Blog
Pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH)
Pyruvate dehydrogenase is a complex enzyme involved in the conversion of pyruvate, a product of glycolysis, into acetyl-CoA, a crucial molecule in energy production and intermediary metabolism.
Table of Contents
Jump to a section:
- PDH Structure & Function
- PDH Regulation
- PDH & Cancer
- PDH Related Kits
- PDH & PDC
.nav__list {
list-style: none;
}
.nav__list a{
font-family: Poppins;
font-size: 18px;
color: #29aae1;
}
.nav__list li{
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
.nav__list a:hover{
color:#0e2f51;
}
{
"@context": "http
…
7th Jul 2023
Plasma Membrane Markers
What is a Plasma Membrane?
The plasma membrane, also known as the cell membrane, is a vital component of all cells. It is a thin, semi-permeable barrier that separates the cell's internal environment from the external surroundings. This crucial structure plays a fundamental role in maintaining the integrity and functionality of the cell.
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "BlogPosting",
"mainEntityOfPage": {
"@type": "WebPage",
"@id": "https://www.assaygenie.com/plasma-membrane-markers"
},
"headline": "Plasma Membrane Markers",
"description": "Explore the role of plasma membrane markers in cell biology and disease
…
7th Jul 2023
Research Universities in Ireland
Since I am from Ireland I thought I would give as comprehensive view as possible for Research Universities in Ireland. By now you are probably considering looking for a PhD or PostDoc position in Ireland which is a great start. Known as the Land of the scholars,there are 10 international standard Research Universities in Ireland and colleges that focus on a range of life science, chemistry, physics and engineering research.
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "BlogPosting",
"mainEntityOfPage": {
"@type": "WebPage",
"@id": "https://www.assaygenie.com/blog/research-universities-in-ireland/"
},
"headline": "Research Universities in Ireland",
"image": ""
…
6th Jul 2023
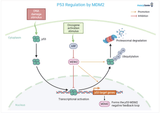
The p53 Protein: Tumor Suppressor Protein
p53, encoded by the TP53 gene on chromosome 17, is a fundamental protein safeguarding against tumor formation. It orchestrates cellular responses to DNA damage and stress, crucially managing cell division. By activating a range of mechanisms like cell cycle regulation, DNA repair, apoptosis, and senescence, p53 maintains cellular integrity and prevents cancerous growths.
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "Article",
"mainEntityOfPage": {
"@type": "WebPage",
"@id": "https://www.assaygenie.com/blog/p53-protein-mutations-cancer-cell-signalling"
},
"headline": "The p53 Protein: Tumor Suppressor Protein",
"description": "This article contains an overview of th
…
5th Jul 2023
Alternative Complement Pathway: Activation, Regulation, and Significance
As a vital component of the immune system, the Alternative Complement Pathway plays a crucial role in defending the body against pathogens and maintaining immune homeostasis. In this blog, we will explore the underlying mechanisms of its activation, examine the key components involved, and shed light on its intricate biological functions. Key Takeaways: The Alternative Complement Pathway is crucial for immune defense, activating spontaneously or in response to pathogens. It contributes to inflammation, opsonization, and the clearance of immune complexes. Regulated by proteins like factor H and I to prevent damage to healthy cells. Dysregulation of this pathway is linked
…
5th Jul 2023
Personalized Vaccines in Cancer Treatment: The Future of Immunotherapy
What Are Personalized Cancer Vaccines?
Personalized cancer vaccines are a cutting-edge approach in cancer treatment that are designed to activate a patient's immune system against their specific tumor. Unlike traditional vaccines that target infectious agents, personalized cancer vaccines are tailored to each individual's unique tumor characteristics. These vaccines are customized to exploit the specific genetic mutations and alterations present in the patient's tumor cells.
How Do Personalized Cancer Vaccines Work?
Personalized cancer vaccines work by utilizing neoantigens, which are mutated proteins expressed on the surface o
…
4th Jul 2023
Lactobacilli - Structure, Metabolism, and Testing
Delving into the world of Lactobacilli, this piece explores their structural intricacies, metabolic functions, and the pivotal role they play in human health. These bacteria, key components in probiotic supplements, demonstrate abilities that span from enhancing immunity to optimizing digestive health and mitigating inflammation. Key Takeaways: Lactobacilli are crucial lactic acid bacteria, offering various health benefits, including immune boosting, digestive improvement, and inflammation reduction. They are prevalent in probiotic supplements and possess unique characteristics such as structure, metabolism, and specific health benefits.
