Blog
Ivuxolimab: Redefining Cancer Immunotherapy and Research
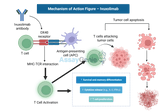
Quick Facts About IvuxolimabWhat is ivuxolimab?Ivuxolimab is a monoclonal antibody targeting CD47, a "don't eat me" signal that cancer cells exploit to evade immune destruction.How does ivuxolimab work?By blocking CD47, ivuxolimab restores macrophage activity, enhancing the immune system’s ability to recognize and destroy cancer cells.What are the clinical applications of ivuxolimab?It is being explored in treating hematologic malignancies and solid tumors, with ongoing studies highlighting its potential in combination therapies.Is ivuxolimab safe?Early studies suggest a manageable safety profile, with most adverse events being mild to moderate and related to on-target effects.
…
1st Feb 2025
Ramucirumab: Mechanism, Clinical Applications, and Biosimilars in Cancer Research
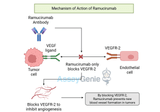
Quick Facts About RamucirumabWhat is Ramucirumab?Ramucirumab is a monoclonal antibody that targets vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR-2), inhibiting angiogenesis, a process crucial for tumor growth.How Does Ramucirumab Work?It blocks VEGFR-2 signaling, preventing blood vessel formation that tumors need to grow and spread, making it effective in various cancers.What Are the Clinical Applications of Ramucirumab?It is approved for treating advanced gastric cancer, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), and colorectal cancer, often in combination with chemotherapy.What Are the Side Effects of Ramucirumab?Common side effects include hypertension, proteinuria, fatigue,
…
31st Jan 2025
Ponsegromab: A Breakthrough in Heart Failure and Cachexia Research
Quick Facts About PonsegromabWhat is Ponsegromab?Ponsegromab is an investigational monoclonal antibody developed by Pfizer, primarily studied for its potential in treating heart failure and cancer-associated cachexia.What is the Mechanism of Action of Ponsegromab?Ponsegromab targets Growth Differentiation Factor 15 (GDF-15), a cytokine linked to inflammation, appetite regulation, and muscle wasting. By inhibiting GDF-15, Ponsegromab aims to counteract cachexia and improve patient outcomes in cardiovascular and cancer-related conditions.What Are the Clinical Applications of Ponsegromab?Ponsegromab is being evaluated for its potential to mitigate muscle wasting in heart failure a
…
29th Jan 2025
Ianalumab: Exploring Its Mechanism, Clinical Applications, and Research Potential
Quick Facts About IanalumabWhat is Ianalumab?Ianalumab is a monoclonal antibody currently being investigated for its potential in treating autoimmune diseases, particularly lupus and immune thrombocytopenia (ITP). It is developed to target and inhibit B-cell activation, a critical mechanism in autoimmune responses.What is the mechanism of action for Ianalumab?Ianalumab works by targeting and inhibiting the B-lymphocyte stimulator (BLyS), which is essential for the survival and activation of B cells. By blocking BLyS, it reduces the number of autoreactive B cells responsible for autoimmune damage.What are the clinical applications of Ianalumab?Ianalumab has shown promise in trea
…
28th Jan 2025
Belimumab: Unveiling Its Role in Lupus and Beyond
Quick Facts About BelimumabWhat is Belimumab?Belimumab is a monoclonal antibody used to treat systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), an autoimmune disease. It is marketed under the brand name Benlysta.What is the mechanism of action for Belimumab?Belimumab works by inhibiting the B-lymphocyte stimulator (BLyS), a protein that plays a central role in the survival and activity of B cells, which are involved in autoimmune responses.What are the clinical applications of Belimumab?Belimumab is primarily used to treat lupus, including lupus nephritis, by reducing disease activity and flares in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.1.) Understanding BelimumabBelimumab, sold under th
…
28th Jan 2025
Siltuximab: Exploring IL-6 Inhibition in Castleman’s Disease and Research
Quick Facts About SiltuximabWhat is Siltuximab?Siltuximab is a monoclonal antibody targeting interleukin-6 (IL-6), a cytokine involved in inflammation and immune regulation.What is the mechanism of action for Siltuximab?Siltuximab binds to IL-6, preventing it from interacting with its receptor and mitigating downstream pro-inflammatory signaling.What are the clinical applications of Siltuximab?Siltuximab is approved for treating multicentric Castleman’s disease (MCD) in patients negative for HIV and HHV-8.1.) Understanding SiltuximabWhat Makes Siltuximab Unique?Siltuximab is a chimeric monoclonal antibody specifically designed to neutralize interleukin-6 (IL-6), a pro-inflammat
…
16th Jan 2025
