Blog
IL-9 Signaling and Its Impact on Immune Cell Regulation
Interleukin-9 (IL-9) plays a critical role in the immune system, influencing a variety of biological functions across different immune cell types. This article provides an in-depth look at the signaling mechanisms of IL-9 and its widespread effects on immune regulation, specifically focusing on its impact on T cells, mast cells, basophils, B cells, and regulatory T cells (Tregs). IL-9 Signaling Pathway Overview of IL-9 Receptor Activation IL-9 interacts with the IL-9 receptor (IL-9R), composed of the IL-9Rα chain and the common gamma chain (γc), initiating the JAK-STAT signaling cascade. This activation promotes the transcription of genes that regulate cell proliferation, d
…
1st Feb 2024
p38 MAPK Signaling Review
The p38 MAPK signaling pathway is an intracellular signaling pathway that plays a crucial role in cellular responses to various stressors and inflammatory stimuli. It is a part of the larger MAPK superfamily, which also includes ERK and JNK pathways. The p38 MAPK pathway is involved in regulating a wide range of cellular processes, including cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, inflammation, and immune responses. Key Takeaways: p38 MAPK, part of the MAPK family, is key in cellular responses to stress and inflammation. This pathway regulates cell processes like proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and immune responses. The MAPK family includes ERKs, JNKs, and p38
…
1st Feb 2024
The Intricacies of IL-21 Signaling: Impact on Diverse Immune Cell Types
Interleukin-21 (IL-21) stands out as a pivotal cytokine in the complex network of immune system communication. Its role in regulating various immune cell types has drawn considerable attention from researchers seeking to unravel the intricate web of signaling pathways and biological effects it elicits. In this article, we will delve into the nuanced world of IL-21 signaling and explore its profound impacts on different immune cell populations. IL-21: An Overview IL-21 belongs to the family of cytokines, which are small proteins crucial for intercellular communication. Produced mainly by activated CD4+ T cells, particularly T follicular helper (Tfh) cells and Th17 cells, IL-
…
31st Jan 2024
Understanding the Autophagy Pathway: A Critical Process in Cellular Maintenance
Autophagy, a fundamental cellular process, is crucial for maintaining cellular homeostasis and responding to various stressors. This self-eating mechanism involves the degradation and recycling of cellular components, playing a pivotal role in numerous physiological and pathological contexts. What is Autophagy? Autophagy, derived from the Greek words 'auto' (self) and 'phagy' (eating), is a process where cells degrade and recycle their own components. This process is essential for removing damaged organelles, misfolded proteins, and pathogens, and for providing nutrients during starvation. Types of Autophagy: There are three main types of autophagy: Macroautophagy: The m
…
31st Jan 2024
Nod-Like Receptor Signaling Pathway: A Keystone in Innate Immunity
The innate immune system, a primary line of defense against pathogens, comprises various cellular and molecular mechanisms. Among these, the Nod-like Receptor (NLR) signaling pathways play a critical role. They are central to the immune response, acting as intracellular sensors of pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and danger-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs). This article delves into the basic components of NLR signaling pathways, their key steps, roles in development, and implications in disease. Basic Components of Nod-Like Receptor Signaling Pathways: Nod-like receptors (NLRs) belong to the pattern recognition receptor (PRR) family and are primarily located in
…
30th Jan 2024
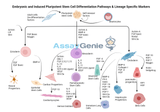
Embryonic Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Differentiation: Pathways and Lineage-Specific Markers
Embryonic induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) hold immense potential in the field of regenerative medicine due to their ability to differentiate into various cell types. Understanding the differentiation pathways and identifying lineage-specific markers are crucial for advancing stem cell research and therapy. Overview of Embryonic iPSC Differentiation: Embryonic iPSCs are characterized by their pluripotency, the ability to differentiate into any cell type of the three primary germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm. This pluripotency is maintained through specific transcription factors such as Oct4, Sox2, and Nanog. The differentiation process involves a complex interpl
