Blog
Cellular Senescence in Cancer Immunotherapy: The Double-Edged Sword
Cellular Senescence in Cancer Immunotherapy: The Double-Edged Sword
In the intricate world of cancer biology, some of our body's most potent defense mechanisms can paradoxically turn against us. Cellular senescence, a process where cells stop dividing in response to stress, has long been hailed as a powerful tumor suppressor. However, recent discoveries have revealed a more complex and fascinating story. It appears that these same senescent cells, under certain conditions, can create a microenvironment that shields tumors from the immune system and even fuels their growth. This surprising twist has led scientists to explore a new frontier in cancer treatment: targeting senescent cells to un
…
29th Nov 2025
Unlocking the Next Wave of Cancer Treatment: The Rise of CAR-T Cell Therapy
A New Era in Oncology
Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR)-T cell therapy represents a paradigm shift in the fight against cancer, offering a personalized and powerful immunotherapy that trains a patient's own immune cells to recognize and destroy malignant cells. This revolutionary approach has already achieved remarkable success in treating various hematologic malignancies, and ongoing research is rapidly expanding its potential to tackle solid tumors and even autoimmune diseases. In this post, we will explore the latest breakthroughs in CAR-T cell therapy, from innovative engineering strategies to novel clinical applications, and discuss the challenges and future directions of this transform
…
25th Nov 2025
The Double-Edged Sword: How Neutrophil Traps Can Both Help and Hinder Cancer's Spread
The Double-Edged Sword: How Neutrophil Traps Can Both Help and Hinder Cancer's Spread
In the intricate battlefield of the human body, the immune system’s foot soldiers, neutrophils, have long been recognized for their heroic role in fighting off infections. But what if these same soldiers, in their attempt to protect, inadvertently create pathways for an even greater enemy to advance? Recent research has uncovered a fascinating and complex story about neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs)—web-like structures neutrophils release to ensnare pathogens—and their paradoxical role in cancer metastasis. While these traps can sometimes help the immune system fight tumors, studies are revealing that
…
21st Nov 2025
Tumor-Associated Macrophages: Double Agents in the Cancer Battlefield
Tumor-Associated Macrophages: Double Agents in the Cancer Battlefield
In the intricate theater of the human body, the immune system acts as a vigilant guardian, dispatching cellular soldiers to seek and destroy invaders like cancer. But what happens when some of these soldiers turn traitor? This is the complex reality of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), which often act as double agents within the tumor microenvironment (TME). While they possess the ability to eliminate malignant cells, they are frequently co-opted by tumors to support their growth and shield them from attack. Recent research has begun to unravel this dual nature, revealing that TAMs represent the predominant immune cell
…
20th Nov 2025
Liquid Biopsy and ctDNA: The New Frontier in Cancer Detection
Imagine a future where a simple blood test could detect cancer in its earliest stages, long before symptoms appear. This isn't science fiction; it's the rapidly advancing reality of liquid biopsy, a revolutionary diagnostic approach poised to transform oncology. For decades, tissue biopsies have been the gold standard for cancer diagnosis, but their invasive nature, cost, and inability to capture the full picture of a patient's disease have created significant limitations. Now, researchers are harnessing the power of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) to create non-invasive, real-time monitoring tools that promise to usher in a new era of precision medicine. A recent surge in publications through
…
20th Nov 2025
Exosomes: Tiny Messengers Revolutionizing Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy
In the intricate world of cancer biology, a silent conversation is constantly unfolding between tumor cells and their environment. For decades, we viewed this dialogue as a one-way street, with cancer cells dictating terms. But what if the body’s own cellular messaging system could be harnessed to fight back? Recent breakthroughs have illuminated the role of exosomes—tiny vesicles once dismissed as cellular debris—as critical mediators in this conversation, capable of both driving and suppressing cancer. A groundbreaking study now reveals that engineering these exosomes can dramatically enhance immunotherapy outcomes, turning a tumor's own weapon against it.
