Blog
Immunophenotyping: A Comprehensive Analysis of Cellular Immune Profiles
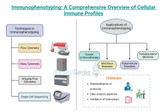
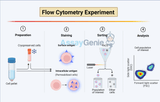
Immunophenotyping, a cornerstone of modern immunology, involves identifying and characterizing cell populations based on their surface markers. This technique provides insights into the heterogeneity and functionality of immune cells, enabling researchers and clinicians to elucidate immune responses in health and disease. Immunophenotyping has evolved significantly over the years, from early flow cytometry approaches to multiparameter analyses using advanced technologies such as mass cytometry and single-cell sequencing. Techniques in Immunophenotyping: 1. Flow Cytometry: Flow cytometry remains the gold standard technique in immunophenotyping, allowing for the simultaneous
…
20th Mar 2024
How to Thaw Cells: Best Practices for Cell Culture Success
Cell culture techniques are fundamental to biomedical research, providing crucial insights into cellular functions, drug discovery, and disease mechanisms. A critical step in cell culture is the process of cell thawing, which, if not performed correctly, can adversely affect cell viability and experimental outcomes. This comprehensive guide outlines the best practices for thawing cells to ensure cell culture success. Understanding the Basics of Cell Thawing Cell thawing is the process of warming cryopreserved cells to reinitiate their metabolic activities. Cryopreservation is a method used to store cells at extremely low temperatures to halt their metabolism and preserve their ge
…
19th Mar 2024
How to Choose a Secondary Antibody
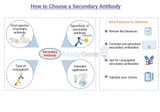
The selection of a secondary antibody is a critical step in the experimental design of various immunodetection methods, including Western Blot, ELISA, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF). Secondary antibodies serve as crucial tools for the amplification of signal detection, enabling researchers to observe specific antigens with high sensitivity and specificity. This article provides a comprehensive guide on how to choose the right secondary antibody for your research, ensuring the success of your immunodetection assays. Understanding Secondary Antibodies Secondary antibodies are antibodies that bind to the primary antibodies, which are directly bound to the ta
…
19th Mar 2024
Agarose vs Polyacrylamide: A Comparative Analysis
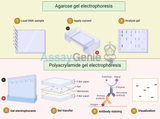
In the realm of molecular biology and biochemistry, gel electrophoresis stands as a cornerstone technique for the separation and analysis of macromolecules such as DNA, RNA, and proteins. Central to this method are the matrices used to form the gels: agarose and polyacrylamide. Each has unique properties and applications, making them indispensable tools for researchers. This article delves into the differences between agarose and polyacrylamide gels, exploring their composition, mechanism of action, and specific uses in laboratory settings. Understanding Gel Electrophoresis Before comparing agarose and polyacrylamide, it is essential to grasp the principle of gel electrophoresis.
…
19th Mar 2024
The Strategic Role of Secondary Antibody Incubation Times in Immunodetection Techniques
Secondary antibodies are pivotal in the detection of target antigens in various immunodetection assays such as Western blotting, ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay), and immunohistochemistry (IHC). The choice of secondary antibody incubation time is crucial for achieving optimal signal-to-noise ratios, thereby enhancing the specificity and sensitivity of the assay. This article delves into the principles guiding secondary antibody incubation times, factors influencing these times, and practical tips for optimizing assay outcomes. Introduction In immunodetection assays, secondary antibodies are employed to bind to primary antibodies, which directly recognize the target antig
…
19th Mar 2024
Understanding Antibody Staining for Antigen Detection in Flow Cytometry
Flow cytometry stands as a pivotal technique in the realms of molecular biology and immunology, enabling the analysis of physical and chemical characteristics of cells or particles as they flow in a fluid stream through a beam of light. The core of its application lies in the ability to identify and quantify specific antigens present on the surface or inside cells. This detailed exploration aims to dissect the intricacies of antibody staining—a cornerstone method for antigen detection in flow cytometry, elucidating its principles, methodologies, applications, and the challenges it presents. Introduction to Antibody Staining Antibody staining in flow cytometry is a method that emp
…
19th Mar 2024
