Oxidative Phosphorylation (OXPHOS) Pathway & Assays
What is Oxidative Phosphorylation (OXPHOS)?
Oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) is a metabolic pathway in which enzymes oxidize nutrients to release stored chemical energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). OXPHOS consists of five protein complexes I-V and takes place in the mitochondria.
Key Takeaways
- Oxidative Phosphorylation (OXPHOS) in mitochondria is crucial for ATP production.
- It involves electron transfer, creating a proton gradient used by ATP synthase.
- OXPHOS also plays a role in immunometabolism and obesity.
Jump to a section:
An Overview of Oxidative Phosphorylation
Electrons are passed along the electron transport chain (ETC) from two possible donors, reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) and reduced flavin adenine dinucleotide (FADH2), which are produced from glycolysis, the citric acid (TCA) cycle and fatty acid oxidation (FAO). The electrons taken from these donors during oxidation pass through the four protein complexes of the ETC; I (NADH dehydrogenase), II (succinate dehydrogenase), III (cytochrome C reductase) and IV (cytochrome C oxidase), which are embedded in the mitochondrial membrane. The downstream transport of electrons results in a proton gradient as protons are pumped into the intermembrane space. The electrons are passed to the final electron acceptor O2 that becomes H2O. Complex V, commonly referred to as ATP synthase, is a membrane spanning enzyme which harnesses the proton gradient created during OXPHOS, converting adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and Pi into ATP.