Introduction
The tumor microenvi
…
20th Nov 2025
Tertiary Lymphoid Structures: The Body's Hidden Arsenals in the Fight Against Cancer
Tertiary Lymphoid Structures: The Body's Hidden Arsenals in the Fight Against Cancer
Imagine a battlefield within the body, where the immune system stands as the last line of defense against the relentless advance of cancer. For decades, scientists have focused on the well-known lymphoid organs like the spleen and lymph nodes as the primary training grounds for cancer-fighting immune cells. However, a series of groundbreaking discoveries has revealed the existence of hidden immune arsenals, known as tertiary lymphoid structures (TLS), that form directly within tumors. These structures are now emerging as a critical factor in determining a patient's response to immunotherapy, and their manip
…
20th Nov 2025
Ferroptosis: A New Frontier in Cancer Therapy
For decades, the primary strategy in cancer treatment has been to trigger apoptosis, a form of programmed cell death, in malignant cells. However, many cancers develop resistance to apoptosis-inducing therapies, leading to treatment failure and relapse. This clinical challenge has spurred a search for alternative ways to eliminate cancer cells. Now, a groundbreaking area of research is focused on a different form of cell death called ferroptosis, an iron-dependent process that overcomes resistance to existing cancer therapies and offers a powerful new strategy in the fight against cancer.
Introduction
Ferroptosis is a unique form of regulated cell death characterized by the iron-dependen
…
20th Nov 2025
Unlocking a New Immune Checkpoint: The CD47-Thrombospondin-1 Pathway in Cancer
Cancer immunotherapy has revolutionized oncology, offering powerful new ways to treat various malignancies by harnessing the body's own immune system. Central to this success are immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), which release the brakes on T cells, allowing them to attack and destroy cancer cells. For years, the PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 pathways have been the primary targets for these therapies. However, a significant portion of patients do not respond to these treatments, and many who initially respond eventually develop resistance. This has driven researchers to explore new mechanisms of immune evasion. A groundbreaking study recently published in Nature Immunology has unveiled a novel im
…
20th Nov 2025
CAR-NK Cell Therapy: The Next Frontier in Cancer Immunotherapy
For decades, the fight against cancer has been a relentless battle of incremental gains. While immunotherapies like CAR-T cell therapy have offered revolutionary hope, their personalized nature, high cost, and severe side effects have limited their reach. But what if there was a readily available, “off-the-shelf” solution that could overcome these hurdles? Recent breakthroughs in cellular immunotherapy are pointing to a powerful new contender: Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR)-Natural Killer (NK) cells. These engineered immune cells are demonstrating the ability to effectively target and destroy cancer cells with a safety profile that could make cutting-edge treatments accessible to more pati
…
20th Nov 2025
Targeting USP22 to Boost Anticancer Immunity
Targeting USP22: A New Approach to Enhance Anticancer Immunity
Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of cancer research, the intricate relationship between immune evasion and tumor biology remains a focal point of investigation. The immune system, with its remarkable ability to recognize and eliminate malignant cells, is often thwarted by various mechanisms employed by tumors to evade detection. Among the myriad of proteins involved in this complex interplay, USP22 (Ubiquitin Specific Peptidase 22) has emerged as a significant player. This deubiquitinating enzyme is not only pivotal in regulating protein stability but also plays a crucial role in modulatin
…
1st Aug 2025
EGFR Pathway and YAP in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Understanding the EGFR Pathway and YAP in Non-Small Cell Lung CancerThe epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) pathway plays a pivotal role in the development and progression of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). This article delves into the intricate relationship between the EGFR pathway, Yes-associated protein (YAP), and the tumor microenvironment, highlighting their implications for cancer progression and treatment strategies.IntroductionNon-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is one of the most prevalent forms of lung cancer, characterized by its aggressive nature and poor prognosis. The EGFR pathway is a well-established oncogenic pathway that significantly influences tumor growth and meta
