Gut Inflammation and Inflammatory Diseases
What is Gut Inflammation?
The gut, or gastrointestinal (GI) tract is a long tube that starts from the mouth and extends to the anus. It includes various organs such as the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and rectum, responsible for digestion, absorption of nutrients, and elimination of waste. The gut plays a vital role in our overall health. However, inflammation can occur within the gut, leading to various inflammatory diseases. Gut inflammation is an immune response triggered by factors such as infections or autoimmune reactions. This immune response releases molecules that cause inflammation, resulting in tissue damage. Conditions like Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, celiac disease, IBS, diverticulitis, and gastroenteritis are examples of gut inflammation and inflammatory diseases.
Schematic of the GI Tract
What Causes Gut Inflammation?
Gut inflammation can arise from various causes and triggers, ranging from infections to dietary factors and underlying medical conditions. Understanding these factors can shed light on the development and progression of gut inflammation and associated inflammatory diseases. Biomarkers are commonly used in research and clinical settings to evaluate inflammation levels and disease activity in the gut.
1. Infections
Infections can be a significant cause of gut inflammation. Bacterial, viral, and parasitic infections have the potential to trigger an immune response within the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, resulting in inflammation. Pathogens like Escherichia coli, Salmonella, Helicobacter pylori, norovirus, and rotavirus are commonly associated with gut infections that lead to inflammation.
CRP is a general marker of inflammation and its levels can increase in response to infections, including gut infections. Measuring CRP levels using an ELISA kit can provide an indication of the presence and severity of inflammation.
2. Autoimmune Disorders
Certain autoimmune disorders can contribute to gut inflammation. In these conditions, the immune system mistakenly attacks the cells and tissues of the GI tract, leading to chronic inflammation. Notable examples of autoimmune disorders affecting the gut include Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. The immune system's malfunction in these disorders causes persistent inflammation in the gut.
TNF-alpha is a pro-inflammatory cytokine that plays a crucial role in autoimmune disorders, including those affecting the gut. Elevated levels of TNF-alpha have been observed in conditions like Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Measuring TNF-alpha using an ELISA kit can help assess the degree of inflammation and monitor treatment response.
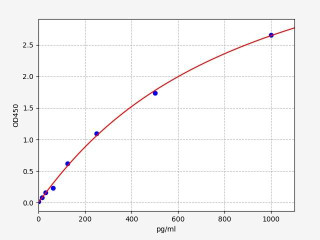
| Human TNF alpha ELISA Kit | |
|---|---|
| ELISA Type | Sandwich |
| Sensitivity | 9.375pg/ml |
| Range | 15.625-1000pg/ml |
3. Dietary Factors
Dietary factors play a significant role in gut inflammation. Consuming a diet high in processed foods, unhealthy fats, and added sugars while lacking adequate fiber can contribute to inflammation in the gut. Furthermore, specific food intolerances or sensitivities, such as gluten or lactose intolerance, can trigger inflammation in susceptible individuals. Poor dietary choices and sensitivities can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria and promote inflammation.
Fecal calprotectin is a specific biomarker associated with gut inflammation. It is released by immune cells in the gut during inflammation. Elevated levels of fecal calprotectin can indicate the presence of inflammation, making it a useful marker to assess the impact of dietary factors on gut health.
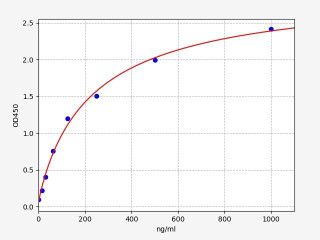
| Human calprotectin ELISA Kit | |
|---|---|
| ELISA Type | Sandwich |
| Sensitivity | 9.375ng/ml |
| Range | 15.625-1000ng/ml |
4. Chronic Diseases
Chronic diseases can contribute to gut inflammation. Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, type 1 diabetes, and systemic lupus erythematosus involve immune system dysregulation, which can affect the GI tract and lead to inflammation. The immune dysfunction associated with these diseases can contribute to the development and persistence of gut inflammation.
IL-6 is a pro-inflammatory cytokine that is elevated in various chronic diseases, including those affecting the gut. It is involved in the regulation of immune responses and can contribute to the development and maintenance of chronic inflammation. Measuring IL-6 levels using an ELISA kit can help evaluate the inflammatory status and disease activity.
5. Environmental Factors
Environmental factors can also play a role in gut inflammation. Exposure to pollutants, toxins, or certain medications can contribute to inflammation in the GI tract. Environmental triggers can interact with the gut microbiota and the immune system, potentially leading to gut inflammation.
Intestinal fatty acid-binding protein (I-FABP) is a biomarker of gut epithelial cell damage and is associated with gut inflammation. Exposure to environmental factors, such as pollutants or toxins, can lead to intestinal damage and subsequent release of I-FABP. Measuring I-FABP levels using an ELISA kit can help assess the impact of environmental factors on gut health and inflammation.
| Human IFABP ELISA Kit (HUES01431) | |
|---|---|
| ELISA Type | Sandwich |
| Sensitivity | 0.09ng/mL |
| Range | 0.16-10ng/mL |
Inflammatory Diseases Affecting the Gut
Inflammatory diseases can impact the GI tract in distinct ways. Several notable examples include Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, celiac disease, diverticulitis, and gastroenteritis. These conditions vary in their specific characteristics, symptoms, diagnostic methods, and treatment approaches of the GI tract.
Crohn's Disease is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that can affect any part of the GI tract. It is characterized by inflammation that extends through the entire thickness of the intestinal wall, leading to symptoms such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, and weight loss. Diagnostic procedures for Crohn's disease may include laboratory tests (such as CRP and fecal calprotectin), imaging studies (such as CT or MRI scans), and endoscopies (such as colonoscopy) with biopsies. Treatment options include medication (such as anti-inflammatory drugs, immunomodulators, and biologics), lifestyle modifications, and in some cases, surgery to remove affected portions of the GI tract.