Sodium and Potassium Indicators and Ionophores: A Comprehensive Insight
Understanding the dynamics of sodium and potassium ions within biological systems is crucial for deciphering cellular processes and developing therapeutic strategies. Sodium and potassium indicators, alongside ionophores, serve as essential tools in the study of these ions' roles within cells. This article delves into the mechanisms, applications, and recent advancements in sodium and potassium indicators and ionophores, providing a thorough understanding of their significance in biological research. Introduction to Sodium and Potassium in Biological Systems Sodium (Na⁺) and potassium (K⁺) are pivotal for numerous cellular functions, including the generation of action potentials,
…
18th Mar 2024
Labeling Non-Antibody Proteins and Small Molecules: An Advanced Guide
In the evolving landscape of biochemical research and diagnostic assay development, the ability to label non-antibody proteins and small molecules with high precision has become indispensable. This advanced guide delves into the methodologies, challenges, and applications of labeling these crucial biomolecules, providing insights for researchers and developers aiming to enhance the specificity and sensitivity of their assays. Understanding the Basics of Biomolecule Labeling Biomolecule labeling encompasses a set of techniques used to attach detectable tags or labels to proteins, peptides, and small molecules. These tags can be fluorescent dyes, biotin, radioactive isotopes, or en
…
18th Mar 2024
The Importance of Immunohistochemistry Training in Modern Scientific Research
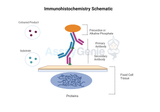
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) stands as a critical tool in the realm of biomedical research and diagnostic practices, offering a bridge between molecular insights and the intricate visualization of tissues. This technique, leveraging the specificity of antibodies to bind to antigens in biological tissues, unveils not only the presence but also the localization of proteins within cells and tissues. The evolution of IHC from a rudimentary staining procedure to a pivotal methodology in scientific investigations underscores the necessity for comprehensive training programs. Such programs equip researchers and diagnosticians with the knowledge and skills to implement IHC effectively, thereby adv
…
17th Mar 2024
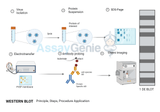
Western Blot Training: A Comprehensive Guide
Western blotting, a cornerstone technique in molecular biology, biochemistry, and immunogenetics, is pivotal for detecting specific proteins in a sample. Its applications span various scientific fields, including research and diagnostic processes. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of western blot training, encompassing its principles, procedural steps, and troubleshooting strategies, aiming to equip practitioners with a thorough understanding of this essential technique. Understanding Western Blotting: Western blotting is a highly specific and sensitive technique used to detect and quantify the presence of specific proteins in a complex mixture. The method invo
…
17th Mar 2024
Data Analysis in Flow Cytometry: Harnessing Complexity for Scientific Insight
Flow cytometry is a powerful analytical technology employed in cell biology, immunology, and oncology research. It enables the rapid measurement of physical and chemical characteristics of cells or particles as they pass through a laser beam. The core of this technology's utility lies in its ability to analyze thousands of particles per second, providing a wealth of data on cell populations. This article delves into the intricacies of data analysis in flow cytometry, focusing on its principles, methodologies, and applications, and highlighting the critical role of advanced data analysis software and algorithms in extracting meaningful insights from complex datasets. Principles of Flo
…
16th Mar 2024
Histamine Receptors: Gatekeepers of Immunological and Neurological Responses
Histamine, a biogenic amine, plays a crucial role in various physiological processes, including immune responses, gastric acid secretion, and neurotransmission. Central to the action of histamine are histamine receptors, which are distributed broadly across different tissues and cell types. This article delves into the nature, types, and functions of histamine receptors, highlighting their significance in immunological and neurological processes. Understanding Histamine Receptors: Histamine exerts its effects by binding to specific receptors on the surfaces of target cells. These receptors are part of the G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) family, characterized by their seven tran
…
15th Mar 2024
