Blog
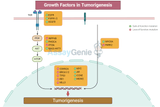
Growth Factors Can Cooperate to Promote Tumorigenesis
Introduction Tumorigenesis, the process by which normal cells transform into cancer cells, is a multifaceted and complex event influenced by various internal and external factors. Among these, growth factors play a pivotal role in cellular communication and regulation, often being the critical elements that can tip the balance towards cancer development when dysregulated. This article delves into how growth factors, through their intricate network and interactions, can cooperate to promote tumorigenesis, highlighting the mechanisms behind their action and the implications for cancer therapy. The Role of Growth Factors in Cell Regulation Growth factors are proteins that bin
…
3rd May 2024
Illuminating the Multifaceted Role of Acetylation: Bridging Chemistry and Biology Introduction:
Acetylation, a chemical process characterized by the addition of an acetyl functional group to a molecule, stands as a cornerstone in both biochemical and biological landscapes. Its significance traverses diverse realms, ranging from fundamental cellular processes to intricate disease pathogenesis. This article endeavors to delve deeper into the multifaceted world of acetylation, exploring its intricate mechanisms, diverse functions, and far-reaching implications in health and disease. Chemistry of Acetylation: Acetylation, at its essence, involves the transfer of an acetyl group (-COCH3) to a substrate molecule, a process catalyzed by enzymes known as acetyltransferases. T
…
16th Apr 2024
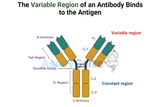
Unraveling the Complexities of Antibodies: Light Chains, Heavy Chains, Constant Regions, and Tumor-Associated Antigens
Antibodies, also known as immunoglobulins, play a pivotal role in the immune system's ability to recognize and neutralize pathogens. This comprehensive article delves into the structural and functional nuances of antibodies, focusing on the antibody light chain, tumor-associated antigens, constant regions of antibodies, and the interplay between heavy and light chains. By exploring these components in detail, we aim to enhance understanding of their significance in immunology and their implications in cancer research. Contents 1. Introduction to Antibodies 2. Structure of Antibodies Heavy Chain and Light Chain Constant Region of Antibody 3. Antibody Light Chain Types of Light
…
28th Mar 2024
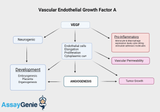
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A (VEGFA): A Cornerstone in Angiogenesis and Beyond
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A (VEGFA) is a pivotal signaling protein involved in both vasculogenesis and angiogenesis, processes essential for the formation of blood vessels during embryonic development and the growth of new blood vessels from pre-existing ones. As a member of the VEGF family, VEGFA plays a critical role in the regulation of endothelial cell function, affecting vascular permeability and endothelial cell proliferation. The Molecular Biology of VEGFA VEGFA is characterized by its gene located on chromosome 6p21.1, encoding a heparin-binding protein that promotes endothelial cell growth, migration, and survival. The VEGFA protein undergoes complex post-transl
…
9th Mar 2024
Exploring the Frontier of Immunotherapy: T Cell Expansion
In the realm of immunotherapy, T cell expansion has emerged as a pivotal strategy, holding promise in the treatment of various diseases, particularly cancer. T cells are a critical component of the adaptive immune system, orchestrating immune responses against pathogens and malignant cells. Harnessing the potential of T cells through expansion techniques offers a novel avenue for enhancing their therapeutic efficacy. This article delves into the mechanisms, applications, and advancements in T cell expansion, illuminating its transformative impact on medical science. Understanding T Cell Expansion T cells, a type of lymphocyte, play a central role in adaptive immunity by rec
…
8th Mar 2024
Targeting Immune Checkpoints as Cancer Therapy
In recent years, the field of oncology has witnessed a paradigm shift with the advent of immunotherapy, a treatment modality that harnesses the body's immune system to combat cancer. Among the most promising approaches in immunotherapy is the targeting of immune checkpoints. These molecular pathways are crucial for maintaining self-tolerance and modulating the immune response to prevent autoimmunity. However, cancer cells cleverly exploit these pathways to evade immune detection and destruction. This article delves into the mechanisms of immune checkpoint pathways, their role in cancer evasion, and the therapeutic strategies designed to inhibit these checkpoints, thereby reactivating the