Steps of Oxidative Phosphorylation
(Click to enlarge!)
OXPHOS Assays
View Oxidative Phosphorylation ELISA Kits
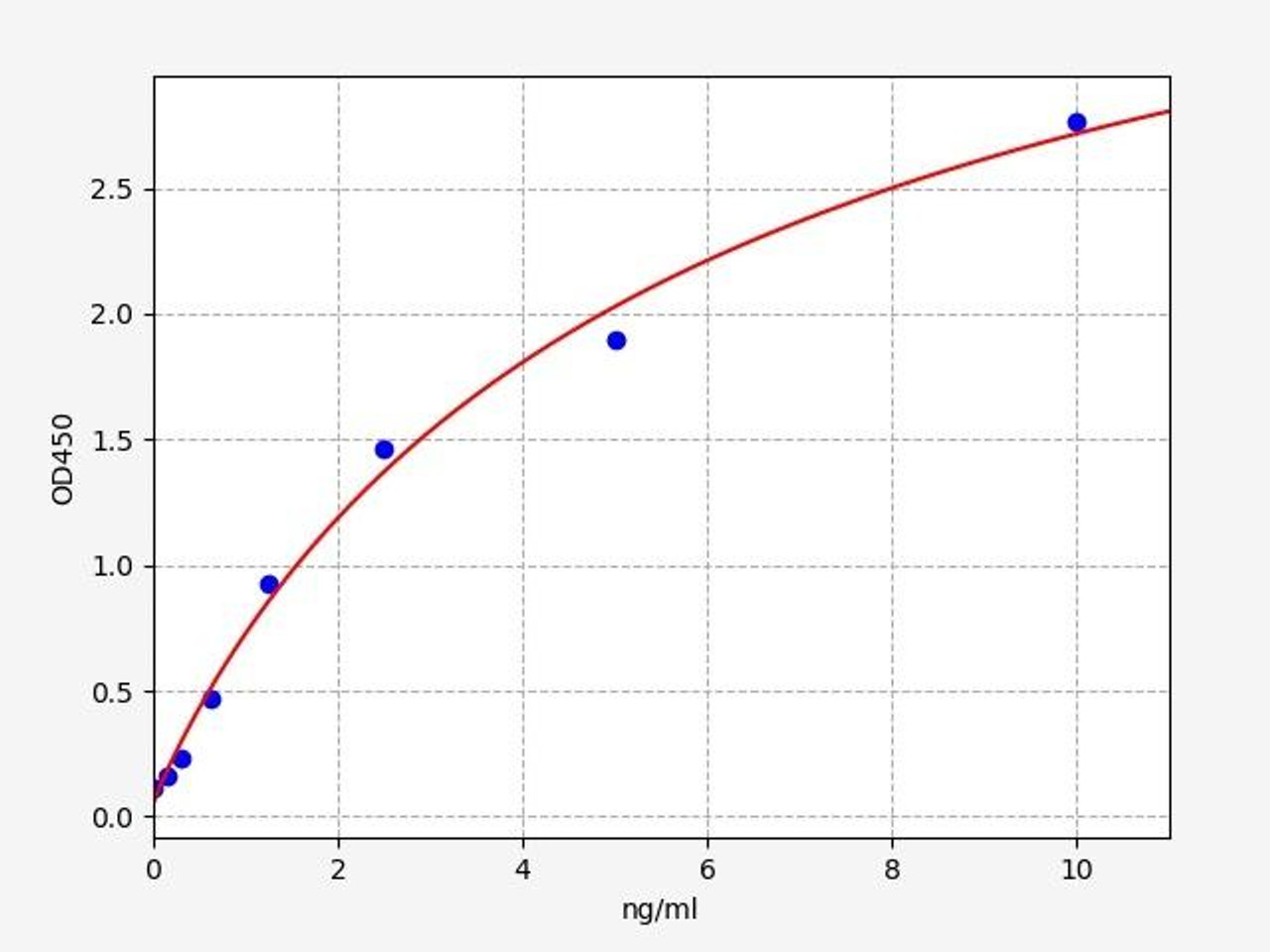
| Cytochrome P450 Reductase ELISA | |
|---|---|
| Sensitivity | 0.094ng/ml |
| Range | 0.156-10ng/ml |
| ELISA Type | Sandwich ELISA |
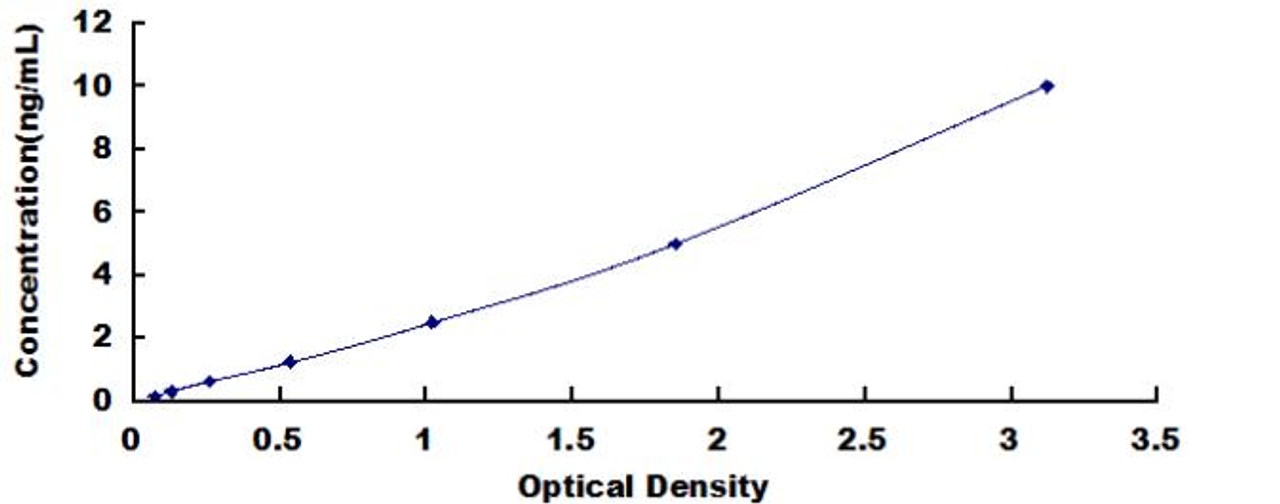
| NADH Dehydrogenase ELISA | |
|---|---|
| Sensitivity | 0.068ng/mL |
| Range | 0.156-10ng/mL |
| ELISA Type | Sandwich ELISA |
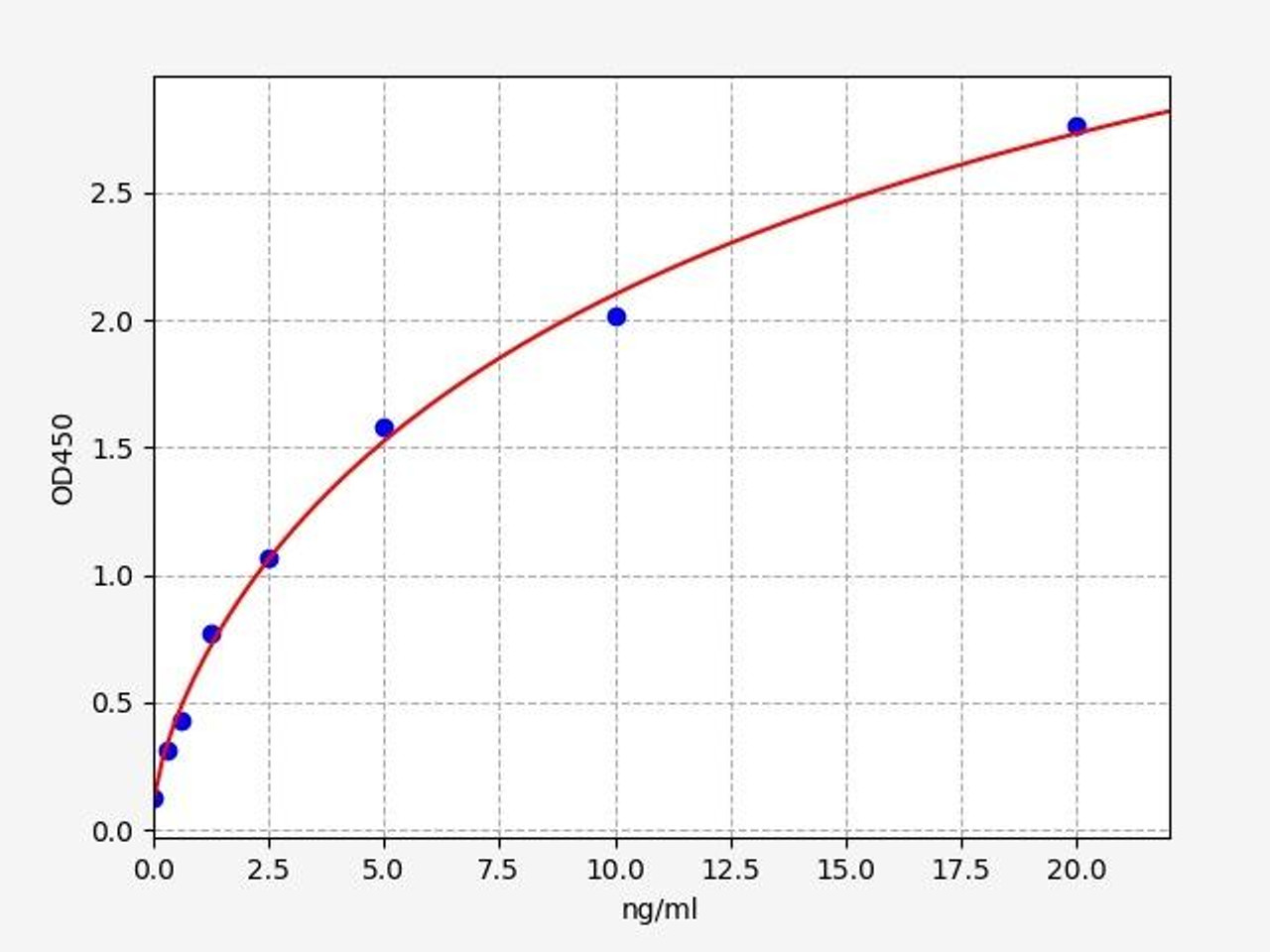
| Succinate Dehydrogenase ELISA | |
|---|---|
| Sensitivity | 0.188ng/ml |
| Range | 0.313-20ng/ml |
| ELISA Type | Sandwich ELISA |
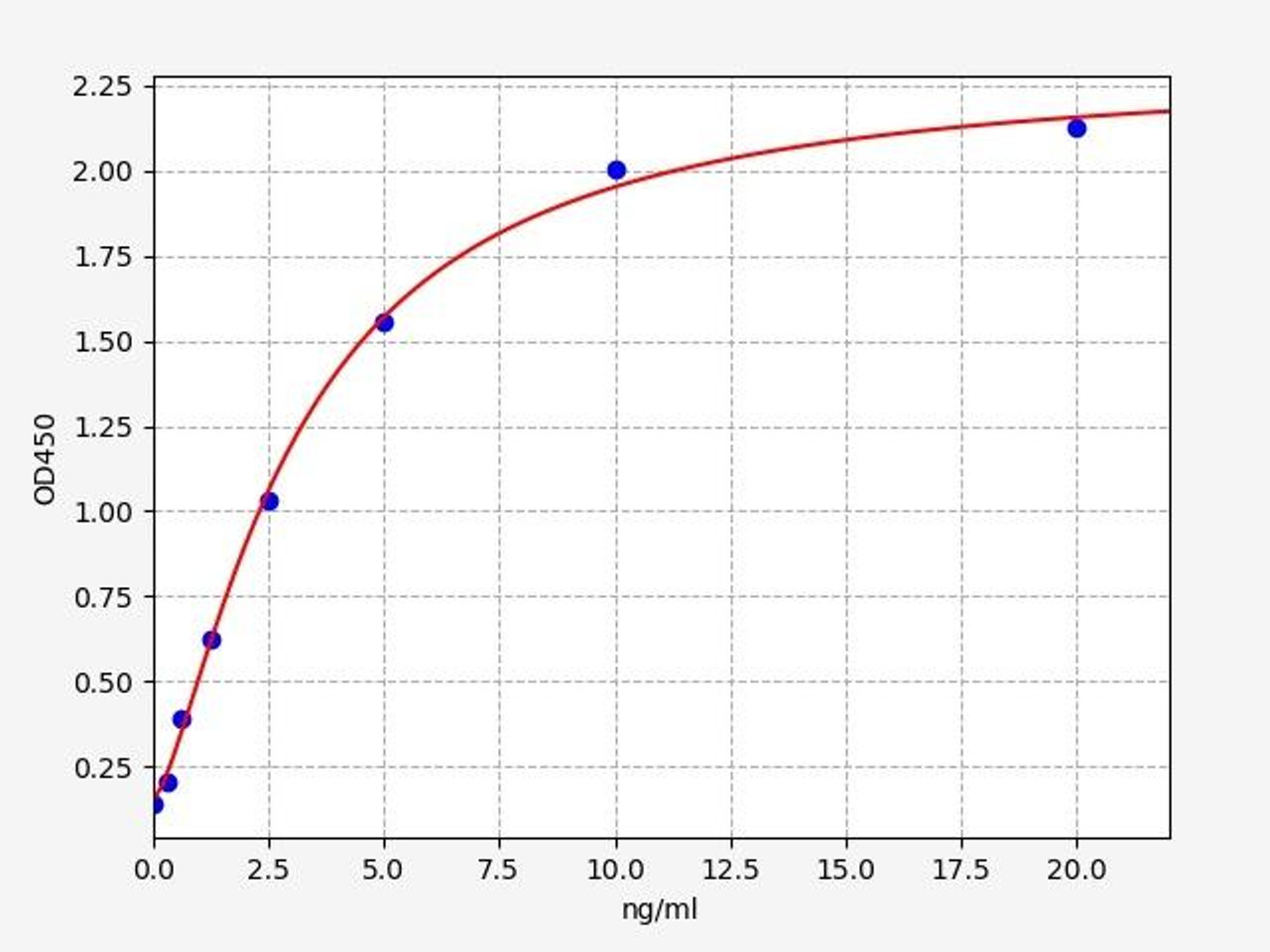
| Cytochrome C Oxidase ELISA | |
|---|---|
| Sensitivity | 0.188ng/ml |
| Range | 0.313-20ng/ml |
| ELISA Type | Sandwich ELISA |
| Succinate Dehydrogenase Complex ELISA | |
|---|---|
| Sensitivity | 0.067ng/mL |
| Range | 0.156-10ng/mL |
| ELISA Type | Sandwich ELISA |
View Oxidative Phosphorylation Assays
| ADP Assay Kit | |
|---|---|
| Product Code | BA0063 |
| Read-out | Fluorometric |
| Sample Type | Cells & other biological samples |

| ADP/ATP Ratio Assay Kit | |
|---|---|
| Product Code | BA0127 |
| Read-out | Luminescence |
| Sample Type | Cells, etc. |
| NAD/NADH Assay Kit | |
|---|---|
| Product Code | BA0106 |
| Read-out | Fluorometric |
| Sample Type | Cells, Tissue extracts, etc. |

| NAD/NADH Assay Kit | |
|---|---|
| Product Code | BA0067 |
| Read-out | Colorimetric |
| Sample Type | Cell or Tissue extracts |

| NADP+/NADPH Assay Kit | |
|---|---|
| Product Code | MAES0200 |
| Read-out | Colorimetric |
| Sample Type | Animal Tissues, Cells |
Have a Question?