Treponema pallidum Antibodies: Comprehensive Guide to Diagnostic and Clinical Relevance
Treponema pallidum, the causative agent of syphilis, triggers an immune response that produces antibodies detectable by laboratory tests. Diagnosing syphilis often involves detecting these antibodies through serological tests, which are categorized as non-treponemal and treponemal. Each type of test has unique features that help identify active infections, monitor treatment, and confirm historical exposure. Understanding these antibodies and the tests that detect them is essential for effective syphilis management.Assay Genie · Treponema pallidum Antibodies_ Comprehensive Guide to Diagnostic and Clinical Relevance1. Treponema pallidum and the Immune ResponseTreponema pallidum, a
…
20th Nov 2024
Streptococcus pneumoniae: Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Streptococcus pneumoniae, commonly known as pneumococcus, is a Gram-positive, encapsulated bacterium that is a leading cause of respiratory and invasive diseases worldwide. It is part of the natural flora in the human nasopharynx but can become pathogenic under certain conditions. Diseases caused by S. pneumoniae include pneumonia, meningitis, otitis media, and sepsis, particularly in young children, older adults, and immunocompromised individuals.Assay Genie · Streptococcus pneumoniae_ Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment1. Biology and Characteristics of Streptococcus pneumoniae Morphology and ClassificationShape: Gram-positive, lancet-shaped diplococci.Encapsulation: Th
…
19th Nov 2024
Horseshoe Crab Blood and Endotoxin Testing: A Comprehensive Guide
Horseshoe crabs, often referred to as "living fossils," are invaluable to modern medicine due to their unique blue blood. This blood is the source of Limulus Amebocyte Lysate (LAL), a substance critical for detecting endotoxins in vaccines, pharmaceuticals, and medical devices. However, the reliance on horseshoe crabs raises ecological and ethical concerns, prompting the development of sustainable alternatives. This guide explores the science, applications, and future of endotoxin testing.Assay Genie · Horseshoe Crab Blood and Endotoxin Testing_ A Comprehensive Guide1. The Unique Properties of Horseshoe Crab Blood Why Horseshoe Crab Blood is BlueHorseshoe crab blood contain
…
19th Nov 2024
Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma: Understanding, Diagnosing, and Treating NSCLC
Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma (NSCLC) is the most common type of lung cancer, representing about 85% of all lung cancer cases. NSCLC includes several subtypes, with distinct biological characteristics that influence treatment options and prognosis. Advances in targeted therapies and immunotherapies have significantly improved NSCLC treatment, especially in advanced stages.1. What is Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma?NSCLC encompasses a group of lung cancers that arise from different types of lung cells and grow at varying rates. Unlike small cell lung carcinoma (SCLC), which is more aggressive, NSCLC generally progresses more slowly. The main types of NSCLC are:Adenocarcinoma:
…
14th Nov 2024
Renal Cell Carcinoma: Understanding, Diagnosing, and Treating Kidney Cancer
Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC) is the most common form of kidney cancer, originating in the lining of the proximal renal tubules. RCC accounts for approximately 90% of all kidney cancers and often develops as a single tumor in one kidney, though it can also appear bilaterally or as multiple tumors. Understanding RCC's causes, symptoms, treatment options, and the role of advanced therapies can guide patients and healthcare providers in managing this complex disease.1. What is Renal Cell Carcinoma?Renal cell carcinoma arises from epithelial cells of the renal tubules in the kidney. RCC can remain undetected until it reaches an advanced stage due to its location and lack of early sympt
…
12th Nov 2024
Illuminating the Multifaceted Role of Acetylation: Bridging Chemistry and Biology Introduction:
Acetylation, a chemical process characterized by the addition of an acetyl functional group to a molecule, stands as a cornerstone in both biochemical and biological landscapes. Its significance traverses diverse realms, ranging from fundamental cellular processes to intricate disease pathogenesis. This article endeavors to delve deeper into the multifaceted world of acetylation, exploring its intricate mechanisms, diverse functions, and far-reaching implications in health and disease. Chemistry of Acetylation: Acetylation, at its essence, involves the transfer of an acetyl group (-COCH3) to a substrate molecule, a process catalyzed by enzymes known as acetyltransferases. T