…
16th Feb 2024
Unraveling the Synergy: How Growth Factors Cooperate to Promote Tumorigenesis
In the intricate ballet of cellular communication and regulation, growth factors play pivotal roles in guiding the processes of cell growth, division, and differentiation. These proteins are essential for normal development and tissue repair. However, when their signaling pathways become co-opted or dysregulated, they can also act as key players in the development and progression of cancer. This article delves into the complex interplay of growth factors and their cooperation in promoting tumorigenesis, shedding light on the molecular mechanisms that underlie cancer development and offering insights into potential therapeutic interventions. The Fundamental Role of Growth Factors in C
…
15th Feb 2024
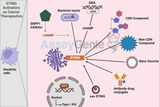
STING Activators As Cancer Therapeutics
The STING (Stimulator of Interferon Genes) pathway plays a pivotal role in the innate immune system's response to cancerous cells and DNA viruses. Exploiting this pathway through STING activators presents a promising avenue for cancer therapeutics. This article delves into the mechanism of action of STING activators, their therapeutic potential, challenges in their development, and the latest advancements in the field. Understanding the STING Pathway The Biological Role of STING The STING pathway is integral to the innate immune response, detecting cytosolic DNA to trigger the production of type I interferons and other cytokines. This response is crucial for the immune syst
…
15th Feb 2024
Targeting Immune Checkpoints as Cancer Therapy
The advent of immune checkpoint targeting marks a significant milestone in the oncological field, offering a beacon of hope for patients battling cancer. This innovative approach leverages the body's immune system to recognize and combat cancer cells, a method that stands in stark contrast to traditional therapies. This article delves deep into the essence of immune checkpoint therapy, exploring its mechanisms, benefits, challenges, and the horizon it promises for future cancer treatments. Introduction to Immune Checkpoints Immune checkpoints are critical regulators of the immune system's response to various cells, including cancer cells. They are designed to prevent the immune s
…
13th Feb 2024
Deciphering B Cell Cancers With a Rituximab Biosimilar
The fight against B cell cancers, a challenging spectrum of hematologic malignancies, has entered a new era with the introduction of rituximab biosimilars. These biosimilars promise to extend the revolutionary benefits of rituximab, a cornerstone in the treatment of diseases like non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), to a broader patient population. This detailed exploration covers the complex nature of B cell cancers, the therapeutic mechanism of rituximab, and the significant potential of its biosimilars. Introduction B cell cancers represent a diverse group of malignancies that require nuanced therapeutic approaches. The advent of biosimilar thera
…
5th Feb 2024
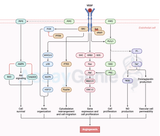
Cell Death Pathways: Intrinsic vs Extrinsic Apoptosis Guide
At Assay Genie we have created a comprehensive guide outlining everything you need to know about apoptosis! Key Takeaways: Apoptosis is a programmed cell death process, vital for tissue maintenance and disease prevention. Distinct from necrosis, apoptosis involves cellular shrinkage, nuclear breakdown, membrane disruption, and fragmentation into apoptotic bodies. p53 pathway, intrinsic and extrinsic pathways, and caspase cascades are key mechanisms in apoptosis. Apoptosis vs. Necrosis: Apoptosis is controlled and natural, while necrosis is uncontrolled and harmful. p53 Pathway: Activated by DNA damage, involves proteins like Bax, Bak, Bad. Intrinsic Apoptosis: Triggered intern
…
24th Jan 2024
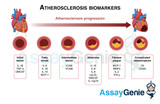
Biomarkers & Inflammatory markers of atherosclerosis
As atherosclerosis is a complex inflammatory disease, there are many influential biomarkers that contribute to the disease’s progression as well as biomarkers from atherosclerosis related diseases such as periodontal disease and autoimmune diseases i.e. Diabetes, RA, SLE. Biomarkers can be proteins, DNA and mRNA which are measured to asses biological, pathological processes and pharmacological responses. Biomarkers can be classified as early, predictive and prognostic biomarkers depending on disease stage (Huang et al., 2010). Identifying biomarkers for disease and finding therapeutic targets is crucial to research and treatment and overall a populations mortality and morbidity rat
…
23rd Jan 2024
VEGF-A VEGFR-2 Signaling: Decoding the Blueprint of Angiogenesis for Therapeutic Insights
The orchestration of angiogenesis, the process by which new blood vessels form from pre-existing ones, is a complex symphony regulated by various molecular players. At the forefront of this intricate dance is the VEGF-A VEGFR-2 signaling pathway, a pivotal mechanism that propels the growth and maintenance of blood vessels. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the molecular details of this pathway, shedding light on its fundamental role in angiogenesis and its implications in both health and disease. VEGF-A: A Master Regulator of Angiogenesis: Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A (VEGF-A) stands as a beacon among the VEGF family of growth factors. Produced
…
18th Jan 2024
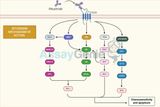
Positive Control vs Negative Control
T cell activation is a crucial process in the immune response, playing a pivotal role in how the body responds to pathogens and maintains immune homeostasis. This intricate process involves several key stages and molecules, each contributing to the effective functioning of T cells in the immune system. Understanding the Basics of T Cell Activation Direct conjugation involves the direct covalent attachment of the molecule to the antibody. This method is straightforward but requires careful control of reaction conditions to ensure specificity and retain antibody functionality. Indirect Conjugation Indirect conjugation uses a two-step process. Initially, a reactive group is
…
24th Aug 2023
Antibody Conjugation: Techniques and Applications
Antibody conjugation is a pivotal technique in biomedical research and diagnostic applications. This process involves the covalent attachment of a molecule, such as a drug, toxin, enzyme, or fluorescent dye, to an antibody. The specificity of antibodies to their antigens makes antibody conjugation a powerful tool for targeted delivery in therapeutic contexts and for specific detection in diagnostic assays.
window.SHOGUN_IMAGE_V2_ELEMENTS = window.SHOGUN_IMAGE_V2_ELEMENTS || new Array();
window.SHOGUN_IMAGE_V2_ELEMENTS.push({ uuid: 's-244b29f5-4261-4ef7-974d-e802c13cdca5' })
Overview of Antibody Conjugation Techniques Direc
…
24th Aug 2023
The Role of Tumor Suppressor Genes in Cancer: Knudson Hypothesis & Oncogenes
The focus of this article is Tumor Suppressor Genes. There are various different types of tumor suppressor genes, with BRCA being one of the most popular. The role of Tumor Suppressor Genes in Cancer, Oncogenes and Knudson Hypothesis are also discussed. Key Takeaways Tumor suppressor genes help prevent tumor formation by controlling cell growth. Mutations in these genes can lead to cancer by disrupting their normal functions. Examples include p53, BRCA1, BRCA2, and PTEN. The Knudson Two-Hit Hypothesis explains how mutations in these genes can lead to cancer. Understanding tumor suppressor genes aids in developing cancer treatments. What are Tumor Suppressor Gene
…
24th Aug 2023
Myeloid Lineage: Pioneers of Immune Cell Production
Delve into the myeloid lineage, a cornerstone of the immune system and blood cell production, understanding its vital roles and implications in health and disease. Key Takeaways: Myeloid lineage is critical in immune response and blood cell formation. It includes cell types like granulocytes, monocytes, and dendritic cells. Myeloid cells are essential for phagocytosis, antigen presentation, and cytokine production. Dysregulation in myeloid cells can lead to diseases like leukemia and autoimmune disorders. Myeloid lineage plays a crucial role in the immune system and hematopoiesis, encompassing various cell types involved in defending the body against infections and ma
…
25th Jul 2023
Fibroblast Markers
Fibroblasts, essential components of connective tissues, play vital roles in maintaining tissue structure and function. Their remarkable ability to produce and organize the extracellular matrix forms the foundation for tissue integrity and repair processes. Identifying and characterizing fibroblasts amidst complex biological environments rely on fibroblast markers, specific molecular indicators that aid researchers in distinguishing these cells. In this blog post, we delve into Fibroblast, their markers and their significance in cancers. fibroblast markers in research, their potential applications in disease investigation, and their implications in regenerative medicine and therapeutic
…
20th Jul 2023
von Willebrand Factor and Cancer
What is von Willebrand Factor?
