Blog
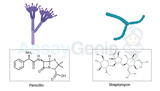
The Battle of Antibiotics: Penicillin vs. Streptomycin
In the realm of medicine, antibiotics are akin to superheroes, combating bacterial infections with unwavering efficacy. Among these, two stalwarts stand out: penicillin and streptomycin. These antibiotics revolutionized the treatment of bacterial infections, saving countless lives since their discovery. However, understanding their differences and applications is crucial for effective medical management. Let's delve into the fascinating world of penicillin versus streptomycin and explore the unique properties of Penicillin-Streptomycin Solution. Penicillin: The Pioneer Discovered accidentally by Alexander Fleming in 1928, penicillin marked the dawn of the antibiotic era. Fl
…
8th Feb 2024
What is the difference between PBS and dPBS?
In the realm of biological and biochemical research, solutions play a pivotal role in various experimental procedures, from cell culture to molecular biology assays. Among the plethora of solutions utilized, phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and Dulbecco’s phosphate-buffered saline (DPBS) stand out as crucial components. While both solutions share similarities, they possess distinct compositions and applications that merit exploration and understanding. Phosphate-Buffered Saline (PBS): A Versatile Solution PBS, a staple in laboratories worldwide, serves as a fundamental isotonic buffer solution utilized across diverse applications. Its composition typically consists of
…
8th Feb 2024
Transduction vs Transfection: Understanding Gene Delivery Techniques
In the realm of molecular biology and genetic engineering, the ability to deliver genetic material into cells is fundamental for various research and therapeutic purposes. Two common methods employed for this purpose are transduction and transfection. While both techniques facilitate the introduction of exogenous genetic material into cells, they differ significantly in their mechanisms and applications. This article aims to elucidate the distinctions between transduction and transfection, highlighting their respective advantages, limitations, and applications. Transduction: Transduction is a process by which genetic material is transferred into a cell via a viral vector.
…
8th Feb 2024
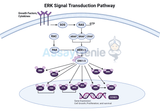
Erk Signal Transduction Explained: Step-by-Step Process & Key Concepts
The ERK signal transduction pathway stands as a fundamental mechanism in cellular biology, orchestrating a wide array of physiological processes, including cell division, differentiation, and survival. This pathway, part of the larger mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) family, is instrumental in conveying signals from the cell surface to the nucleus, thereby influencing gene expression and cellular outcomes in response to external stimuli. Understanding the ERK Pathway: The Extracellular signal-Regulated Kinase (ERK) pathway is initiated by the binding of growth factors, cytokines, and other extracellular ligands to their respective receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) on the ce
…
8th Feb 2024
Apoptosis Caspase Pathways: A Closer Look at Cellular Suicide
Apoptosis, or programmed cell death, is a fundamental process that plays a critical role in the development and maintenance of healthy tissues. Central to this process are caspases, a family of cysteine proteases that, once activated, orchestrate the cell's orderly demise. Understanding the caspase pathways not only sheds light on how our bodies maintain cellular balance but also provides insights into the mechanisms underlying various diseases, including cancer and neurodegenerative disorders. The Initiation of Apoptosis: Intrinsic and Extrinsic Pathways Apoptosis can be triggered through two primary pathways: intrinsic and extrinsic, both of which eventually converge on the act
…
8th Feb 2024
Understanding Parkinson's Disease: Insights and Innovations
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a progressive neurological disorder that predominantly affects the motor system, leading to a wide range of symptoms including tremors, rigidity, bradykinesia (slowness of movement), and postural instability. This article delves into the pathophysiology, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for Parkinson's disease, providing a comprehensive understanding of this complex condition. Understanding Parkinson's Disease Pathophysiology Parkinson's disease is characterized by the degeneration of dopamine-producing neurons in the substantia nigra, a region of the brain that plays a critical role in regulating movement. The decline in dopamine leve
