein.