Cytokine Storms: What happens when the immune system overreacts?
Discover the critical role of cytokines as signaling molecules in immune responses, their functions, and the impact of their dysregulation, including cytokine storms.
Key Takeaways:
- Cytokines are crucial immune system proteins regulating immune responses.
- Dysregulated cytokines can lead to cytokine storms, causing severe immune reactions.
- Cytokine storms are treated with immunosuppressives and are common in severe infections like COVID-19.
- Prevention includes vaccination and managing underlying health conditions.
What are Cytokines?
Cytokines are a diverse group of small proteins that serve as key signaling molecules in the immune system. Produced by various cells of the immune system, cytokines play a crucial role in regulating and coordinating immune responses. These proteins facilitate communication between different immune cells, allowing them to work together effectively in response to infections, injuries, or other immune challenges.
Cytokines can be classified into different categories based on their functions and the cells that produce them. Some of the well-known cytokines include interferons (IFNs), interleukins (ILs), tumor necrosis factors (TNFs), and chemokines. Each cytokine has specific effects on target cells and can either enhance or dampen immune responses. Cytokines act by binding to specific receptors on target cells, triggering a cascade of intracellular signaling pathways that influence gene expression and cellular functions. These signals enable immune cells to communicate and coordinate their actions, leading to an effective immune response.
While cytokines are essential for maintaining immune homeostasis and defending against infections, dysregulation in cytokine production and signaling can have detrimental effects. Excessive or prolonged release of pro-inflammatory cytokines can lead to an uncontrolled immune response, resulting in the development of a cytokine storm.
What is a Cytokine Storm?
A cytokine storm refers to an exaggerated immune response characterized by the excessive secretion of proteins called cytokines, which play a crucial role in regulating the immune system. Cytokines can have both pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory effects. When the body overreacts to an infection or other threat, it can trigger a cytokine storm, leading to widespread inflammation and potential tissue damage. This phenomenon is commonly observed in individuals with severe infections like sepsis, COVID-19, or influenza, but can also occur in those with specific autoimmune disorders or following vaccination.
Schematic of a Cytokine Storm
Cytokine storms can be life-threatening and require prompt intervention. Treatment generally involves immunosuppressive medications to suppress the hyperactive immune response. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary, with supportive care provided, such as oxygen therapy and intravenous fluids. The symptoms of a cytokine storm can include fever, chills, rash, shortness of breath, and organ failure. The onset of symptoms is often sudden, and the condition can progress rapidly, potentially leading to shock and the need for intensive medical care.
To address cytokine storms, drugs like corticosteroids, including prednisone, are frequently used to mitigate inflammation. Additionally, medications like cyclosporine and etoposide may be employed in certain cases. While cytokine storms can affect individuals of any age, they are most commonly observed in young children and older adults. People with underlying medical conditions, such as cancer, autoimmune diseases, and chronic infections, face an increased risk of experiencing cytokine storms. With timely and appropriate treatment, most individuals recover fully from this serious complication.
The Role of Cytokines in the Immune System
Cytokines play a crucial role in the immune system, and they encompass various types such as interferon (IFN), interleukin (IL), and tumor necrosis factor (TNF). These proteins can exhibit either pro-inflammatory or anti-inflammatory properties. Pro-inflammatory cytokines are instrumental in initiating the body's response to infection or injury, helping to activate the immune system. Anti-inflammatory cytokines help to reduce inflammation once the initial response is over. Examples of pro-inflammatory cytokines include IL-6 and TNF-alpha, whereas IL-10 and TGF-beta are representative of anti-inflammatory cytokines.
Interferon beta 1b is a specific type of interferon utilized in the treatment of multiple sclerosis. It works by reducing the activity of the immune system. Typically, interferon beta 1b is administered through subcutaneous or intramuscular injections. The usual dosage entails 0.25 mg once a day for 7 days, followed by 0.5 mg once a week for 4 weeks, and then a maintenance dose of 1 mg once a week indefinitely. Side effects of interferon beta 1b include flu-like symptoms, such as fever, chills, muscle aches, and fatigue. These side effects usually go away after the first few doses.
Cytokine-Producing Cells
Pathways Involved in Cytokine Storms
Cytokine storms are complex immune responses characterized by an excessive release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, leading to uncontrolled inflammation and tissue damage. Several signaling pathways play a crucial role in orchestrating these storms, including the JAK-STAT, MAPK, and NF-kB pathways. Dysregulation or inappropriate activation of these signaling pathways can occur due to genetic mutations, infections, or other triggers, leading to an uncontrolled and amplified cytokine response.
The JAK-STAT pathway is a signaling pathway that is involved in the body's response to infection or injury. The pathway is activated when a cytokine binds to its receptor on the surface of a cell. This activates the JAK kinases, which then phosphorylate the STAT proteins. The STAT proteins then translocate to the nucleus and regulate gene expression.
The MAPK pathway is a signaling pathway that is involved in the body's response to infection or injury. The pathway is activated when a cytokine binds to its receptor on the surface of a cell. This activates the MAPK kinases, which then phosphorylate and activate transcription factors. The transcription factors then regulate gene expression.
The NF-kB pathway is a signaling pathway that is involved in the body's response to infection or injury. The pathway is activated when a cytokine binds to its receptor on the surface of a cell. This activates the IKK complex, which then phosphorylates the NF-kB proteins. The phosphorylated NF-kB proteins migrate to the nucleus, where they regulate the transcription of genes involved in inflammation, immune cell recruitment, and tissue damage.
Causes and Triggers of Cytokine Storms
Cytokine storms can be triggered by various factors, including severe infections, autoimmune disorders, certain medications, and immunotherapies. Infections caused by pathogens like viruses, bacteria, and fungi can provoke an exaggerated immune response, leading to cytokine storm development. Additionally, certain autoimmune conditions, where the immune system mistakenly targets healthy tissues, can also result in cytokine storms. Furthermore, immunotherapeutic interventions, such as CAR-T cell therapy, can induce cytokine storms as an adverse reaction.
Covid-19 and Cytokine Storms
The COVID-19 pandemic has brought attention to the occurrence of cytokine storms as a severe complication in infected individuals. Cytokine storms in COVID-19 are characterized by an excessive release of pro-inflammatory cytokines triggered by the SARS-CoV-2 virus. The virus enters the body and infects host cells, activating the immune system's response. In some cases, the immune system goes into overdrive, leading to an uncontrolled and exaggerated inflammatory response. This hyperinflammation can result in significant tissue damage, especially in the lungs, and contribute to the severity of respiratory symptoms observed in severe COVID-19 cases. Key cytokines involved in COVID-19-related cytokine storms include interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), and interferons.
Current treatment approaches for cytokine storms in COVID-19 often involve immunomodulatory therapies, such as monoclonal antibodies targeting specific cytokines or their receptors, corticosteroids, and other anti-inflammatory agents. Efforts are ongoing to further investigate the pathogenesis of cytokine storms in COVID-19 and develop more targeted interventions to mitigate their impact on patient outcomes.
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) is a severe lung condition that can be closely associated with cytokine storms. ARDS occurs when there is inflammation in the lungs, leading to fluid accumulation in the air sacs, impaired oxygen exchange, and difficulty breathing. Cytokine storms can contribute to the development and progression of ARDS by triggering excessive and uncontrolled inflammation in the lungs. ARDS is regarded as a prominent manifestation in response to SARS-CoV-2 by the immune system.
Cancer and Cytokine Storms
Cytokine storms can occur in several types of cancers, including leukemia and lymphoma, which are blood cancers originating in the bone marrow and lymph nodes, respectively. These malignancies can trigger an abnormal immune response, leading to the development of cytokine storms. In the treatment of leukemia and lymphoma, immune system suppression is often employed to manage the disease. This may involve the use of corticosteroids, cyclosporine, methotrexate, or other immunosuppressive drugs. By targeting the immune system, these medications aim to reduce the production of excessive cytokines and mitigate the harmful effects of cytokine storms in individuals with leukemia and lymphoma.
Immunotherapy and Cytokine Storms
Patients receiving immunotherapies such as CAR-T therapy are at risk for developing cytokine storms. CAR-T therapy is a type of immunotherapy that uses genetically engineered T cells to attack cancer cells. These therapies work by stimulating the immune system to attack cancer cells. While they can be very effective, they can also cause the immune system to overreact and produce too many cytokines. This can lead to a cytokine storm. Symptoms of a CAR-T-related cytokine storm typically begin within 2 weeks of receiving treatment. They may include fever, chills, rash, shortness of breath, and organ failure. Treatment for a CAR-T-related cytokine storm typically involves using drugs to suppress the immune system, such as corticosteroids and cyclosporine.
Rheumatoid Arthritis and Cytokine Storms
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) are also at risk for developing cytokine storms. RA is a type of autoimmune disorder that causes the immune system to attack the joints. This can lead to inflammation and pain. Treatment for RA typically involves using drugs to suppress the immune system, such as methotrexate, leflunomide, and hydroxychloroquine.
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Cytokine Storms
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is another autoimmune disorder that can lead to cytokine storms. SLE is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. This can cause the immune system to attack healthy tissue, leading to inflammation and pain. Symptoms of an SLE-related cytokine storm typically begin in early adulthood. They may include fever, rash, and organ failure. Treatment for an SLE-related cytokine storm typically involves using drugs to suppress the immune system, such as corticosteroids, methotrexate, and hydroxychloroquine.
Symptoms of a Cytokine Storm
A cytokine storm can manifest in various body systems, resulting in a wide spectrum of symptoms that can vary in severity, posing a potential threat to life. Commonly observed symptoms include fever, fatigue, weakness, chills, body aches, loss of appetite, nausea, rapid heart rate, and skin rash. The manifestation of these symptoms reflects the widespread inflammatory response triggered by the excessive release of cytokines
Treatment for a Cytokine Storm
Treatment for cytokine storms involves a comprehensive approach aimed at addressing the immune response and alleviating symptoms. The specific treatment regimen depends on the severity of the cytokine storm and the underlying cause. Typically, a combination of strategies is employed, including the use of immunomodulatory drugs like corticosteroids (e.g., prednisone) to suppress the immune system. Cytokine inhibitors, such as interleukin-6 (IL-6) inhibitors, may also be employed to target specific pro-inflammatory cytokines. Additionally, disease-specific therapies are implemented to address the underlying condition contributing to the cytokine storm. The treatment plan is tailored to the individual patient, taking into account the specific clinical presentation and needs. Collaborative efforts among healthcare professionals from various specialties are essential to ensure comprehensive care and improve patient outcomes.
Preventing a Cytokine Storm
There is no sure way to prevent cytokine storms. However, there are some things you can do to lower your risk:
- Get vaccinated against infections such as influenza and SARS-CoV-2.
- Avoid contact with people who are sick.
- Wash your hands often with soap and water.
- Avoid close contact with those who are sick.
- Stay home if you are sick.
- Cover your mouth and nose when you sneeze or cough.
- Avoid touching your face.
- Clean and disinfect surfaces that are often touched, such as doorknobs, light switches, and countertops.
If you have an autoimmune disorder or cancer, work with your doctor to keep your condition under control. This may help lower your risk of developing a cytokine storm.
What is Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS)?
Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) also known as cytokine storm syndrome is a potentially life-threatening condition that can occur when the immune system overreacts to an infection or injury. This overreaction causes the release of too many inflammatory cytokines into the bloodstream, which can lead to fever, chills, rash, and organ failure. CRS can be very dangerous, and potentially life-threatening. Treatment for CRS typically involves using drugs to suppress the immune system, such as corticosteroids and cyclosporine.
Cytokine Related Kits
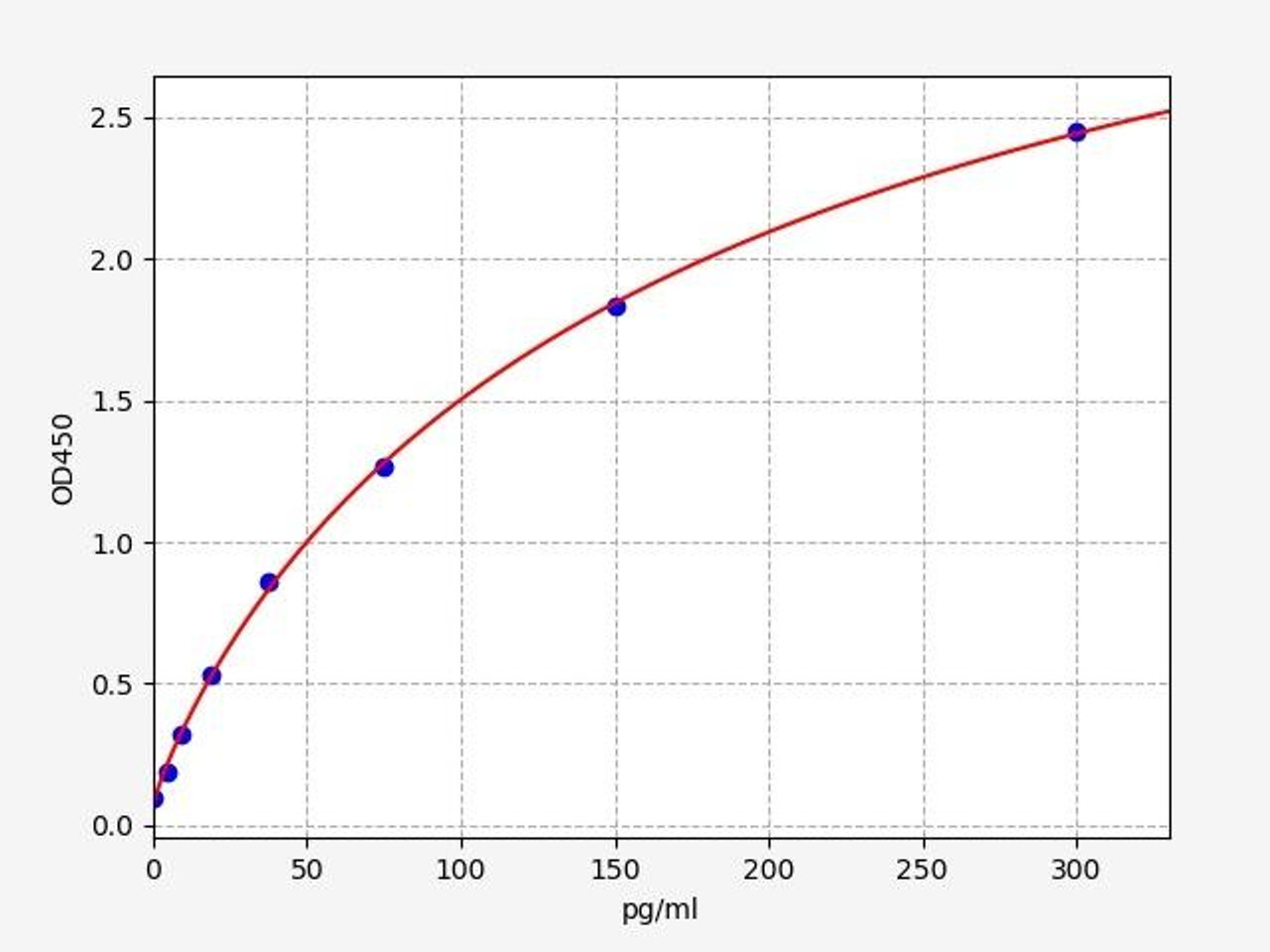
| Human TNF alpha ELISA Kit | |
|---|---|
| ELISA Type | Sandwich |
| Sensitivity | 9.375pg/ml |
| Range | 15.625-1000pg/mlL |
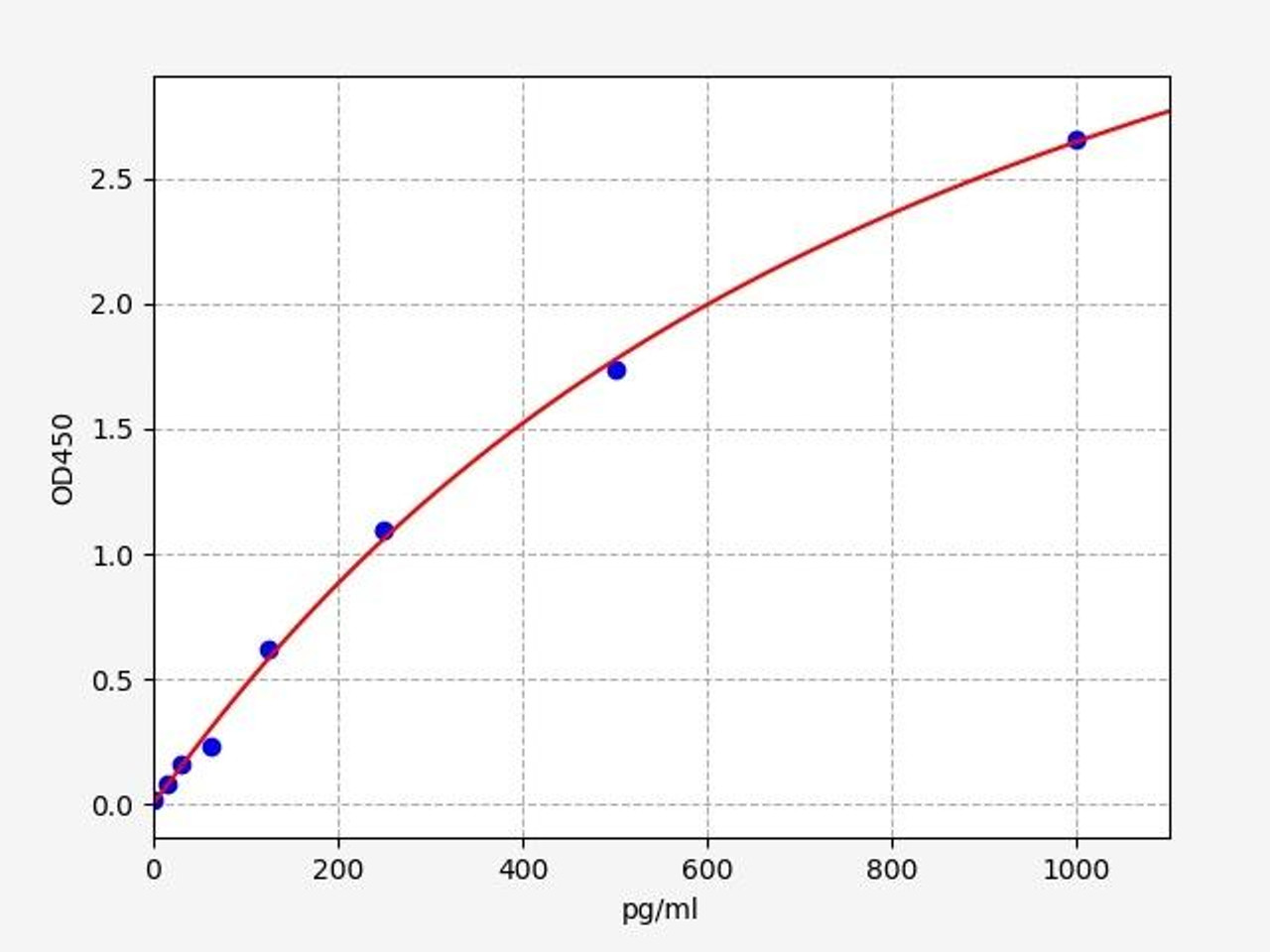
| Human Interferon beta / IFN beta ELISA Kit | |
|---|---|
| ELISA Type | Sandwich |
| Sensitivity | 37.5pg/ml |
| Range | 62.5-4000pg/ml |
Written by Lauryn McLoughlin
Lauryn McLoughlin completed her undergraduate degree in Neuroscience before completing her masters in Biotechnology at University College Dublin.
Recent Posts
-
IgG1 Plasma Cells: The Emerging Biomarker for Predicting Cancer Immunotherapy Success
In the relentless fight against cancer, immunotherapy has emerged as a beacon of hope, harnessing t …24th Feb 2026 -
The Rise of Cancer Neuroscience: How Neural Circuits Drive Tumor Progression
For decades, we viewed cancer as a rogue army of cells, a biological glitch driven solely by geneti …23rd Feb 2026 -
CRISPR-Powered Light Sensors: A New Frontier in Ultra-Sensitive Cancer Detection
Cancer detection often relies on advanced imaging or invasive procedures, frequently catching the d …20th Feb 2026