Blog
CD80: Amplifying Immune Activation Through Co-Stimulatory Pathways
Introduction to CD80 and Its Role in Immune Activation CD80 is a critical immune checkpoint molecule that plays an essential role in T cell activation through co-stimulatory pathways. Expressed primarily on antigen-presenting cells (APCs) such as dendritic cells, B cells, and macrophages, CD80 interacts with receptors on T cells to regulate immune responses. Specifically, CD80 engages CD28 to provide a crucial co-stimulatory signal necessary for full T cell activation, proliferation, and differentiation. This co-stimulation amplifies the immune system's ability to recognize and attack pathogens, as well as cancer cells.In addition to its role in immune activation, CD80 can
…
23rd Oct 2024
TLR4: Unraveling the Role of Inflammation in Cancer Progression
Introduction to TLR4 and Cancer Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) is a key component of the innate immune system, primarily responsible for detecting infections and initiating inflammatory responses. This receptor recognizes pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs), such as lipopolysaccharides (LPS) from bacteria, and damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) from injured or stressed cells. Once activated, TLR4 triggers the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which are crucial for defending the body against infections.However, the role of TLR4 in cancer is more complex. While TLR4-mediated inflammation is essential for immune protection, chronic inflammation driven by
…
22nd Oct 2024
CD73: Combating Tumor Immunosuppression by Targeting Adenosine
Introduction to CD73 and Tumor Immunosuppression CD73, also known as ecto-5'-nucleotidase, is an enzyme found on the surface of various cells, including tumor cells and immune cells. It plays a central role in producing adenosine, a molecule with potent immunosuppressive effects, particularly in the tumor microenvironment. By breaking down extracellular ATP (a danger signal) into adenosine, CD73 contributes to creating an environment that dampens immune responses, allowing tumors to evade immune surveillance and grow unchecked.The adenosine pathway has emerged as a critical target in cancer immunotherapy, as elevated adenosine levels within tumors lead to the suppression of
…
21st Oct 2024
CD39: A Novel Target to Overcome Immunosuppression in Cancer
Introduction to CD39 and Cancer Immunosuppression CD39 is an ectonucleotidase enzyme that plays a crucial role in generating adenosine, a powerful immunosuppressive molecule within the tumor microenvironment. By converting extracellular ATP (a danger signal that activates the immune system) into AMP, CD39 initiates the adenosine production pathway, which is completed by CD73. Adenosine, in turn, suppresses immune cell activity, particularly that of T cells, natural killer (NK) cells, and dendritic cells, thus protecting tumor cells from immune destruction.Targeting CD39 with therapies like BU69, a monoclonal antibody that inhibits CD39 activity, is a promising strategy to r
…
21st Oct 2024
CD122: Fine-Tuning T Cell Responses in Immunotherapy
Introduction to CD122 in Immunotherapy CD122, also known as the interleukin-2 receptor beta chain (IL-2Rβ), is a critical component of the immune system's response to pathogens and malignancies. Its primary function is to mediate signaling through the IL-2 and IL-15 cytokine pathways, which are essential for T cell proliferation, survival, and differentiation. These T cells, particularly CD8+ T cells and natural killer (NK) cells, play a central role in the body’s immune defense against cancer and infections.In recent years, immunotherapy has become a transformative approach in cancer treatment. The ability to harness and modify the body's own immune system to fight tumors
…
15th Oct 2024
CD27 Activation: Strengthening the Immune Army Against Cancer
Harnessing the immune system to fight cancer has become a pivotal strategy in modern oncology. A key component in this fight is CD27, a receptor that plays a crucial role in T-cell activation and immune memory. CD27 stimulation can enhance the immune system’s ability to detect and destroy cancer cells, making it an attractive target for immunotherapy. Antibodies such as AT124-5 are being developed to activate CD27, offering new hope for strengthening the immune response against cancer. What is CD27? CD27 is a member of the TNF receptor superfamily, expressed primarily on T cells and B cells. Its primary function is to enhance T-cell activation, support the formation of
…
14th Oct 2024
B7-H4: A New Frontier in Immune Checkpoint Inhibition
The recent advances in cancer immunotherapy have brought new opportunities to harness the body’s immune system against tumors. Among these advancements is the targeting of immune checkpoints, which play a significant role in immune suppression within the tumor microenvironment. A relatively new target of interest is B7-H4, a member of the B7 family of immune-regulatory proteins. Emerging research indicates that blocking B7-H4 with antibodies such as MIH43 may offer promising therapeutic benefits in various cancers. This article explores the role of B7-H4, its biological functions, and how anti-B7-H4 therapies may improve cancer treatment outcomes.Assay Genie · B7 - H4 A New Fron
…
14th Oct 2024
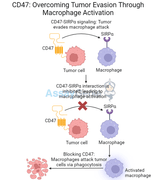
CD47: Overcoming Tumor Evasion Through Macrophage Activation
One of the greatest challenges in cancer therapy is how tumors evade immune detection. Among the mechanisms cancer cells exploit, the CD47 pathway has emerged as a major player in helping tumors avoid immune attack. CD47, known as the “don’t eat me” signal, interacts with immune cells to prevent their destruction by the body’s defense systems. However, novel therapies targeting CD47, such as anti-CD47 antibodies like MIAP301, are showing promising results in reversing this evasion strategy by activating macrophages and enhancing the body's ability to eliminate tumor cells.Assay Genie · CD47 Overcoming Tumor Evasion Through Macrophage ActivationWhat is CD47?CD7 is a transmembrane
…
8th Oct 2024
4-1BB: Energizing Immune Cells to Overcome Tumor Resistance
Immunotherapy has become a central pillar in the fight against cancer, with a focus on enhancing the body’s natural defenses. Among the molecules at the forefront of immunotherapeutic research is 4-1BB (CD137), a co-stimulatory receptor that plays a key role in amplifying immune cell responses. Agonists like 1D8 target 4-1BB, unleashing potent anti-tumor immunity. This article delves into the function of 4-1BB, how agonists enhance immune responses, and their potential in https://www.assaygenie.com/blog/targetting-immune-checkpoints-as-cancer-therapyAssay Genie · 4 - 1BB Energizing Immune Cells To Overcome Tumor ResistanceWhat is 4-1BB (CD137)?4-1BB, also known as CD137, is a co
…
8th Oct 2024
OX40 Agonists: Revitalizing the Immune Response in Cancer
Cancer immunotherapy has revolutionized treatment options, offering strategies to harness the immune system to target and destroy tumors. One emerging area of interest is the use of OX40 agonists, like OX86, which play a crucial role in amplifying the immune response against cancer cells. OX40 agonists show promise in several cancer models, potentially improving the efficacy of existing immunotherapies. This article will explore the mechanism of OX40, the role of OX40 agonists in cancer treatment, and ongoing clinical developments. Understanding OX40 and Its Role in Immunity OX40, also known as CD134, is a costimulatory receptor that belongs to the tumor necrosis facto
…
8th Oct 2024
Targeting VISTA: Unleashing the Power of T Cells in Cancer Therapy
V-domain Ig suppressor of T cell activation (VISTA) is an emerging immune checkpoint receptor that plays a key role in suppressing T cell activity within the tumor microenvironment (TME). As a negative regulator of immune responses, VISTA helps tumors evade detection by dampening the immune system’s ability to attack cancer cells. Recent research into targeting VISTA has highlighted its potential as a therapeutic target in cancer immunotherapy. By inhibiting VISTA, scientists aim to unleash the full power of T cells and other immune cells to attack and destroy tumors. This article explores VISTA’s function in immune regulation, its role in cancer progression, and the potential o
…
3rd Oct 2024
CD4+ T Cells: Unveiling the Role of Helper and Regulatory T Cells
CD4+ T cells are central to the immune system, functioning as coordinators of immune responses and regulators of immune tolerance. These cells are divided into two primary subtypes: Helper T cells (Th cells) and Regulatory T cells (Tregs). Both subsets of CD4+ T cells perform distinct roles, influencing the immune system's ability to attack pathogens or suppress excessive immune activity. Understanding the specialized functions of these cells sheds light on their importance in diseases such as infections, autoimmune disorders, and cancer.Assay Genie · CD4+ T Cells Unveiling The Role Of Helper And Regulatory T CellsCD4+ T Cells: Structure and DifferentiationCD4+ T cells are a sub
…
25th Sep 2024
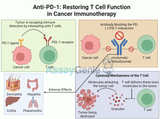
Anti-PD-1: Restoring T Cell Function in Cancer Immunotherapy