…
16th Apr 2024
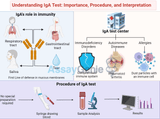
IgA Testing: Complete Diagnostic Guide + Interpretation Methods | Expert Protocols
The IgA test, also known as immunoglobulin A test, is a diagnostic tool used to measure the levels of IgA antibodies in the blood. Immunoglobulin A (IgA) is a type of antibody that plays a crucial role in the immune system's defense against infections. This test helps in diagnosing certain medical conditions related to the immune system, such as autoimmune diseases and allergies. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve deeper into the importance of the IgA test, its procedure, interpretation of results, factors affecting IgA levels, and clinical significance. Importance of IgA Test: Immunoglobulin A is primarily found in mucous membranes, particularly those lining the re
…
15th Apr 2024
Biomarker Testing: Advancements, Applications, and Future Directions
Biomarkers, measurable indicators of biological processes or responses to therapeutic interventions, play a pivotal role in modern healthcare. They provide clinicians with valuable information for disease detection, prognosis assessment, and treatment optimization. Biomarker testing encompasses a wide array of techniques and platforms, ranging from simple immunoassays to sophisticated genomic analyses. Over the past few decades, significant advancements in biomarker research have revolutionized clinical practice, leading to more personalized and precise approaches to patient care. Types of Biomarkers: Biomarkers encompass a diverse array of molecular entities that reflect v
…
14th Apr 2024
The Rat Effectively Models Signature Cytokines of T Helper Cells
Understanding the immune system's intricacies requires models that accurately reflect its complexity. The rat, as a model organism, plays a crucial role in immunological research, particularly in the study of T helper (Th) cells and their signature cytokines. This article explores how rats model the signature cytokines of Th cells, shedding light on their contributions to immunological research. Introduction to T Helper Cells and Their Cytokines T helper cells, a subset of T cells, are pivotal in the immune system's adaptive response. They assist other cells in the immune system through the secretion of cytokines, signaling molecules that modulate the immune response. These cell
…
26th Mar 2024
Understanding Blotchy Western Blots: Causes and Remedies
Western blotting is a powerful and widely used technique in molecular biology, essential for detecting and quantifying specific proteins in complex biological samples. However, despite its popularity, Western blotting can sometimes yield frustrating results, with one of the most common issues being blotchy or uneven bands. Blotchy Western blots can arise from various factors, ranging from sample preparation to technical errors during the blotting process. In this article, we'll delve into the potential causes of blotchy Western blots and provide some tips to rectify them. What are Blotchy Western Blots? Blotchy Western blots refer to the uneven distribution of bands across
…
13th Mar 2024
Advantages of Small Molecule Inhibitors in Therapeutic Interventions
Small molecule inhibitors represent a significant advancement in the field of therapeutic interventions, offering a versatile approach to treating a myriad of diseases, including cancer, viral infections, and chronic inflammatory conditions. These compounds, typically with a molecular weight of less than 900 daltons, can modulate biological processes by interacting with specific protein targets within the cell. This article explores the multifaceted advantages of small molecule inhibitors, highlighting their role in the development of targeted therapies. Target Specificity and Selectivity: One of the paramount advantages of small molecule inhibitors is their ability to selectivel
…
13th Mar 2024
Decoding Parkinson's Disease: Insights into a Complex Neurological Disorder
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a progressive neurological disorder that primarily affects the motor system, leading to a wide array of symptoms ranging from tremors and stiffness to bradykinesia (slowness of movement) and postural instability. Beyond these hallmark motor symptoms, Parkinson's disease can manifest in non-motor symptoms such as cognitive decline, mood disorders, and autonomic dysfunction, making it a multifaceted condition that challenges both individuals and healthcare systems worldwide. This article delves into the etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and therapeutic strategies for Parkinson's disease, shedding light on the complexities of this debilitating d
…
16th Feb 2024
