Blog
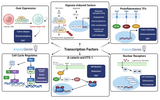
Unraveling the Synergy: How Growth Factors Cooperate to Promote Tumorigenesis
In the intricate ballet of cellular communication and regulation, growth factors play pivotal roles in guiding the processes of cell growth, division, and differentiation. These proteins are essential for normal development and tissue repair. However, when their signaling pathways become co-opted or dysregulated, they can also act as key players in the development and progression of cancer. This article delves into the complex interplay of growth factors and their cooperation in promoting tumorigenesis, shedding light on the molecular mechanisms that underlie cancer development and offering insights into potential therapeutic interventions. The Fundamental Role of Growth Factors in C
…
15th Feb 2024
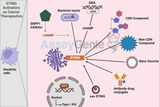
STING Activators As Cancer Therapeutics
The STING (Stimulator of Interferon Genes) pathway plays a pivotal role in the innate immune system's response to cancerous cells and DNA viruses. Exploiting this pathway through STING activators presents a promising avenue for cancer therapeutics. This article delves into the mechanism of action of STING activators, their therapeutic potential, challenges in their development, and the latest advancements in the field. Understanding the STING Pathway The Biological Role of STING The STING pathway is integral to the innate immune response, detecting cytosolic DNA to trigger the production of type I interferons and other cytokines. This response is crucial for the immune syst
…
15th Feb 2024
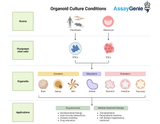
Optimizing Organoid Culture Conditions: Paving the Way for Revolutionary Advances in Biomedical Research
In the dynamic landscape of biomedical research, organoids have emerged as a groundbreaking tool, offering three-dimensional (3D) models that mimic the complex architecture and functionality of human organs. These miniature, self-organizing structures have revolutionized our approach to understanding human development, disease modeling, and drug discovery. However, the key to harnessing their full potential lies in optimizing organoid culture conditions. This intricate process involves fine-tuning the biochemical and physical environment to support the growth, differentiation, and maturation of organoids. This article delves into the critical aspects of organoid culture, including the se
…
14th Feb 2024
Understanding Platelet Activation: A Comprehensive Overview
Platelet activation plays a pivotal role in hemostasis, the process that stops bleeding and initiates tissue repair after vascular injury. This complex biological mechanism involves the transformation of platelets from a resting state to an active state, enabling them to adhere to the site of injury, aggregate with other platelets, and interact with the coagulation cascade to form a stable blood clot. This article delves into the mechanisms of platelet activation, its significance in hemostasis, and the implications for pathological conditions when dysregulated. The Mechanisms of Platelet Activation Platelet activation is initiated by several triggers, including vascular injury,
…
14th Feb 2024
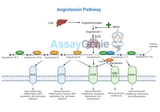
Angiotensin Pathways: Unlocking the Secrets to Blood Pressure Regulation and Beyond
The angiotensin pathway is a pivotal hormonal system that plays a crucial role in regulating blood pressure and maintaining fluid and electrolyte balance within the body. This complex biochemical cascade not only underpins essential physiological processes but also serves as a target for therapeutic interventions in conditions such as hypertension, heart failure, and chronic kidney disease. Understanding the Renin-Angiotensin System (RAS): At the heart of the angiotensin pathway lies the renin-angiotensin system (RAS), a regulatory circuit that influences systemic vascular resistance and, consequently, arterial blood pressure. The RAS pathway initiates with the synthesis of angio
…
14th Feb 2024
Targeting Immune Checkpoints as Cancer Therapy
The advent of immune checkpoint targeting marks a significant milestone in the oncological field, offering a beacon of hope for patients battling cancer. This innovative approach leverages the body's immune system to recognize and combat cancer cells, a method that stands in stark contrast to traditional therapies. This article delves deep into the essence of immune checkpoint therapy, exploring its mechanisms, benefits, challenges, and the horizon it promises for future cancer treatments. Introduction to Immune Checkpoints Immune checkpoints are critical regulators of the immune system's response to various cells, including cancer cells. They are designed to prevent the immune s
…
13th Feb 2024
Macrophage Activation: A Keystone in Immune Response and Therapeutic Potential