Cancer immunotherapy has revolutionized the treatment landscape for various malignancies. One of the most promising therapeutic strategies is the use of immune checkpoint inhibitors, particularly anti-PD-1 (programmed death-1) antibodies. These drugs enhance the immune system's ability to recognize and destroy cancer cells by restoring the function of T cells, which are often suppressed in cancer patients.Assay Genie · Anti-PD-1: Restoring T Cell Function in Cancer ImmunotherapyIntroduction to PD-1 and Its Role in Immune EvasionPD-1 is an immune checkpoint receptor expressed on T cells. It plays a critical role in maintaining immune homeostasis by preventing overactivation of T
…
24th Sep 2024
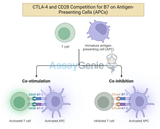
Anti-CTLA-4: Unleashing the Power of T Cells in Combination Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy has revolutionized cancer treatment by harnessing the body's immune system to fight malignancies. Among the notable advancements in this field is the development of immune checkpoint inhibitors. One of the key players is anti-CTLA-4 (cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4), a monoclonal antibody that disrupts immune checkpoints and enhances T cell activation. Anti-CTLA-4 has shown immense promise, especially when used in combination immunotherapy. This article delves into how anti-CTLA-4 works, its role in unleashing the power of T cells, and its synergistic effects in combination therapies.Assay Genie · Anti - CTLA - 4 Unleashing The Power Of T Cells In Combi
…
24th Sep 2024
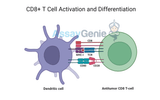
CD8+ T Cells: Understanding the Role of Cytotoxic T Cells in Immunity
CD8+ T cells, also known as cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), are a critical component of the immune system. They play a vital role in defending the body against viral infections, intracellular pathogens, and tumor cells. This article will delve into the biology of CD8+ T cells, their mechanisms of action, and their clinical relevance, particularly in immunotherapy and infectious disease control.Assay Genie · CD8+ T Cells Understanding The Role Of Cytotoxic T Cells In ImmunityWhat Are CD8+ T Cells?CD8+ T cells are a subset of T lymphocytes that express the CD8 glycoprotein on their surface. This marker distinguishes them from other T cells, such as CD4+ helper T cells. CD8+ T cell
…
23rd Sep 2024
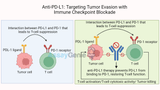
Anti-PD-L1: Targeting Tumor Evasion with Immune Checkpoint Blockade
IntroductionCancer cells have developed sophisticated mechanisms to evade the immune system, particularly through the inhibition of T-cell responses. One such mechanism involves the programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1), which binds to its receptor PD-1 on T cells, leading to the suppression of immune activity. Anti-PD-L1 therapies, as part of the broader category of immune checkpoint inhibitors, have transformed cancer treatment by restoring immune system function and enhancing the body's ability to recognize and eliminate tumor cells. This article explores the role of PD-L1 in immune evasion and how its inhibition can significantly impact cancer therapy outcomes.Assay Genie · Anti
…
22nd Sep 2024
Th17 Cell Differentiation: Insights into Immunological Dynamics
Th17 cells, a subset of T helper cells characterized by their production of interleukin-17 (IL-17), play a significant role in the immune system's response to pathogens and in the pathology of autoimmune diseases. This article delves into the mechanisms of Th17 cell differentiation, exploring the interplay of cytokines, transcription factors, and their implications for health and disease. Initiation of Th17 Differentiation: The Cytokine Prelude The Role of TGF-β and IL-6 Th17 differentiation begins with the orchestration of specific cytokines, notably transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). TGF-β sets the stage for a bifurcated pathway that can le
…
25th May 2024
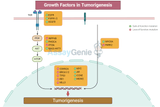
Growth Factors Can Cooperate to Promote Tumorigenesis
Introduction Tumorigenesis, the process by which normal cells transform into cancer cells, is a multifaceted and complex event influenced by various internal and external factors. Among these, growth factors play a pivotal role in cellular communication and regulation, often being the critical elements that can tip the balance towards cancer development when dysregulated. This article delves into how growth factors, through their intricate network and interactions, can cooperate to promote tumorigenesis, highlighting the mechanisms behind their action and the implications for cancer therapy. The Role of Growth Factors in Cell Regulation Growth factors are proteins that bin
…
3rd May 2024
Inflammasome Activation Pathways: A Comprehensive Overview