…
29th Jan 2024
Decoding the Language of Cells: Chemokine Signaling Pathways Unveiled
Chemokines are small signaling proteins that play a crucial role in the immune system by directing the movement of cells, orchestrating immune responses, and maintaining tissue homeostasis. The intricate network of chemokine signaling pathways governs the trafficking and positioning of immune cells throughout the body, contributing to various physiological and pathological processes. This article aims to delve into the complexity of chemokine signaling pathways, shedding light on their diverse functions and significance in cellular communication. Chemokines and Their Receptors: Chemokines belong to a family of chemotactic cytokines that guide the migration of immune cells b
…
28th Jan 2024
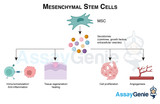
Mesenchymal Stem Cell Differentiation Pathways: Unraveling Lineage-Specific Markers
The intricate process of mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) differentiation is a cornerstone of developmental biology and regenerative medicine. Mesenchymal stem cells, renowned for their self-renewal capacity and multipotency, can differentiate into various cell types, contributing significantly to tissue repair and homeostasis. This article delves into the differentiation pathways of MSCs, focusing on lineage-specific markers that are pivotal in identifying and understanding these pathways. Understanding Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Mesenchymal stem cells are characterized by their ability to differentiate into osteoblasts, chondrocytes, adipocytes, and other cell types. Found in numerous
…
27th Jan 2024
Neural Stem Cell Differentiation: Pathways and Lineage-Specific Markers
Understanding the differentiation pathways of neural stem cells (NSCs) and the identification of lineage-specific markers is a cornerstone in the field of neurobiology and regenerative medicine. This knowledge is pivotal in unraveling the complexities of brain development and for advancing therapeutic strategies for neurological disorders. Introduction to Neural Stem Cell Differentiation Neural stem cells are unique in their ability to self-renew and differentiate into various neural lineages. This process is tightly regulated through intricate signaling pathways and the expression of specific lineage markers. NSC differentiation involves a stepwise progression into multipotent p
…
26th Jan 2024
Cortisol and the Immune Response
What is Cortisol? Cortisol is a steroid hormone, classified as a member of the glucocorticoid family of hormones. Cortisol is involved in a plethora of physiological processes in order to maintain homeostatic conditions in the body (McEwan et al, 2007). Cortisol is produced by the adrenal gland in response to stress and reduced levels of blood-sugar (Kamba et al, 2016); however, importantly cortisol is also released in a circadian fashion under homeostatic conditions (Krieger et al, 1971). Key Takeaways Cortisol, a glucocorticoid hormone, is crucial for stress response, immune regulation, and maintaining homeostasis. It modulates inflammation through specific
…
26th Jan 2024
B Cell Types, Antigen Recognition & Activation
B Cell Types, Antigen Recognition & Activation A comprehensive guide to B cells! Introduction B cells, a vital component of the immune system, play a pivotal role in defending the body against pathogens and infected cells. This article provides an overview of B cells, their functions, and development. Key Takeaways B cells are white blood cells that produce antibodies and are crucial for the adaptive immune system. They recognize antigens on pathogens and infected cells, leading to their activation. B cells can differentiate into plasma cells for immediate antibody production and memory cells for long-term
…
25th Jan 2024
IL-10 signalling and regulation
Explore the complexities of Interleukin-10 (IL-10) signaling and regulation, a crucial aspect in immune response modulation and its dual roles in cancer development and therapy. Key Takeaways: Interleukin-10 (IL-10) is an anti-inflammatory cytokine expressed in many immune cells. IL-10 signals via the JAK/STAT pathway, modulating inflammation and immune responses. It plays a dual role in cancer, both inhibiting and promoting tumor development. IL-10's effects on TILs, MHC-II downregulation, and STAT3 phosphorylation are key in cancer immunity. Therapeutic strategies targeting IL-10 or its receptor show promise but require careful consideration due to potential side effects.