In the intricate tapestry of the immune system, macrophages play a pivotal role, orchestrating a wide range of biological responses that protect the body against pathogens, remove cellular debris, and promote tissue repair. Macrophage activation is a complex process, integral to both innate and adaptive immunity, influencing disease outcomes and offering promising avenues for therapeutic intervention. This comprehensive exploration delves into the mechanisms of macrophage activation, its dualistic nature, and the implications for disease treatment and immune modulation. The Fundamentals of Macrophage Activation: Macrophages, derived from monocytes, are versatile cells present in
…
13th Feb 2024
Ionotropic Glutamate Receptors: Gateways to Neural Communication
Ionotropic glutamate receptors (iGluRs) are pivotal in the fast excitatory synaptic transmission in the mammalian central nervous system (CNS). These receptors are not only crucial for normal brain function, including learning and memory but are also implicated in various neurological disorders, making them a significant subject of neuropharmacological research. The Basics of Glutamate and Its Receptors: Glutamate is the primary excitatory neurotransmitter in the CNS. It exerts its effects through two main types of receptors: ionotropic and metabotropic glutamate receptors. Ionotropic receptors are ligand-gated ion channels, which, upon binding of glutamate, open to allow the flo
…
13th Feb 2024
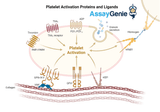
Platelet Adhesion Proteins and Ligands: Key Players in Hemostasis and Thrombosis
Platelet adhesion is a critical process in the maintenance of hemostasis, the body's response to bleeding. This intricate process involves a series of interactions between platelets, the cellular components of blood, and the vascular endothelium, the inner lining of blood vessels. At the core of this process are specific proteins and ligands that mediate the initial steps of platelet adhesion, activation, and aggregation, ultimately leading to the formation of a platelet plug that aids in the cessation of bleeding. This article delves into the vital roles of platelet adhesion proteins and their ligands, shedding light on their significance in both physiological and pathological contexts.
…
13th Feb 2024
NRF2 Signaling: A Keystone in Inflammation and Disease Management
Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2–Related Factor 2 (NRF2) orchestrates a principal defense mechanism against oxidative stress and plays a pivotal role in inflammation and disease pathogenesis. This article explores the mechanism of NRF2 signaling, its intricate relationship with inflammation, its implications in various diseases, and the therapeutic potential of NRF2 modulation. Understanding NRF2 Signaling Basic Mechanism of Action NRF2 is a transcription factor that, upon activation, migrates to the nucleus to bind to Antioxidant Response Elements (ARE) in the DNA, promoting the expression of genes involved in antioxidant defense, detoxification, and cellular homeostasis. Re
…
12th Feb 2024
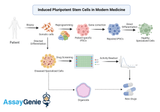
The Transformative Era of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells in Modern Medicine
The inception of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) has heralded a new dawn in the realm of biomedical research and regenerative medicine, setting the stage for groundbreaking advancements in disease treatment, drug discovery, and the prospect of personalized medicine. This pioneering technology, which allows the reprogramming of adult somatic cells back to an embryonic-like pluripotent state, has not only expanded our understanding of cellular biology but also opened up new avenues for therapeutic interventions, challenging the very paradigms of medical science. The Genesis of iPSC Technology: The journey of iPSC technology began with the landmark discovery by Shinya Yamanak
…
12th Feb 2024
Unraveling the Mysteries of Platelet-Activating GPCR Signaling
Platelet activation plays a pivotal role in hemostasis, the process that stops bleeding and initiates wound healing. Central to this process is the activation of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), which serve as key signal transducers on the surface of platelets. These receptors detect extracellular signals and initiate a cascade of intracellular events leading to platelet activation. This article delves into the mechanisms of platelet-activating GPCR signaling, highlighting its significance in thrombosis and potential therapeutic implications. The Role of GPCRs in Platelet Activation: GPCRs represent a vast and diverse family of receptors that are critical in various physiolog
…
9th Feb 2024
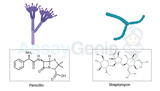
The Battle of Antibiotics: Penicillin vs. Streptomycin
In the realm of medicine, antibiotics are akin to superheroes, combating bacterial infections with unwavering efficacy. Among these, two stalwarts stand out: penicillin and streptomycin. These antibiotics revolutionized the treatment of bacterial infections, saving countless lives since their discovery. However, understanding their differences and applications is crucial for effective medical management. Let's delve into the fascinating world of penicillin versus streptomycin and explore the unique properties of Penicillin-Streptomycin Solution. Penicillin: The Pioneer Discovered accidentally by Alexander Fleming in 1928, penicillin marked the dawn of the antibiotic era. Fl
…
8th Feb 2024
What is the difference between PBS and dPBS?