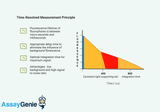
Time-Resolved Fluorescence (TRF): A Comprehensive Introduction
Time-Resolved Fluorescence (TRF) technology is a cutting-edge analytical technique that has revolutionized the fields of biochemistry, immunology, and molecular biology. By offering a refined approach to measuring fluorescent signals, TRF circumvents many of the limitations associated with traditional fluorescence measurements, providing researchers with a tool of unparalleled sensitivity and specificity. Understanding Time-Resolved Fluorescence TRF is based on the principle of delayed fluorescence detection. Unlike conventional fluorescence methods that measure signals immediately after excitation, TRF allows a short delay before measuring the fluorescence. This delay is crucial
…
14th Mar 2024
Understanding Blotchy Western Blots: Causes and Remedies
Western blotting is a powerful and widely used technique in molecular biology, essential for detecting and quantifying specific proteins in complex biological samples. However, despite its popularity, Western blotting can sometimes yield frustrating results, with one of the most common issues being blotchy or uneven bands. Blotchy Western blots can arise from various factors, ranging from sample preparation to technical errors during the blotting process. In this article, we'll delve into the potential causes of blotchy Western blots and provide some tips to rectify them. What are Blotchy Western Blots? Blotchy Western blots refer to the uneven distribution of bands across
…
13th Mar 2024
Advantages of Small Molecule Inhibitors in Therapeutic Interventions
Small molecule inhibitors represent a significant advancement in the field of therapeutic interventions, offering a versatile approach to treating a myriad of diseases, including cancer, viral infections, and chronic inflammatory conditions. These compounds, typically with a molecular weight of less than 900 daltons, can modulate biological processes by interacting with specific protein targets within the cell. This article explores the multifaceted advantages of small molecule inhibitors, highlighting their role in the development of targeted therapies. Target Specificity and Selectivity: One of the paramount advantages of small molecule inhibitors is their ability to selectivel
…
13th Mar 2024
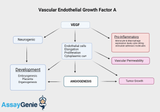
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A (VEGFA): A Cornerstone in Angiogenesis and Beyond
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A (VEGFA) is a pivotal signaling protein involved in both vasculogenesis and angiogenesis, processes essential for the formation of blood vessels during embryonic development and the growth of new blood vessels from pre-existing ones. As a member of the VEGF family, VEGFA plays a critical role in the regulation of endothelial cell function, affecting vascular permeability and endothelial cell proliferation. The Molecular Biology of VEGFA VEGFA is characterized by its gene located on chromosome 6p21.1, encoding a heparin-binding protein that promotes endothelial cell growth, migration, and survival. The VEGFA protein undergoes complex post-transl
…
9th Mar 2024
Exploring the Frontier of Immunotherapy: T Cell Expansion
In the realm of immunotherapy, T cell expansion has emerged as a pivotal strategy, holding promise in the treatment of various diseases, particularly cancer. T cells are a critical component of the adaptive immune system, orchestrating immune responses against pathogens and malignant cells. Harnessing the potential of T cells through expansion techniques offers a novel avenue for enhancing their therapeutic efficacy. This article delves into the mechanisms, applications, and advancements in T cell expansion, illuminating its transformative impact on medical science. Understanding T Cell Expansion T cells, a type of lymphocyte, play a central role in adaptive immunity by rec
…
8th Mar 2024
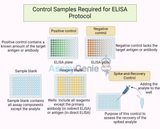
Control Samples Required for ELISA Protocol
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) is a powerful analytical biochemistry assay that utilizes antibodies and color change to identify a substance. It is widely used in the field of immunology to detect the presence of antibodies or antigens in a sample. The accuracy and reliability of ELISA depend significantly on the use of appropriate control samples throughout the protocol. This article delves into the essential control samples required for ELISA to ensure the validity and reproducibility of the assay's results. Positive and Negative Controls Positive ControlA positive control is an integral component of the ELISA protocol, serving as a benchmark to confirm that the ass
…
2nd Mar 2024
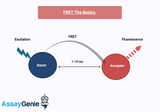
Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) Assays: An Insight into Molecular Interactions
Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) assays represent a pivotal technique in the molecular and cellular biology fields, enabling the examination of protein interactions, nucleic acid structures, and membrane dynamics. This non-invasive method relies on the energy transfer between two light-sensitive molecules, providing insights into molecular distances and interactions with high sensitivity. Understanding FRET: The Basics FRET is a distance-dependent interaction between the electronic excited states of two dye molecules, a donor and an acceptor. When these molecules are within 1-10 nm of each other, energy transfer can occur, leading to fluorescence emission from the ac
…
1st Mar 2024
Unveiling the Potential of Cy3 Wavelength: Illuminating the Path to Advanced Biomedical Imaging
In the realm of biomedical imaging, the quest for precision and clarity drives researchers to explore innovative technologies. One such breakthrough is the Cy3 wavelength, a powerful tool revolutionizing fluorescence imaging techniques. This article delves into the significance, applications, and advancements of Cy3 wavelength in biomedical research. Understanding Cy3 Wavelength:: Cy3, short for Cyanine 3, is a fluorescent dye belonging to the cyanine dye family. Its exceptional properties make it a popular choice for labeling biomolecules and tracking biological processes under a microscope. Cy3 emits light in the red-orange spectrum, typically around 570 to 590 nanometer
…
23rd Feb 2024
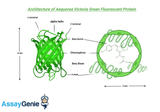
Choosing a Fluorescent Protein: A Comprehensive Guide
Fluorescent proteins (FPs) have revolutionized the field of molecular and cellular biology, allowing scientists to visualize and track biological processes in live cells with unprecedented clarity and specificity. Originating from the green fluorescent protein (GFP) discovered in the jellyfish Aequorea victoria, the palette of available FPs has expanded to include a rainbow of colors. This article provides a detailed overview of factors to consider when choosing a fluorescent protein for your research, ensuring optimal results for your specific applications. Understanding Fluorescent Proteins The Basics of FluorescenceFluorescence occurs when a substance absorbs light at one wav
…
17th Feb 2024
Understanding Glutamate Receptors: Classification, Function, and Implications in Neurological Disorders
Glutamate receptors are pivotal in mediating excitatory neurotransmission in the central nervous system (CNS), playing crucial roles in synaptic transmission, plasticity, learning, and memory. These receptors are classified into two main categories: ionotropic glutamate receptors (iGluRs) and metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs), each with distinct subtypes, signaling mechanisms, and functional roles. This article delves into the classification of glutamate receptors, their functional roles within the CNS, the intricate signaling pathways they mediate, mechanisms regulating their activity, and their involvement in various neurological disorders. Types of Glutamate Receptors
…
16th Feb 2024
Targeting Immune Checkpoints as Cancer Therapy
In recent years, the field of oncology has witnessed a paradigm shift with the advent of immunotherapy, a treatment modality that harnesses the body's immune system to combat cancer. Among the most promising approaches in immunotherapy is the targeting of immune checkpoints. These molecular pathways are crucial for maintaining self-tolerance and modulating the immune response to prevent autoimmunity. However, cancer cells cleverly exploit these pathways to evade immune detection and destruction. This article delves into the mechanisms of immune checkpoint pathways, their role in cancer evasion, and the therapeutic strategies designed to inhibit these checkpoints, thereby reactivating the
…
16th Feb 2024
Navigating the Intricacies of Intracellular Flow Cytometry: Key Considerations
In the evolving landscape of cellular biology, intracellular flow cytometry (ICFC) stands out as a powerful technique for analyzing the complexities within cells. This advanced method extends the capabilities of traditional flow cytometry by allowing researchers to investigate intracellular proteins, signaling pathways, and specific gene expressions within individual cells. ICFC has become indispensable in various fields, including immunology, oncology, and drug discovery, offering insights that are pivotal for understanding disease mechanisms and developing therapeutic strategies. However, harnessing the full potential of ICFC requires meticulous attention to several critical considerat
…
16th Feb 2024