Looking for a specific OXPHOS kit? Use our Live Chat (bottom right) to talk to an expert! Alternatively, you can submit a contact form and a memeber of staff will get back to you within one working day!
Oxidative Phosphorylation Complexes and Enzymes
Assay Genie provides a range of products such as complex I, complex II, complex III, complex IV and complex V. Each complex has a different number of subunits whereby complex I has 45, complex II has 4, complex III has 11, complex IV has 13 and complex V has 17.
As well as this, Assay Genie provides mitochondrial Complex I and III Activity Assay Kits which measures the activity of these complexes and the effects which toxicants, drugs and other environmental conditions have on their activity.
Oxidative Phosphorylation Electron Carriers
The electron carriers which transport the electrons from NADH and FADH2 to O2 are cytochrome c and coenzyme Q (ubiquinone/CoQ10).
Oxidative Phosphorylation Cofactors Assays
NADH and FADH2, which are produced in previous metabolic pathways, deposit their electrons in the ETC during OXPHOS, resulting in them being converted back into NAD+ and FAD. As these electrons are transported down the ETC, proton ions are pumped out of the mitochondrial matrix, creating a proton gradient. ATP synthase harnesses this proton gradient and 28 ATP are produced during OXPHOS from ADP and Pi.
Oxidative Phosphorylation and Immunometabolism
In the last number of years it has become clear that the process of OXPHOS is not solely used for the production of energy for metabolism, but can also be harnessed to provide cellular immunity in response to infection. These discoveries have led to the creation of the field of immunometabolism; the idea that cellular metabolism may dictate immune responses. In a broad example, macrophages appear to utilize OXPHOS when in an anti-inflammatory state however, they shift to a glycolysis focus following pathogen detection, instead utilizing the mitochondrial machinery to combat infection.
Obesity has been shown to impact our cellular metabolism. Immune cells in obese patients are less metabolically active and are underprepared to modulate OXPHOS and other cellular responses to combat infection. In particular, obesity leads to mitochondrial dysfunction and reduced oxygen consumption which directly affects OXPHOS and the immune response in obese individuals. Further studies in this exciting new area will no doubt reveal new therapies for future treatments. Assay Genie provides a wide range of extensively validated kits that can be used to interrogate the process of OXPHOS to generate robust and reliable results for expert researchers.
Fatty Acid Oxidation (FAO)
FAO is a major metabolic pathway utilized by living organisms to generate energy to perform a variety of functions. In particular FAO occurs in various tissue types such as cardiac and skeletal muscle, where there is a demand for high-efficiency energy production.
FAO precedes OXPHOS and it converts fatty acids to acetyl-CoA with concomitant production of FADH2 and NADH in the mitochondria. This aerobic oxidative pathway primarily consists of four main steps such as the dehydrogenation of acyl-CoA by acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, a hydration step by enoyl-CoA hydratase, a dehydrogenation step by the enzyme 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase and finally a thiolytic cleavage step by the enzyme beta-ketothiolase.