Inflammasomes are complex intracellular structures that play a pivotal role in the immune response by detecting pathogenic microorganisms and sterile stressors. Their activation is a critical step in the host defense system, leading to the maturation and secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines like IL-1β and IL-18. This article provides a detailed examination of the mechanisms underlying inflammasome activation. Understanding the Inflammasome: Structure and Function Inflammasomes are multiprotein oligomers, primarily composed of a sensor (typically a pattern recognition receptor), the adaptor protein ASC, and the effector protein pro-caspase-1. The most well-studied inflammasomes
…
29th Apr 2024
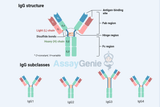
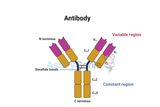
Comprehensive Analysis of Antibody Structure and Function
Antibodies, or immunoglobulins, stand as critical components of the immune system, orchestrating the identification and neutralization of pathogens like viruses and bacteria. This extensive article aims to provide a thorough understanding of the sophisticated architecture and multifaceted roles of antibodies, delving into their molecular composition, mechanisms behind their diversity and specificity, and their integral functions within the immune response. Fundamental Architecture of Antibodies Antibodies are Y-shaped molecules composed of four polypeptide chains: two identical heavy chains and two identical light chains. These chains are linked together by disulfide bonds and n
…
2nd Apr 2024
Immunoglobulin vs Antibody: Unveiling the Intricacies
In the realm of immunology, the terms "immunoglobulin" and "antibody" often find themselves used interchangeably, sparking confusion among those keen on understanding the immune system's fine details. While closely related, these terms encapsulate nuances vital for a comprehensive grasp of how the body defends itself against pathogens. This article embarks on a deep dive into the definitions, functions, structures, and types of immunoglobulins and antibodies, unveiling their similarities and differences. Defining the Players Immunoglobulin (Ig) Immunoglobulins, commonly abbreviated as Igs, are glycoprotein molecules produced by plasma cells (a type of white blood cell). The
…
30th Mar 2024
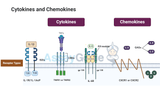
Chemokines versus Cytokines: A Detailed Comparative Study
The complex interplay between chemokines and cytokines is fundamental to the immune system's function, orchestrating the body's response to infection, inflammation, and injury. This detailed analysis explores the distinctions and connections between these two pivotal types of signaling molecules, highlighting their roles in health and disease. Deep Dive into Chemokines What Are Chemokines? Chemokines are a specialized subgroup of cytokines characterized by their ability to induce directed chemotaxis in nearby responsive cells. These molecules are crucial for the migration of cells, particularly immune cells, to sites of infection or injury. The Four Families of Chemokin
…
30th Mar 2024
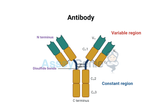
Understanding Immunoglobulin Antibodies: Structure, Function, and Types
Immunoglobulin antibodies stand at the forefront of the immune defense system, offering a sophisticated mechanism for recognizing and neutralizing a vast array of pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and other potentially harmful foreign bodies. These antibodies, also known as immunoglobulins (Ig), are produced by specialized cells in the immune system and serve as a critical component of both innate and adaptive immunity. This article provides a deeper understanding of the structure, function, and classification of immunoglobulin antibodies, highlighting their essential role in maintaining health and combating diseases. Detailed Structure of Immunoglobulin Antibodies At the
…
29th Mar 2024
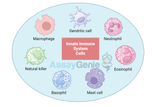
Innate Immune Systemc Explained: Step-by-Step Process & Key Concepts
The innate immune system is the first line of defense against pathogens, providing a rapid response to infections. This system comprises various cell types, each with specialized roles in detecting and eliminating invaders. In this article, we delve into the intricate world of innate immune system cells, exploring their functions, types, and contributions to the body's defense mechanisms. Introduction to the Innate Immune System The innate immune system is a crucial component of the body's defense, capable of immediate action upon encountering pathogens. Unlike the adaptive immune system, which requires time to develop a specific response, the innate immune system provides a gene
…
28th Mar 2024