Ulcerative Colitis is another form of inflammatory bowel disease that primarily affects the colon and rectum. It causes inflammation and ulcers in the lining of the colon, leading to symptoms like bloody diarrhea, abdominal cramping, and urgency to have bowel movements. Diagnostic procedures for ulcerative colitis may involve laboratory tests, imaging studies, and endoscopic examinations with biopsies. Treatment options include medication, lifestyle modifications, and in severe cases, surgery to remove the colon and rectum.
Celiac Disease is an autoimmune condition triggered by gluten ingestion. It results in an immune response that damages the small intestine, leading to symptoms such as diarrhea, bloating, fatigue, and nutrient deficiencies. Diagnostic procedures for celiac disease include blood tests to detect specific antibodies (such as anti-tissue transglutaminase antibodies) and an endoscopic biopsy of the small intestine to assess damage to the villi. The primary treatment for celiac disease is strict adherence to a gluten-free diet, which helps alleviate symptoms and prevent long-term complications.
Diverticulitis occurs when small pouches called diverticula in the colon become inflamed or infected. Symptoms may include abdominal pain (usually in the lower left side), fever, changes in bowel habits, and nausea. Diagnosis of diverticulitis often involves physical examination, blood tests (such as white blood cell count), imaging studies (such as CT scans), and sometimes colonoscopy. Treatment options for diverticulitis may include antibiotics, dietary changes (such as a high-fiber diet), pain management, and in severe cases, surgery to remove the affected portion of the colon.
Gastroenteritis refers to inflammation of the stomach and intestines, typically caused by viral, bacterial, or parasitic infections. Symptoms include diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and dehydration. Diagnosis of gastroenteritis is typically based on medical history, physical examination, and stool tests to identify the infectious agent. Treatment focuses on supportive care, including oral rehydration, maintaining proper fluid and electrolyte balance, and in some cases, antidiarrheal medications or antibiotics for specific infections.
Reducing Inflammation and Improving Gut Health
Maintaining a healthy gut is essential for overall well-being and can contribute to the prevention and management of gut inflammatory diseases. Fortunately, there are several strategies individuals can incorporate into their lifestyle to promote optimal gut health. Let's explore some effective methods, including specific nutrients, to improve gut health:
-
Dietary Modifications: A balanced diet rich in fiber, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains supports a healthy gut microbiota. Additionally, incorporating specific nutrients can be beneficial. Glutamine, an amino acid, plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of the intestinal lining and supporting gut health. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish like salmon and in flaxseeds and chia seeds, have anti-inflammatory properties and may help reduce gut inflammation. Vitamin D, which can be obtained from sunlight exposure and certain foods, has been linked to improved gut barrier function and immune modulation.
-
Probiotics and Prebiotics: Probiotics are beneficial live bacteria that can be consumed through supplements or certain foods. They can help restore the gut microbiota's balance and improve digestion. Prebiotics, on the other hand, are dietary fibers that serve as food for beneficial bacteria. Consuming prebiotic-rich foods such as garlic, onions, and bananas can support the growth of beneficial gut bacteria.
-
Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity has been linked to a healthier gut microbiota composition. Exercise promotes better digestion, reduces inflammation, and enhances overall gut health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, such as brisk walking, jogging, or cycling.
-
Stress Management: Chronic stress can negatively impact gut health. Incorporating stress management techniques like meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or engaging in hobbies can help reduce stress levels and promote a healthier gut.
-
Adequate Sleep: Prioritizing sufficient sleep is crucial for maintaining gut health. Poor sleep patterns can disrupt the gut microbiota and increase the risk of inflammation. Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep per night.
- Hydration: Drinking an adequate amount of water is essential for proper digestion and gut health. Staying hydrated helps maintain the integrity of the gut lining and supports overall gastrointestinal function.
Understanding the Difference Between IBD and IBS
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) are both gastrointestinal disorders, but they differ in their underlying causes, diagnostic criteria, and treatment approaches. While both involve gastrointestinal symptoms, IBD is characterized by chronic inflammation of the digestive tract (Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis), whereas IBS is a functional disorder without visible inflammation. Accurate diagnosis and understanding these differences are crucial for appropriate management and treatment strategies tailored to each condition.
The Role of Bacteria in Gut Inflammation
The gut is home to trillions of bacteria that make up the gut microbiota, playing a crucial role in maintaining gut health. However, certain bacteria can contribute to gut inflammation. Imbalances in the composition of the gut microbiota, such as an overgrowth of harmful bacteria or a decrease in beneficial bacteria, can trigger an immune response and promote inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract. The interaction between the gut microbiota and the immune system is complex, and disruptions in this delicate balance can lead to gut inflammation and contribute to the development of inflammatory diseases.
Written by Lauryn McLoughlin
Lauryn McLoughlin completed her undergraduate degree in Neuroscience before completing her masters in Biotechnology at University College Dublin.
Recent Posts
-
IgG1 Plasma Cells: The Emerging Biomarker for Predicting Cancer Immunotherapy Success
In the relentless fight against cancer, immunotherapy has emerged as a beacon of hope, harnessing t …24th Feb 2026 -
The Rise of Cancer Neuroscience: How Neural Circuits Drive Tumor Progression
For decades, we viewed cancer as a rogue army of cells, a biological glitch driven solely by geneti …23rd Feb 2026 -
CRISPR-Powered Light Sensors: A New Frontier in Ultra-Sensitive Cancer Detection
Cancer detection often relies on advanced imaging or invasive procedures, frequently catching the d …20th Feb 2026