Von Willebrand Factor (VWF) is a crucial glycoprotein that plays a fundamental role in blood clotting and hemostasis. Produced by endothelial cells and megakaryocytes, VWF circulates in the bloodstream as large multimers. Its primary function is to mediate platelet adhesion at sites of vascular injury, forming a temporary platelet plug to stop bleeding. VWF also serves as a carrier protein for Factor VIII, protecting it and extending its availability during the clotting process.
Von Willebrand Disease (VWD) is an inherited bleeding disorder caused by deficiencies or abnormalities in von Willebrand Factor.
{
"@context":
…
18th Jul 2023
Cancer Metabolism: Tumorigenesis, Metabolic Therapy & The Warburg Effect
Cancer Metabolism is the mechanism by which cancer cells make energy in order for them to grow and spread. Even in the presence of oxygen, cancer cells increase glucose uptake and produce lactate, which is defined by the Warburg Effect. This article also discusses areas related to cancer metabolism such as Tumorigenesis and Metabolic Therapy.
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "Article",
"mainEntityOfPage": {
"@type": "WebPage",
"@id": "https://www.assaygenie.com/blog/an-overview-of-cancer-metabolism-tumorigenesis-metabolic-therapy-and-the-warburg-effect"
},
"headline": "Cancer Metabolism: Tumorigenesis, Metabolic Therapy & The Warburg Effect",
"descr
…
14th Jul 2023
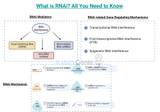
What is RNAi? All You Need to Know
RNA interference (RNAi), also referred to as Post-Transcriptional Gene Silencing (PTGS), is the process by which RNA molecules silence genes in response to double-stranded RNA. RNA interference (RNAi) causes the downregulation or silencing of specific genes at the post-transcriptional level. It can lead to several effects depending on the targeted gene and its biological function.This article discusses RNAi, the various types of RNAi, its mechanism of action and RNAi therapeutics.
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "BlogPosting",
"mainEntityOfPage": {
"@type": "WebPage",
"@id": "https://www.assaygenie.com/blog/what-is-rna-interference-all-you-need-to-know"
}
…
13th Jul 2023
Mitotic Catastrophe Review
Delving into the intricate world of Mitotic Catastrophe, this blog unveils its critical role in cell division and cancer therapy, offering insights into its mechanisms and potential treatments. Key Takeaways: Mitotic Catastrophe: A response to abnormal mitosis, potentially leading to cell death. Oncosuppressive Role: Prevents proliferation of genetically unstable cells, guarding against cancer. Mitotic Failure and Slippage: Involves death without mitosis exit or progression to G1 phase. Cyclin B Proteolysis: Key in mitotic slippage, leading to Cdk1 inactivation. Prolonged Arrest: Influences cell fate, with a cutoff point for irreversible catastrophe. Targeting Strategies
…
11th Jul 2023
Cyclins and Cyclin Dependent Kinase – Review
Cyclins and CDKs are central to cell cycle control, with specific cyclin-CDK pairs regulating different phases, ensuring orderly progression and genomic integrity in cell division. Key Takeaways: Cyclins and CDKs are vital for cell cycle regulation. Cyclins A, B, D, E each pair with specific CDKs to control cell cycle phases. Cdk1, the prototypical CDK, partners with cyclin B for mitotic entry. Cyclin B upregulation and Cdk1 substrates play key roles in mitosis. Proteomic analysis reveals extensive Cdk1 substrates in mitosis. Positive feedback loops amplify Cdk1/cyclin B activity. Cdk1-Plk1 phosphorylation cascade is crucial for spindle assembly and mitosis. Cyclin degradatio
…
10th Jul 2023
The p53 Protein: Tumor Suppressor Protein
p53, encoded by the TP53 gene on chromosome 17, is a fundamental protein safeguarding against tumor formation. It orchestrates cellular responses to DNA damage and stress, crucially managing cell division. By activating a range of mechanisms like cell cycle regulation, DNA repair, apoptosis, and senescence, p53 maintains cellular integrity and prevents cancerous growths.
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "Article",
"mainEntityOfPage": {
"@type": "WebPage",
"@id": "https://www.assaygenie.com/blog/p53-protein-mutations-cancer-cell-signalling"
},
"headline": "The p53 Protein: Tumor Suppressor Protein",
"description": "This article contains an overview of th
…
5th Jul 2023