…
22nd Jul 2025
Alemtuzumab: Mechanism, Applications, and Biosimilar Advancements
Quick Facts About AlemtuzumabWhat is Alemtuzumab?Alemtuzumab is a monoclonal antibody targeting CD52, primarily used in the treatment of multiple sclerosis (MS) and certain cancers like chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).What is the mechanism of action for Alemtuzumab?Alemtuzumab binds to CD52 on lymphocytes, leading to their depletion via immune-mediated cytotoxicity, resetting the immune system in diseases like MS.What are the clinical applications of Alemtuzumab?Alemtuzumab is FDA-approved for relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS) and is used off-label for various hematologic conditions.What are Alemtuzumab’s common side effects?Side effects include infusion-related
…
26th May 2025
Enavatuzumab: Revolutionizing Cancer Research Through Novel Therapeutics
Quick Facts About EnavatuzumabWhat is Enavatuzumab?Enavatuzumab is a monoclonal antibody targeting the TWEAK receptor (Fn14), pivotal in tumor growth and immune regulation.What is the mechanism of action for Enavatuzumab?Enavatuzumab binds to Fn14, inhibiting signaling pathways that promote tumor cell proliferation and survival while enhancing immune response.What are the clinical applications of Enavatuzumab?It is under investigation for treating solid tumors and hematologic malignancies due to its dual action of direct tumor cell targeting and immune system modulation.Is Enavatuzumab safe?Emerging studies indicate a manageable safety profile, though further trials are crucial
…
26th May 2025
Praluzatamab: Unveiling the Promise of CD47-Targeted Therapy in Cancer Research
Quick Facts About PraluzatamabWhat is Praluzatamab?Praluzatamab is an experimental monoclonal antibody that targets CD47, a “don’t eat me” signal used by cancer cells to evade immune destruction.What role does Praluzatamab play in targeting CD47?It blocks CD47–SIRPα signaling, promoting phagocytosis of tumor cells and enhancing antitumor immune responses.Is Praluzatamab safe?Initial studies reported tolerable safety profiles, but further trials were needed to fully assess its risks and hematologic side effects.What are the clinical applications of Praluzatamab?Praluzatamab has been investigated for treating myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS), acute myeloid leukemia (AML), and soli
…
13th May 2025
Polatuzumab: Redefining Targeted Therapies in B-Cell Lymphoma
What You Need to Know About PolatuzumabWhat is Polatuzumab??Polatuzumab vedotin is an antibody-drug conjugate targeting CD79b, a component of the B-cell receptor, used primarily in B-cell lymphomas like DLBCL.What is the mechanism of action for Polatuzumab?It delivers a cytotoxic payload directly to B cells by binding to CD79b, leading to selective cell death with reduced off-target effects.What are the clinical applications of Polatuzumab?Polatuzumab is used in combination therapies for relapsed/refractory DLBCL and is being explored for front-line treatment.Is Polatuzumab safe?It has a manageable safety profile, with common side effects including neutropenia, peripheral neuro
…
9th May 2025
Milatuzumab: Unveiling Its Role in Cancer Immunotherapy and Research
What You Need to Know About MilatuzumabWhat is Milatuzumab?Milatuzumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody targeting CD74, a molecule involved in antigen presentation and cell signaling.What is the mechanism of action for Milatuzumab?Milatuzumab binds CD74, interrupting survival pathways and triggering antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC).Is Milatuzumab safe?Milatuzumab has shown manageable safety in early trials, though further studies are needed to fully define its toxicity profile.What diseases is Milatuzumab being studied for?Milatuzumab has been investigated in hematological malignancies like multiple myeloma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and autoimmune
…
2nd May 2025
Farletuzumab: Advancing Antibody-Drug Conjugate Research in Ovarian Cancer
Quick Facts About FarletuzumabWhat is Farletuzumab?Farletuzumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody targeting folate receptor alpha (FRα), a protein overexpressed in ovarian and other epithelial cancers.What is the mechanism of action for Farletuzumab?It binds to FRα on tumor cells and mediates cytotoxic effects via antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC), and internalization.What are the clinical applications of Farletuzumab?It has been explored in clinical trials for epithelial ovarian cancer, particularly in combination with agents like carboplatin, paclitaxel, or eribulin.Is Farletuzumab used with Ecteribulin?Yes. Farletuzumab
…
26th Mar 2025
Obinutuzumab: Advancing Targeted Therapy in Hematologic Cancers
Quick Facts About ObinutuzumabWhat is Obinutuzumab?Obinutuzumab is a monoclonal antibody targeting CD20, primarily used in treating B-cell malignancies such as chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and follicular lymphoma.What is the mechanism of action for Obinutuzumab?Obinutuzumab works by binding to CD20 on B-cells, inducing direct cell death and enhancing antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) and phagocytosis.What are the clinical applications of Obinutuzumab?It is approved for CLL and follicular lymphoma, often in combination with other therapies such as venetoclax or bendamustine.1.) Understanding ObinutuzumabObinutuzumab, a next-generation glycoengineered monoclon
…
19th Mar 2025
Abituzumab: Understanding Its Role in Cancer and Fibrosis Research
Quick Facts About AbituzumabWhat is Abituzumab?Abituzumab is a monoclonal antibody that targets αv-integrins, playing a role in cancer treatment and fibrotic diseases.What is the mechanism of action for Abituzumab?It inhibits αv-integrins to prevent tumor cell adhesion, migration, and survival, making it a potential therapy for colorectal and prostate cancer.What are the clinical applications of Abituzumab?It has been investigated for metastatic colorectal cancer (CRC), prostate cancer, systemic sclerosis, and fibrotic diseases like scleroderma.1.) Understanding AbituzumabInitially developed by Merck Serono, Abituzumab has undergone extensive preclinical and clinical evaluation
…
18th Mar 2025
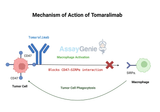
Tomaralimab: Unveiling the Role of Anti-CD47 in Cancer Research
Quick Facts About TomaralimabWhat is Tomaralimab?Tomaralimab is an anti-CD47 monoclonal antibody designed to enhance immune system recognition of cancer cells by blocking the "don't eat me" signal.What is the mechanism of action for Tomaralimab?Tomaralimab inhibits CD47, a protein that allows cancer cells to evade macrophage-mediated phagocytosis. By blocking CD47, it promotes immune clearance of tumors.What are the clinical applications of Tomaralimab?It has been investigated in hematologic malignancies and solid tumors, with ongoing research into its potential combination therapies.1.) Understanding TomaralimabTomaralimab represents a significant advancement in immuno-oncolog
…
11th Mar 2025
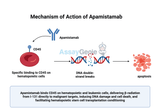
Apamistamab: Advancing Leukemia Treatment through Targeted Radioimmunotherapy
Quick Facts About ApamistamabWhat is Apamistamab?Apamistamab is a monoclonal antibody that targets the CD45 antigen on hematopoietic cells.How does Apamistamab work?When labeled with the radioactive isotope Iodine-131, Apamistamab delivers targeted radiation to CD45-expressing cells, aiding in the eradication of malignant cells.What are the clinical applications of Apamistamab?Apamistamab is primarily used in conditioning regimens before hematopoietic cell transplantation for patients with relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia (AML).1.) Understanding ApamistamabApamistamab, also known as Iomab-B when conjugated with Iodine-131, is an innovative therapeutic agent designe
…
11th Mar 2025
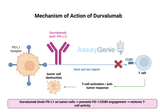
Durvalumab: Advancing Immunotherapy in Cancer Treatment
Quick Facts About DurvalumabWhat is Durvalumab?Durvalumab (Imfinzi) is a PD-L1 checkpoint inhibitor used in immunotherapy to treat various cancers, including non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and small cell lung cancer (SCLC).How does Durvalumab work?Durvalumab blocks PD-L1, restoring the immune system's ability to recognize and attack cancer cells.What are the clinical applications of Durvalumab?It is FDA-approved for treating NSCLC, SCLC, and biliary tract cancer and is being explored in combination therapies.What are the side effects of Durvalumab?Common side effects include fatigue, cough, and immune-related reactions such as pneumonitis and colitis.1.) Understanding Durva
…
8th Mar 2025
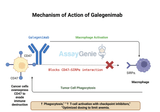
Galegenimab: Unlocking the Potential of Anti-CD47 in Cancer Research
Quick Facts About GalegenimabWhat is Galegenimab?Galegenimab is an anti-CD47 monoclonal antibody designed to block the "don't eat me" signal, enhancing the immune system's ability to eliminate cancer cells.How Does Galegenimab Work?By targeting CD47, Galegenimab prevents cancer cells from evading macrophage-mediated phagocytosis, a critical mechanism in immune response.What Are the Clinical Applications of Galegenimab?Galegenimab is being investigated for its potential in treating hematologic malignancies and solid tumors, particularly in combination with other immunotherapies.1.) Understanding GalegenimabGalegenimab represents a significant advancement in immuno-oncology by ta
…
8th Mar 2025