In the realm of biological and biochemical research, solutions play a pivotal role in various experimental procedures, from cell culture to molecular biology assays. Among the plethora of solutions utilized, phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and Dulbecco’s phosphate-buffered saline (DPBS) stand out as crucial components. While both solutions share similarities, they possess distinct compositions and applications that merit exploration and understanding. Phosphate-Buffered Saline (PBS): A Versatile Solution PBS, a staple in laboratories worldwide, serves as a fundamental isotonic buffer solution utilized across diverse applications. Its composition typically consists of
…
8th Feb 2024
Transduction vs Transfection: Understanding Gene Delivery Techniques
In the realm of molecular biology and genetic engineering, the ability to deliver genetic material into cells is fundamental for various research and therapeutic purposes. Two common methods employed for this purpose are transduction and transfection. While both techniques facilitate the introduction of exogenous genetic material into cells, they differ significantly in their mechanisms and applications. This article aims to elucidate the distinctions between transduction and transfection, highlighting their respective advantages, limitations, and applications. Transduction: Transduction is a process by which genetic material is transferred into a cell via a viral vector.
…
8th Feb 2024
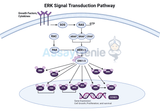
Erk Signal Transduction Explained: Step-by-Step Process & Key Concepts
The ERK signal transduction pathway stands as a fundamental mechanism in cellular biology, orchestrating a wide array of physiological processes, including cell division, differentiation, and survival. This pathway, part of the larger mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) family, is instrumental in conveying signals from the cell surface to the nucleus, thereby influencing gene expression and cellular outcomes in response to external stimuli. Understanding the ERK Pathway: The Extracellular signal-Regulated Kinase (ERK) pathway is initiated by the binding of growth factors, cytokines, and other extracellular ligands to their respective receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) on the ce
…
8th Feb 2024
Apoptosis Caspase Pathways: A Closer Look at Cellular Suicide
Apoptosis, or programmed cell death, is a fundamental process that plays a critical role in the development and maintenance of healthy tissues. Central to this process are caspases, a family of cysteine proteases that, once activated, orchestrate the cell's orderly demise. Understanding the caspase pathways not only sheds light on how our bodies maintain cellular balance but also provides insights into the mechanisms underlying various diseases, including cancer and neurodegenerative disorders. The Initiation of Apoptosis: Intrinsic and Extrinsic Pathways Apoptosis can be triggered through two primary pathways: intrinsic and extrinsic, both of which eventually converge on the act
…
8th Feb 2024
Understanding Parkinson's Disease: Insights and Innovations
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a progressive neurological disorder that predominantly affects the motor system, leading to a wide range of symptoms including tremors, rigidity, bradykinesia (slowness of movement), and postural instability. This article delves into the pathophysiology, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for Parkinson's disease, providing a comprehensive understanding of this complex condition. Understanding Parkinson's Disease Pathophysiology Parkinson's disease is characterized by the degeneration of dopamine-producing neurons in the substantia nigra, a region of the brain that plays a critical role in regulating movement. The decline in dopamine leve
…
8th Feb 2024
Alzheimer's Disease: A Comprehensive Insight