{
"@context": "https:
…
2nd Jul 2023
Microtubule and Mitosis review
Introduction Microtubules are key components of the cytoskeleton and are composed of alpha and beta tubulin. These dimerise in a head to tail fashion to form 13 linear protofilaments. The protofilaments associate initially into sheets and subsequently into hollow tubes with a diameter of roughly 25 nm. These hollow tubes radiate from the microtubule-organising centre (MTOC) located at the centrosome in interphase cells. Microtubules are essential in intracellular trafficking of vesicles and mitochondria, cell polarisation and migration. Furthermore, microtubules are involved in the development and maintenance of cell shape. In mitosis, microtubules undergo dynamic instabili
…
29th Jun 2023
Sepsis and Immune Dysregulation
Exploring sepsis: a critical imbalance in the immune response to infection. Key Takeaways: Sepsis is a severe, immune-driven response to infection causing systemic inflammation and potential organ damage. It progresses through stages: initial sepsis, severe sepsis, and septic shock, each with increasing severity. Complications include organ failure, septic shock, ARDS, blood clots, and long-term impairments. Immune responses in sepsis vary from hypo-inflammation (weak) to hyper-inflammation (excessive). Understanding these responses is key for effective sepsis treatment and management. What is Sepsis? Sepsis is a life-threatening condition that arises when the bod
…
29th Jun 2023
Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)
What is Hepatocyte Growth Factor? Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) is a cytokine that is mainly produced by the liver. HGF is a pleiotrophic cytokine that regulates cell growth, motility, and morphogenesis. The majority of HGF is produced by the liver, but it is also expressed in other organs, such as the kidney, pancreas, and intestine. HGF binds to its cognate receptor, c-Met, which is present on the surface of many types of cells. However, it has no measurable protease activity. Binding of HGF to c-Met leads to activation of multiple signaling pathways that promote cell proliferation, survival, migration, and differentiation. Key Takeaways Hepatocyte Growth Factor
…
29th Jun 2023
Biomarkers in sepsis: Their Role in Early Detection and Management
Sepsis, a life-threatening condition, is characterized by a dysregulated immune response to an infection, leading to systemic inflammation and organ dysfunction. Biomarkers, as measurable indicators of biological processes, hold immense potential in the field of sepsis diagnosis, prognosis, and management. In this article, we explore the critical role that biomarkers play in sepsis, particularly their significance in early detection and diagnosis. We delve into the latest research and advancements in biomarker identification, their association with the immune response duri
…
28th Jun 2023
The Essential Guide to DNA: Components, Purpose and Purification Methods
Exploring DNA's essence, this guide illuminates its structure, function, and purification techniques, essential in fields like medicine and biotechnology. Key Takeaways: DNA's Structure: Composed of nucleotides adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine, forming a double helix. Charge Properties: DNA exhibits a negative charge due to phosphate groups. Central Dogma: DNA's role in protein synthesis and inheritance. Extraction Methods: Techniques for isolating DNA. Purification Techniques: Ensuring DNA's integrity for analysis. Genomic DNA: The complete genetic information in cells. DNA Assays: Tools for DNA analysis and research applications.
{
"@context": "https://schema.
…
28th Jun 2023
GPCRs (G Protein Coupled Receptors): A Guide
What Are GPCRs?
GPCRs, or G protein-coupled receptors, are a large family of membrane proteins that play a crucial role in cell signaling. They are involved in transmitting signals from the extracellular environment to the inside of cells, thereby regulating various physiological processes.
GPCRs are classified into different classes based on their structural and functional characteristics. Some of the major classes include Rhodopsin-like (Class A), Secretin-like (Class B), Metabotropic glutamate/pheromone (Class C), Fungal mating pheromone receptors (Class D), cAMP receptors (Class E) and Frizzled/Smoothened (Class F) receptors. These classes exhibit disti
…
28th Jun 2023
Transformation Protocol – Sample Transformation Protocols
Introduction Transformation of bacteria with plasmids is not only of note for bacterial studies but also can be used for gene expression studies in mammalian cells. Most plasmids are of bacterial origin and contain both a bacterial origin of replication and an antibiotic resistance gene which can be used as a selectable marker. The process of transformation allows foreign DNA to be introduced into a cell. Genetic modifications can be made to various bacterial strains to make them more amenable to transformation. Such modifications will maintain the plasmid without rearranging the plasmid DNA. Certain treatments have been shown to increase the transformation efficiency of bacteria.
…
27th Jun 2023
Gut Inflammation and Inflammatory Diseases
What is Gut Inflammation?