…
8th Feb 2024
Alzheimer's Disease: A Comprehensive Insight
Alzheimer's disease stands as a formidable challenge in the realm of neurological disorders, characterized by its progressive nature and profound impact on cognitive functions. This article delves deeper into the facets of Alzheimer's disease, exploring its causes, mechanisms, clinical manifestations, and current therapeutic strategies, enriched with current scientific insights. Etiology and Risk Factors Genetic Factors The genetic landscape of Alzheimer's disease is complex, with both hereditary (familial AD) and sporadic forms. Key genes implicated in its pathogenesis include the amyloid precursor protein (APP), presenilin-1 (PSEN1), and presenilin-2 (PSEN2). Mutations i
…
7th Feb 2024
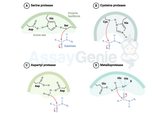
Protease vs Peptidase: Understanding Enzymatic Digestion
In the complex world of biochemical processes, enzymes play a crucial role in catalyzing various reactions necessary for life. Among these enzymes, proteases and peptidases are fundamental players involved in the breakdown of proteins and peptides, respectively. While their names might sound similar and their functions somewhat overlap, they serve distinct purposes in the realm of enzymatic digestion. Let's delve deeper into their definitions, functions, and types to gain a comprehensive understanding. Protease: The Protein Digesters Proteases, also known as proteolytic enzymes or proteinases, are enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of peptide bonds within proteins. These
…
6th Feb 2024
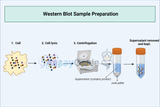
Guide to Western Blot Sample Preparation
Western blotting remains a pivotal technique in the molecular biosciences for the detection, quantification, and analysis of proteins. Its utility spans numerous fields, including immunology, developmental biology, and disease diagnostics. A critical determinant of success in Western blotting is the quality of sample preparation. This guide delves into the nuances of preparing samples for Western blot analysis, ensuring that researchers can achieve reproducible and meaningful results. Key Points to be Discussed Introduction to Western Blotting Sample Collection and Storage Protein Quantification Sample Buffer Preparation and Use Sample Denaturation and Loading Troubleshooting C
…
6th Feb 2024
Deciphering B Cell Cancers With a Rituximab Biosimilar
The fight against B cell cancers, a challenging spectrum of hematologic malignancies, has entered a new era with the introduction of rituximab biosimilars. These biosimilars promise to extend the revolutionary benefits of rituximab, a cornerstone in the treatment of diseases like non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), to a broader patient population. This detailed exploration covers the complex nature of B cell cancers, the therapeutic mechanism of rituximab, and the significant potential of its biosimilars. Introduction B cell cancers represent a diverse group of malignancies that require nuanced therapeutic approaches. The advent of biosimilar thera
…
5th Feb 2024
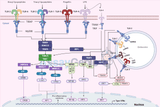
Toll-Like Receptor Signaling Pathways: A Key to Innate Immunity
In the intricate landscape of the immune system, toll-like receptors (TLRs) play a fundamental role in the first line of defense against pathogens. These receptors, essential components of the innate immune response, are adept at recognizing specific microbial patterns, initiating signaling pathways that lead to the activation of immune responses. This article delves into the toll-like receptor signaling pathways, underscoring their importance in immunology and potential therapeutic applications. Understanding Toll-Like Receptors Toll-like receptors are a class of proteins that play a critical role in the immune system by detecting microbial infections and activating the immune r
…
5th Feb 2024
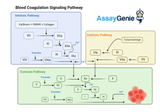
Blood Coagulation Signaling Pathways: A Critical Overview
Blood coagulation is a fundamental physiological process that prevents excessive bleeding when the vascular system is injured. It involves a complex cascade of events that lead to the formation of a stable fibrin clot. This process is tightly regulated by various signaling pathways to ensure that coagulation occurs promptly and appropriately in response to vascular injury, without leading to thrombosis or bleeding disorders. This article delves into the critical signaling pathways involved in blood coagulation, highlighting their roles, mechanisms, and the potential for therapeutic intervention. The Coagulation Cascade: An Overview The coagulation cascade is traditionally divided