…
24th Jan 2024
Rapid COVID Antibody Test | Antibody Tests
What does the COVID-19 Rapid POC CE-IVD Test detect? The test detects the presence of patient-generated antibodies against spike protein, the virus which causes the disease COVID-19. The test can detect two types of antibody isotypes: IgG and IgM. IgM antibodies are the first antibodies to appear in response to a novel antigen. They imply a more recently initiated infection. IgG antibodies have a higher affinity for the target antigen, meaning they are more specifically able to bind the substance which caused the immune response. IgG antibodies are generated later in the course of infection. IgM and IgG antibodies can both be present in a sample. This implies that the conversion fr
…
24th Jan 2024
Cell Death Pathways: Intrinsic vs Extrinsic Apoptosis Guide
At Assay Genie we have created a comprehensive guide outlining everything you need to know about apoptosis! Key Takeaways: Apoptosis is a programmed cell death process, vital for tissue maintenance and disease prevention. Distinct from necrosis, apoptosis involves cellular shrinkage, nuclear breakdown, membrane disruption, and fragmentation into apoptotic bodies. p53 pathway, intrinsic and extrinsic pathways, and caspase cascades are key mechanisms in apoptosis. Apoptosis vs. Necrosis: Apoptosis is controlled and natural, while necrosis is uncontrolled and harmful. p53 Pathway: Activated by DNA damage, involves proteins like Bax, Bak, Bad. Intrinsic Apoptosis: Triggered intern
…
24th Jan 2024
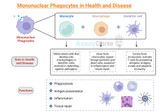
Mononuclear Phagocytes in Health and Disease
Mononuclear phagocytes, essential in immunity and homeostasis, perform diverse roles from phagocytosis to tissue repair, influencing health and disease. Key Takeaways: Mononuclear phagocytes, including monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells, are pivotal in both immune defense and physiological homeostasis. Functions range from phagocytosis and antigen presentation to inflammation and tissue repair. Their roles and behaviors vary in health and disease, with implications for therapeutic targeting. What are phagocytes? Have you ever squeezed a spot and wondered what the white pus is? Or have you ever questioned the science behind tattoos? Breaking out in spots i
…
24th Jan 2024
Serum vs. Plasma: A Deep Dive into Their Molecular Makeup and Implications for ELISA
Blood plasma and serum are essential components of blood and have distinct molecular compositions and uses in the medical and research fields. This article aims to elucidate the differences between serum and plasma and respond to the most frequently asked questions. Key Takeaways: Serum is blood fluid without clotting factors; plasma contains these factors. They're crucial in medical research, including ELISA, to measure various analytes. Different collection methods are used for serum and plasma. What is Serum vs Plasma? Blood consists of red and white cells, platelets, and a liquid portion, known as plasma. When blood is collected and coagulates, the solid components,
…
24th Jan 2024
43 Science Instagrams You Need To Follow: The Instagram Influencer-Ome
Social media has become a powerful tool for science communication, and Instagram is no exception. The platform is home to a diverse array of science influencers, ranging from PhD students to established researchers and science communicators. From immunology to ecology, genetics to neurology, there's an Instagram account out there for every science enthusiast. In this article, we've curated a list of 43 science Instagram accounts that you need to follow to stay informed and inspired. Key Takeaways: Discover groundbreaking insights from 43 science influencers on Instagram. Delve into diverse research areas, including neuroscience, ecology, and biochemistry. Gain educational con
…
24th Jan 2024
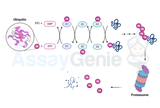
Ubiquitin and Its Role in Cellular Regulation: A Comprehensive Overview of Modifiers and Pathways
Ubiquitin is a small, highly conserved protein found in eukaryotic cells that plays a crucial role in regulating various cellular processes. The process of ubiquitination involves the covalent attachment of ubiquitin molecules to target proteins, marking them for degradation, localization, or signaling. This post-translational modification is a dynamic and tightly regulated process that influences numerous cellular pathways. In this article, we will explore the structure and function of ubiquitin, its related modifiers, and the intricate pathways involved in ubiquitin-mediated cellular regulation. Structure and Function of Ubiquitin: Ubiquitin, a 76-amino acid protein, i
…
23rd Jan 2024
Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Navigating the Frontiers of Regenerative Medicine
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have emerged as pivotal players in the realm of regenerative medicine due to their unique properties and versatile potential. Originally discovered in the bone marrow, MSCs are now known to reside in various tissues, including adipose tissue, umbilical cord, and dental pulp. This article delves into the characteristics, therapeutic applications, and challenges surrounding mesenchymal stem cells, shedding light on their promising role in advancing medical treatments. Characteristics of Mesenchymal Stem Cells: MSCs are multipotent progenitor cells capable of differentiating into various cell types, including osteoblasts, adipocytes, and chondrocytes. T
…
23rd Jan 2024
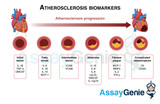
Biomarkers & Inflammatory markers of atherosclerosis
As atherosclerosis is a complex inflammatory disease, there are many influential biomarkers that contribute to the disease’s progression as well as biomarkers from atherosclerosis related diseases such as periodontal disease and autoimmune diseases i.e. Diabetes, RA, SLE. Biomarkers can be proteins, DNA and mRNA which are measured to asses biological, pathological processes and pharmacological responses. Biomarkers can be classified as early, predictive and prognostic biomarkers depending on disease stage (Huang et al., 2010). Identifying biomarkers for disease and finding therapeutic targets is crucial to research and treatment and overall a populations mortality and morbidity rat
…
23rd Jan 2024
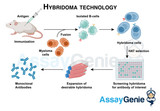
Hybridoma Technology: Revolutionizing Antibody Production
Hybridoma technology, a revolutionary method in immunology pioneered by Georges Köhler and César Milstein in the 1970s, has transformed the landscape of antibody production. This groundbreaking technique has had a profound impact on various scientific domains, from diagnostics to therapeutics and basic research. In this essay, we explore the intricacies of hybridoma technology, its diverse applications, and its pivotal role in advancing our understanding and treatment of diseases. The Birth of Hybridoma Technology: The genesis of hybridoma technology lies in the fusion of two distinct cell types: B cells, responsible for antibody production, and myeloma cells, which possess the a
…
23rd Jan 2024
Articular Cartilage Extracellular Matrix
Articular cartilage, a key player in joint function, owes its unique properties to its extracellular matrix (ECM). This complex, highly specialized structure is not only fundamental in maintaining joint integrity but also in ensuring smooth and efficient movement. The ECM of articular cartilage is a masterful creation of nature, intricately designed to withstand compressive forces while providing a lubricated surface for articulation. Understanding the Composition of ECM in Articular Cartilage Proteoglycans: The Hydration Masters: The ECM of articular cartilage is rich in proteoglycans, primarily aggrecan. These macromolecules play a crucial role in retaining water, giving
…
23rd Jan 2024
CD25 Marker
CD25, a key molecule in immune regulation, is integral to the function of activated lymphocytes and regulatory T cells. It's central in mediating immune responses, with implications in autoimmune diseases and cancer. Key Takeaways: CD25, part of the IL-2 receptor, is crucial in immune response regulation. Found on T cells, NK cells, Tregs, and others; upregulated during immune activation. Vital for cellular immune responses and maintaining immune homeostasis. Serves as a biomarker in autoimmune diseases, allergies, and certain cancers. Targeted in immunotherapy for diseases like multiple sclerosis and various cancers. What is CD25? CD25, also known as Cluster o
…
22nd Jan 2024
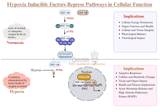
HIF Repress Pathways: An Insight into Cellular Oxygen Homeostasis
Hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs) are pivotal in the cellular response to oxygen deprivation. These transcription factors regulate various aspects of cellular and systemic homeostasis in response to hypoxia. Central to their role is the activation of genes that aid in adaptation to low oxygen conditions. However, equally important, yet less emphasized, is their ability to repress certain pathways. This article delves into the mechanisms and implications of HIF-mediated repression pathways in cells. Mechanisms of HIF-Mediated Repression Transcriptional Repression Through HIF: HIFs function primarily as transcriptional activators. However, they can indirectly repress gene expr
…
22nd Jan 2024