The gut, or gastrointestinal (GI) tract is a long tube that starts from the mouth and extends to the anus. It includes various organs such as the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and rectum, responsible for digestion, absorption of nutrients, and elimination of waste. The gut plays a vital role in our overall health. However, inflammation can occur within the gut, leading to various inflammatory diseases. Gut inflammation is an immune response triggered by factors such as infections or autoimmune reactions. This immune response releases molecules that cause inflammation, resulting in tissue damage. Conditions
…
27th Jun 2023
CD Markers Expression on B Cells
Exploring the realm of B cells, this piece delves into the intricacies of these white blood cells, pivotal in humoral immunity. Through the lens of CD markers and immunophenotyping, we unravel the diversity of B cells, their antibody production, and their profound impact on immune responses. Key Takeaways: B cells, vital in adaptive immunity, are characterized by CD markers and immunophenotyping, crucial for understanding their heterogeneity and immune roles. Immunophenotyping, using flow cytometry, identifies B cell subsets through CD markers, essential for studying B cell development, activation, and disease associations. CD markers on B cells vary across differe
…
26th Jun 2023
Hemocytometer Cell Counting Procedure
Understanding the Functionality of a Hemocytometer
Hemocytometers have been around since the beginning of the nineteenth century, when they were designed to accurately count blood cells for medical purposes. The technique revolutionized the field of hematology by providing a standardized and reliable method for quantifying cellular components in biological samples. Hemocytometers employ innovative concepts from various scientific disciplines, combining principles of physics, chemistry, and biology. By utilizing surface tension, cells are evenly distributed across the
…
25th Jun 2023
Astrocyte Markers: A Guide
Explore the world of astrocytes, crucial star-shaped cells in the brain, and understand how specific markers help study their roles in neural health and disorders. Key Takeaways: Astrocytes are star-shaped glial cells vital for brain function and homeostasis. They regulate the brain environment, neurotransmitter levels, and synaptic signaling. Astrocyte markers, like GFAP and S100B, identify and study astrocyte functions. What Are Astrocytes? Astrocytes are a type of star-shaped glial cell found in the central nervous system. They play essential roles in maintaining neuronal health and supporting brain homeostasis. In order to understand the functions and charac
…
25th Jun 2023
Oligodendrocytes: Complete Guide + Functions & Development
Oligodendrocytes are pivotal CNS cells, integral for myelin formation and nerve function, with implications in various neurological disorders. Key Takeaways Oligodendrocytes are specialized glial cells in the central nervous system (CNS), crucial for myelinating axons, enhancing nerve signal transmission, and supporting neuronal function. They differ from Schwann cells, which myelinate in the peripheral nervous system. Oligodendrocytes are implicated in diseases like multiple sclerosis and Alzheimer's, with treatment strategies focusing on immunomodulation, remyelination, neuroprotection, and symptomatic relief. What Are Oligodendrocytes? Oligodendrocytes are a
…
22nd Jun 2023
A Guide To Tau Proteins & Tauopathies
Explore the essential role of Tau proteins in neuronal health and their impact in neurodegenerative diseases, unfolding the complexity behind their functions and dysfunctions. Key Takeaways: Tau proteins, especially microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT), are crucial for neuron structure maintenance. They stabilize microtubules, which are integral for cell functions like division and neurotransmission. In neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's, tau proteins undergo abnormal changes, leading to neurofibrillary tangles. Tau proteins are present in the brain and peripheral tissues, and their gene is located on chromosome 17. Various neurodegenerative disorders, collectivel
…
21st Jun 2023
Understanding Radial Glial Cells: Insights into Neurodevelopmental Processes
Radial glial cells are essential in shaping the nervous system, serving dual roles in neurogenesis and structural support during the brain's developmental stages. Key Takeaways: Radial glial cells are vital in neurogenesis and brain development, acting as both progenitor cells and structural guides. They exhibit unique radial morphology, extending from the ventricular zone to the pial surface. Radial glial cells differentiate into various neuronal and glial types, influencing neural circuit formation. Table of Contents Jump to a section: - Cell Identification - Radial Glial Stem Cells - Glial Cell Development - Functions and Impacts of RGCs - T
…
21st Jun 2023
The PD-1 Pathway and Cancer Immunotherapy
The initial identification of PD-1 as a potential target for cancer treatment occurred in the late 1990s and early 2000s through studies exploring the regulation of T-cell responses. The development and approval of PD-1 inhibitors, such as pembrolizumab and nivolumab, for the treatment of various cancers have since transformed the landscape of cancer immunotherapy. The use of PD-1 pathway inhibitors in cancer treatment has rapidly gained recognition and has become a cornerstone of modern immunotherapeutic approaches.
Table of Contents
Jump to a section:
- PD-1 Pathway in Cancer
- Immune Checkpoints
- Cancer Immunothera
…
20th Jun 2023
Growth Factors: Key Players in Biological Processes
Growth factors play a vital role in the complex web of biological processes, serving as key regulators in various essential events. They exert significant influence over crucial cellular behaviors such as proliferation, differentiation, and survival.
Acting as molecular messengers, growth factors facilitate communication between cells and tissues, ensuring coordinated functionality.
By exploring the defining characteristics and functions of growth factors, we gain a deeper understanding of their profound contributions to embryonic development, tissue repair, and cellular communication. Join us on this exploration as we delve into the world of growth factors and the
…
20th Jun 2023
Microglial Functions: Immune Response + Neuroinflammation
Key Takeaways: Microglia are immune cells in the CNS, originating from myeloid precursor cells. They surveil the CNS, respond to changes, and maintain neural health. Microglia exist in different states: amoeboid, ramified, and reactive. Their activation is crucial in neurodegenerative diseases and brain health. What are Microglia? Microglia are a specialized type of immune cells that reside within the central nervous system (CNS), including the brain and spinal cord. Originating from myeloid precursor cells, microglia colonize the CNS during early development. In their resting state, microglia exhibit a distinctive morphology with small cell bodies and highly branched p
…
18th Jun 2023