Understanding Platelet Activation: A Comprehensive Overview
Platelet activation plays a pivotal role in hemostasis, the process that stops bleeding and initiates tissue repair after vascular injury. This complex biological mechanism involves the transformation of platelets from a resting state to an active state, enabling them to adhere to the site of injury, aggregate with other platelets, and interact with the coagulation cascade to form a stable blood clot. This article delves into the mechanisms of platelet activation, its significance in hemostasis, and the implications for pathological conditions when dysregulated. The Mechanisms of Platelet Activation Platelet activation is initiated by several triggers, including vascular injury,
…
14th Feb 2024
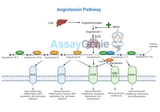
Angiotensin Pathways: Unlocking the Secrets to Blood Pressure Regulation and Beyond
The angiotensin pathway is a pivotal hormonal system that plays a crucial role in regulating blood pressure and maintaining fluid and electrolyte balance within the body. This complex biochemical cascade not only underpins essential physiological processes but also serves as a target for therapeutic interventions in conditions such as hypertension, heart failure, and chronic kidney disease. Understanding the Renin-Angiotensin System (RAS): At the heart of the angiotensin pathway lies the renin-angiotensin system (RAS), a regulatory circuit that influences systemic vascular resistance and, consequently, arterial blood pressure. The RAS pathway initiates with the synthesis of angio
…
14th Feb 2024
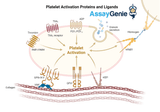
Platelet Adhesion Proteins and Ligands: Key Players in Hemostasis and Thrombosis
Platelet adhesion is a critical process in the maintenance of hemostasis, the body's response to bleeding. This intricate process involves a series of interactions between platelets, the cellular components of blood, and the vascular endothelium, the inner lining of blood vessels. At the core of this process are specific proteins and ligands that mediate the initial steps of platelet adhesion, activation, and aggregation, ultimately leading to the formation of a platelet plug that aids in the cessation of bleeding. This article delves into the vital roles of platelet adhesion proteins and their ligands, shedding light on their significance in both physiological and pathological contexts.
…
13th Feb 2024
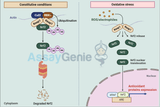
NRF2 Signaling: A Keystone in Inflammation and Disease Management
Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2–Related Factor 2 (NRF2) orchestrates a principal defense mechanism against oxidative stress and plays a pivotal role in inflammation and disease pathogenesis. This article explores the mechanism of NRF2 signaling, its intricate relationship with inflammation, its implications in various diseases, and the therapeutic potential of NRF2 modulation. Understanding NRF2 Signaling Basic Mechanism of Action NRF2 is a transcription factor that, upon activation, migrates to the nucleus to bind to Antioxidant Response Elements (ARE) in the DNA, promoting the expression of genes involved in antioxidant defense, detoxification, and cellular homeostasis. Re
…
12th Feb 2024
The Battle of Antibiotics: Penicillin vs. Streptomycin
In the realm of medicine, antibiotics are akin to superheroes, combating bacterial infections with unwavering efficacy. Among these, two stalwarts stand out: penicillin and streptomycin. These antibiotics revolutionized the treatment of bacterial infections, saving countless lives since their discovery. However, understanding their differences and applications is crucial for effective medical management. Let's delve into the fascinating world of penicillin versus streptomycin and explore the unique properties of Penicillin-Streptomycin Solution. Penicillin: The Pioneer Discovered accidentally by Alexander Fleming in 1928, penicillin marked the dawn of the antibiotic era. Fl
…
8th Feb 2024
What is the difference between PBS and dPBS?
In the realm of biological and biochemical research, solutions play a pivotal role in various experimental procedures, from cell culture to molecular biology assays. Among the plethora of solutions utilized, phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and Dulbecco’s phosphate-buffered saline (DPBS) stand out as crucial components. While both solutions share similarities, they possess distinct compositions and applications that merit exploration and understanding. Phosphate-Buffered Saline (PBS): A Versatile Solution PBS, a staple in laboratories worldwide, serves as a fundamental isotonic buffer solution utilized across diverse applications. Its composition typically consists of
…
8th Feb 2024