FAO Assays
View Fatty Acid Oxidation Assays
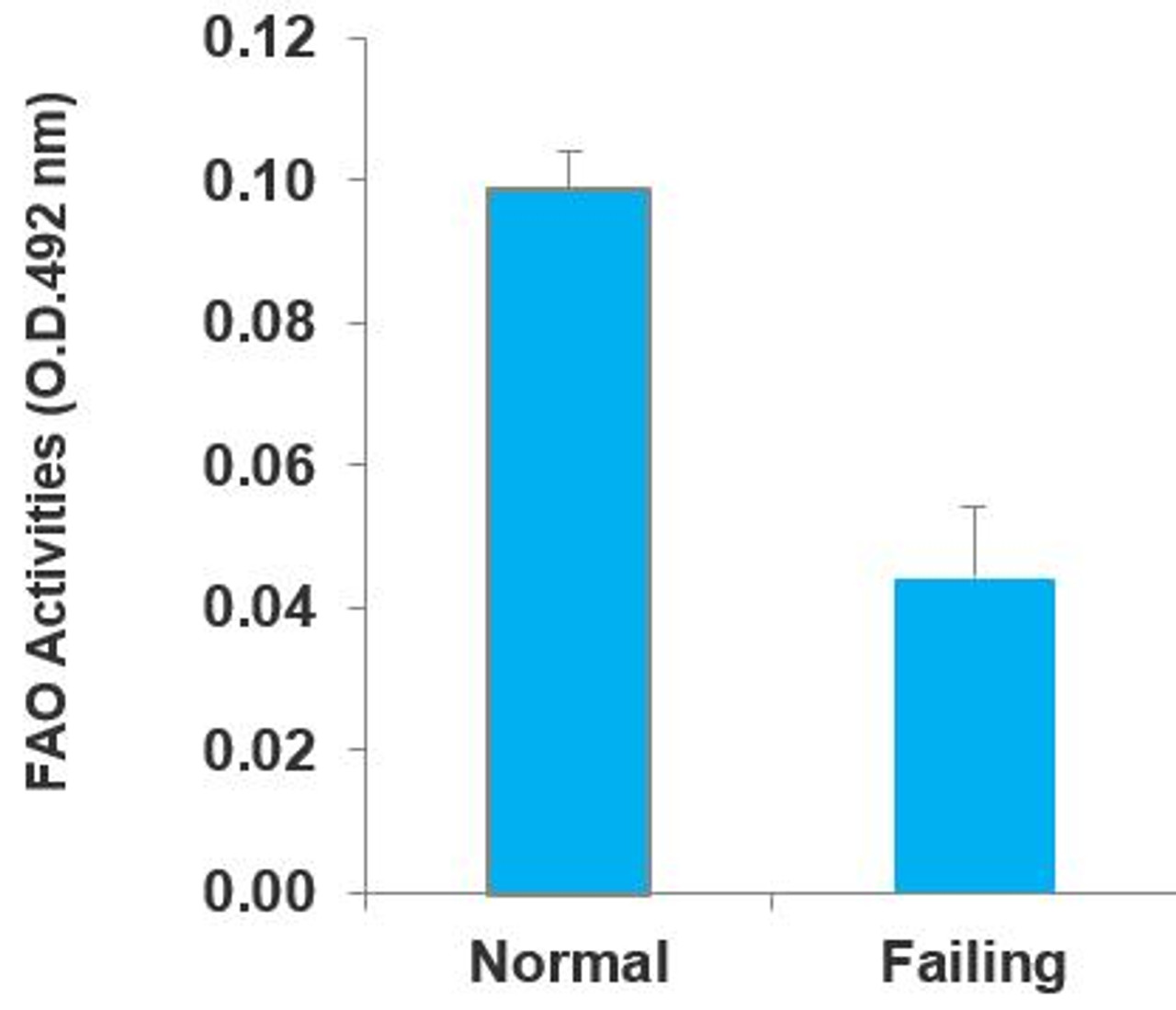
| Fatty Acid Oxidation Assay | |
|---|---|
| Assay Type | Cell based (quantitative) |
| Detection Method | Colorimetric |
| Platform | Microplate reader |
| Sample Type | Cells and tissues |
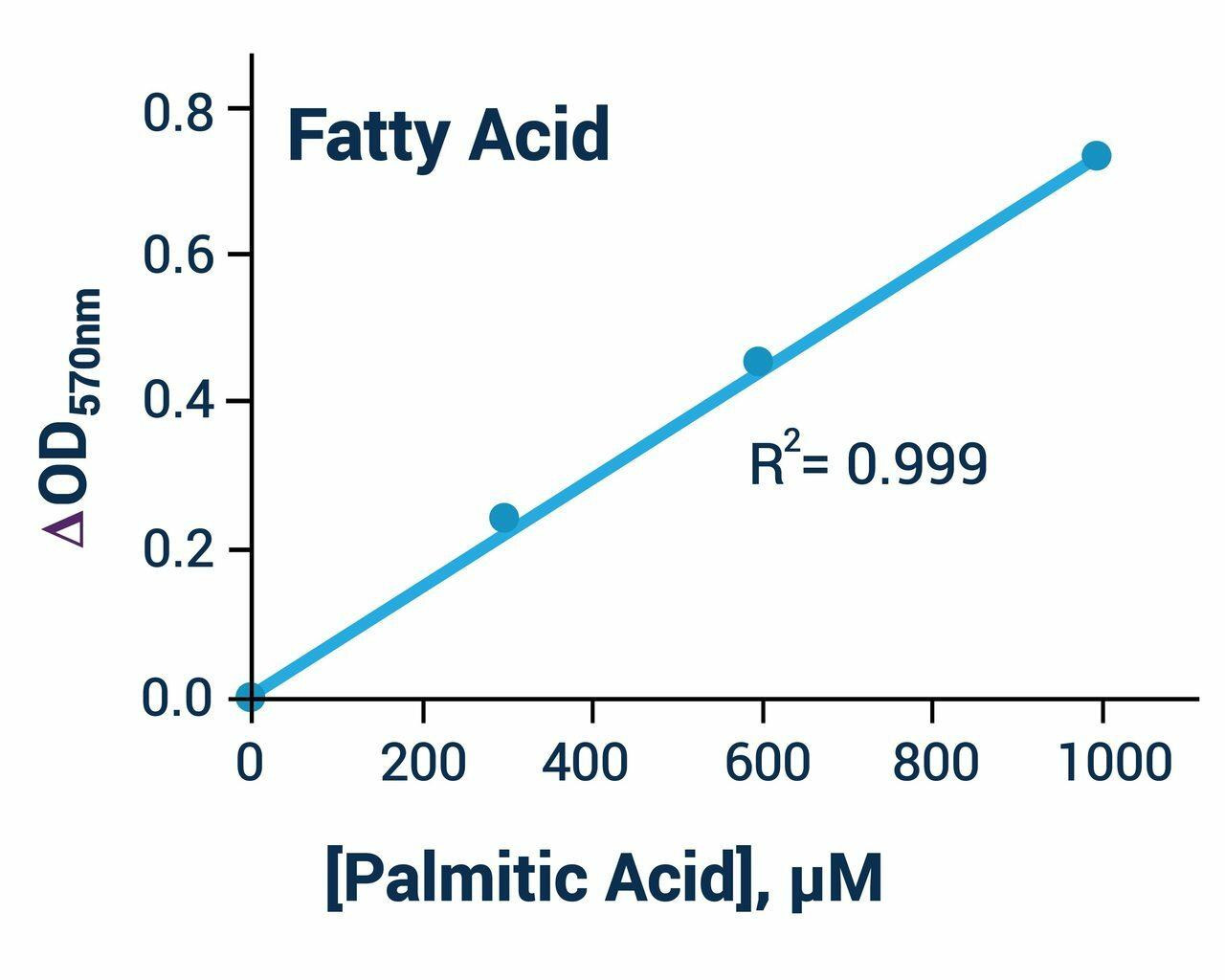
| Free Fatty Acid Measurement Kit | |
|---|---|
| Detection Method | OD570nm or FL530/585nm |
| Detection Limit | 7 uM |
| Sample Type | Serum, plasma, urine, saliva, milk, cell cultures, food |

| Fatty Acid Uptake Assay | |
|---|---|
| Detection Method | FL 488/523nm |
| Species | Universal |
| Sample Type | Adipocytes and other fatty acid transporting cells |