…
5th Feb 2024
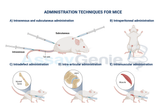
Mouse Injection Guide (Subcutaneous, Instramuscular & Intraperitonael)
In scientific research involving mice, the administration of substances via injection is a common practice. Whether delivering drugs, antibodies, or experimental compounds, precise injection techniques are crucial for obtaining accurate and reliable results. This article provides a comprehensive guide on how to inject mice for scientific research, covering key aspects such as preparation, different types of injection techniques, execution, and post-injection care. Preparation: Before performing any injections, it's essential to properly prepare both the mice and the injection materials. Here's a step-by-step guide to preparation: Mouse Preparation: Handle mi
…
4th Feb 2024
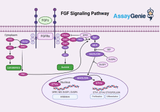
Fgf Signaling Pathway Explained: Step-by-Step Process & Key Concepts
Fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) are pivotal in regulating cellular processes, including proliferation, differentiation, and survival. The FGF signaling pathways play a critical role in embryonic development, tissue repair, metabolism, and cancer progression. This article delves into the mechanisms of FGF signaling, highlighting its significance in biological processes and potential therapeutic applications. Understanding FGF Signaling: FGF signaling is mediated through the interaction of FGFs with their cell-surface receptors, known as FGFRs. This interaction leads to receptor dimerization and activation, initiating a cascade of downstream signaling events. The specificity of FG
…
3rd Feb 2024
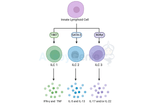
Innate Lymphoid Cells Differentiation: Guardians of Immune Homeostasis
Innate Lymphoid Cells (ILCs) represent a fascinating component of the immune system, playing a crucial role in maintaining tissue homeostasis and mounting rapid responses against pathogens. These cells lack antigen-specific receptors, distinguishing them from their adaptive counterparts, yet their ability to rapidly respond to environmental cues is vital for effective immune surveillance. One of the key aspects of ILCs' functionality lies in their differentiation process, a complex series of events that shape these cells into distinct subsets with specialized functions. Understanding ILC Differentiation: ILCs are broadly categorized into three main subsets based on their cy
…
2nd Feb 2024
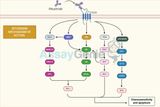
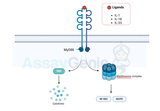
IL-1 Family Signaling: Unraveling the Molecular Orchestra of Immune Regulation
The Interleukin-1 (IL-1) family represents a crucial group of signaling molecules that play a pivotal role in regulating the immune system and inflammatory responses. Comprising 11 members, including IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-18, and IL-33, the IL-1 family members exhibit diverse functions in immune homeostasis, tissue repair, and disease pathogenesis. In this article, we will delve into the intricate details of the IL-1 family signaling pathway, shedding light on its components, activation mechanisms, and physiological significance. Components of the IL-1 Family Signaling Pathway: IL-1 Receptors (IL-1Rs): The IL-1 family signaling cascade begins with the binding of
…
2nd Feb 2024
3D Cell Culture: Assay Guide
References Key Points Three-dimensional (3D) cell cultures are artificially-created environments in which cells are permitted to grow or interact with their surroundings in a 3D fashion. 3D cell culture more closely resembles physiological conditions and can provide a better indicator of success in vivo. Assays and kits exist which can help cultivate and quantify 3D cell cultures. Contents Background What is 3D Cell Culture? Pros and Cons Cultivation Basement Membrane Matrix Alginate Hydrogel Assays Harvesting Kit XTT
…
2nd Feb 2024
The role of IL-18 in health and disease
Exploring IL-18: A key cytokine in inflammation and disease. Key Takeaways: IL-18, a pro-inflammatory cytokine, plays a pivotal role in immune responses, particularly in inducing Type II interferon and activating macrophages. It's produced as an inactive form and activated by caspase-1, signaling through IL-18 receptors to trigger inflammation. IL-18's regulation involves IL-18 binding protein (IL-18BP) and IL-37, which modulate its activity and prevent excessive inflammation. It contributes to T cell differentiation and NK cell cytotoxicity, influencing various immune functions. IL-18 is implicated in several diseases, including Crohn's disease and sepsis, making it a potential
…
1st Feb 2024
IL-9 Signaling and Its Impact on Immune Cell Regulation