Alzheimer's disease stands as a formidable challenge in the realm of neurological disorders, characterized by its progressive nature and profound impact on cognitive functions. This article delves deeper into the facets of Alzheimer's disease, exploring its causes, mechanisms, clinical manifestations, and current therapeutic strategies, enriched with current scientific insights. Etiology and Risk Factors Genetic Factors The genetic landscape of Alzheimer's disease is complex, with both hereditary (familial AD) and sporadic forms. Key genes implicated in its pathogenesis include the amyloid precursor protein (APP), presenilin-1 (PSEN1), and presenilin-2 (PSEN2). Mutations i
…
7th Feb 2024
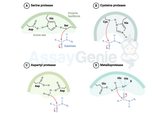
Protease vs Peptidase: Understanding Enzymatic Digestion
In the complex world of biochemical processes, enzymes play a crucial role in catalyzing various reactions necessary for life. Among these enzymes, proteases and peptidases are fundamental players involved in the breakdown of proteins and peptides, respectively. While their names might sound similar and their functions somewhat overlap, they serve distinct purposes in the realm of enzymatic digestion. Let's delve deeper into their definitions, functions, and types to gain a comprehensive understanding. Protease: The Protein Digesters Proteases, also known as proteolytic enzymes or proteinases, are enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of peptide bonds within proteins. These
…
6th Feb 2024
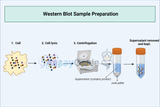
Guide to Western Blot Sample Preparation
Western blotting remains a pivotal technique in the molecular biosciences for the detection, quantification, and analysis of proteins. Its utility spans numerous fields, including immunology, developmental biology, and disease diagnostics. A critical determinant of success in Western blotting is the quality of sample preparation. This guide delves into the nuances of preparing samples for Western blot analysis, ensuring that researchers can achieve reproducible and meaningful results. Key Points to be Discussed Introduction to Western Blotting Sample Collection and Storage Protein Quantification Sample Buffer Preparation and Use Sample Denaturation and Loading Troubleshooting C
…
6th Feb 2024
Deciphering B Cell Cancers With a Rituximab Biosimilar
The fight against B cell cancers, a challenging spectrum of hematologic malignancies, has entered a new era with the introduction of rituximab biosimilars. These biosimilars promise to extend the revolutionary benefits of rituximab, a cornerstone in the treatment of diseases like non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), to a broader patient population. This detailed exploration covers the complex nature of B cell cancers, the therapeutic mechanism of rituximab, and the significant potential of its biosimilars. Introduction B cell cancers represent a diverse group of malignancies that require nuanced therapeutic approaches. The advent of biosimilar thera
…
5th Feb 2024
Toll-Like Receptor Signaling Pathways: A Key to Innate Immunity
In the intricate landscape of the immune system, toll-like receptors (TLRs) play a fundamental role in the first line of defense against pathogens. These receptors, essential components of the innate immune response, are adept at recognizing specific microbial patterns, initiating signaling pathways that lead to the activation of immune responses. This article delves into the toll-like receptor signaling pathways, underscoring their importance in immunology and potential therapeutic applications. Understanding Toll-Like Receptors Toll-like receptors are a class of proteins that play a critical role in the immune system by detecting microbial infections and activating the immune r
…
5th Feb 2024
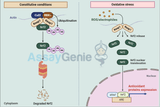
Blood Coagulation Signaling Pathways: A Critical Overview
Blood coagulation is a fundamental physiological process that prevents excessive bleeding when the vascular system is injured. It involves a complex cascade of events that lead to the formation of a stable fibrin clot. This process is tightly regulated by various signaling pathways to ensure that coagulation occurs promptly and appropriately in response to vascular injury, without leading to thrombosis or bleeding disorders. This article delves into the critical signaling pathways involved in blood coagulation, highlighting their roles, mechanisms, and the potential for therapeutic intervention. The Coagulation Cascade: An Overview The coagulation cascade is traditionally divided
…
5th Feb 2024