Interleukin-9 (IL-9) plays a critical role in the immune system, influencing a variety of biological functions across different immune cell types. This article provides an in-depth look at the signaling mechanisms of IL-9 and its widespread effects on immune regulation, specifically focusing on its impact on T cells, mast cells, basophils, B cells, and regulatory T cells (Tregs). IL-9 Signaling Pathway Overview of IL-9 Receptor Activation IL-9 interacts with the IL-9 receptor (IL-9R), composed of the IL-9Rα chain and the common gamma chain (γc), initiating the JAK-STAT signaling cascade. This activation promotes the transcription of genes that regulate cell proliferation, d
…
1st Feb 2024
p38 MAPK Signaling Review
The p38 MAPK signaling pathway is an intracellular signaling pathway that plays a crucial role in cellular responses to various stressors and inflammatory stimuli. It is a part of the larger MAPK superfamily, which also includes ERK and JNK pathways. The p38 MAPK pathway is involved in regulating a wide range of cellular processes, including cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, inflammation, and immune responses. Key Takeaways: p38 MAPK, part of the MAPK family, is key in cellular responses to stress and inflammation. This pathway regulates cell processes like proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and immune responses. The MAPK family includes ERKs, JNKs, and p38
…
1st Feb 2024
The Intricacies of IL-21 Signaling: Impact on Diverse Immune Cell Types
Interleukin-21 (IL-21) stands out as a pivotal cytokine in the complex network of immune system communication. Its role in regulating various immune cell types has drawn considerable attention from researchers seeking to unravel the intricate web of signaling pathways and biological effects it elicits. In this article, we will delve into the nuanced world of IL-21 signaling and explore its profound impacts on different immune cell populations. IL-21: An Overview IL-21 belongs to the family of cytokines, which are small proteins crucial for intercellular communication. Produced mainly by activated CD4+ T cells, particularly T follicular helper (Tfh) cells and Th17 cells, IL-
…
31st Jan 2024
Understanding the Autophagy Pathway: A Critical Process in Cellular Maintenance
Autophagy, a fundamental cellular process, is crucial for maintaining cellular homeostasis and responding to various stressors. This self-eating mechanism involves the degradation and recycling of cellular components, playing a pivotal role in numerous physiological and pathological contexts. What is Autophagy? Autophagy, derived from the Greek words 'auto' (self) and 'phagy' (eating), is a process where cells degrade and recycle their own components. This process is essential for removing damaged organelles, misfolded proteins, and pathogens, and for providing nutrients during starvation. Types of Autophagy: There are three main types of autophagy: Macroautophagy: The m
…
31st Jan 2024
Nod-Like Receptor Signaling Pathway: A Keystone in Innate Immunity
The innate immune system, a primary line of defense against pathogens, comprises various cellular and molecular mechanisms. Among these, the Nod-like Receptor (NLR) signaling pathways play a critical role. They are central to the immune response, acting as intracellular sensors of pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and danger-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs). This article delves into the basic components of NLR signaling pathways, their key steps, roles in development, and implications in disease. Basic Components of Nod-Like Receptor Signaling Pathways: Nod-like receptors (NLRs) belong to the pattern recognition receptor (PRR) family and are primarily located in
…
30th Jan 2024
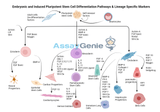
Embryonic Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Differentiation: Pathways and Lineage-Specific Markers
Embryonic induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) hold immense potential in the field of regenerative medicine due to their ability to differentiate into various cell types. Understanding the differentiation pathways and identifying lineage-specific markers are crucial for advancing stem cell research and therapy. Overview of Embryonic iPSC Differentiation: Embryonic iPSCs are characterized by their pluripotency, the ability to differentiate into any cell type of the three primary germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm. This pluripotency is maintained through specific transcription factors such as Oct4, Sox2, and Nanog. The differentiation process involves a complex interpl
…
29th Jan 2024