Blog
Cellular Respiration
Discover the intricacies of cellular respiration, a critical process for energy production in cells, encompassing aerobic and anaerobic pathways and their molecular mechanisms Key Takeaways Cellular respiration is a vital biological process for energy production in cells. It involves converting nutrients into ATP, the primary energy currency. Two types: Aerobic (uses oxygen) and Anaerobic (without oxygen). Key components: Mitochondria in eukaryotes, cytoplasm in prokaryotes. Stages of Aerobic Respiration: Glycolysis, Citric Acid Cycle, Oxidative Phosphorylation. Welcome to our in-depth exploration of cellular respiration—an essential process responsible for ener
…
24th Jul 2023
Waardenburg Syndrome and Klein-Waardenburg Syndrome
Waardenburg Syndrome: A Rare Genetic Disorder Affecting Pigmentation, Hearing, and More
Waardenburg Syndrome (WS) is a fascinating and rare genetic disorder that impacts various aspects of an individual's appearance and sensory abilities. First described by Dutch ophthalmologist Petrus Johannes Waardenburg in the 1950s, WS is characterized by distinctive features, including changes in pigmentation, hearing loss, and facial abnormalities.
Table of Contents
Jump to a section:
- Waardenburg Syndrome Classification
- Waardenburg Syndrome Causes
- Waardenburg Syndrome Type 3
- Related Kits
.nav__list {
list-style:
…
24th Jul 2023
Interleukin-8 signalling
IL-8 Overview
Interleukin-8 (IL-8), also known as CXCL8, was discovered over 30 years ago as a small molecule that could promote chemotaxis and induce the production of both superoxide and hydrogen peroxide (H202) . IL-8 is now recognized as a chemokine, which are small chemoattractant molecules that are secreted by cells of the immune system. Chemokines induce integrin expression and primarily attract leukocytes to the site of infection, although their roles have been discovered to be much more diverse.
44 chemokines and 23 chemokine receptors have been identified to date. Structurally, IL-8 contains two N-terminal cysteine motifs, which classify it as a CX
…
23rd Jul 2023
Neuroimmunology: The Immune System of the CNS
What is Neuroimmunology?
Neuroimmunology is a multidisciplinary scientific field dedicated to investigating the intricate and bidirectional interactions between the central nervous system (CNS) and the immune system. It involves the rigorous study of regulatory influences and cross-talk that govern the functionality and behavior of these once-segregated systems.
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "BlogPosting",
"mainEntityOfPage": {
"@type": "WebPage",
"@id": "https://www.assaygenie.com/blog/neuroimmunology-of-the-cns"
},
"headline": "Neuroimmunology: The Immune System of the CNS",
"description": "The central nervous syste
…
21st Jul 2023
Schwann Cells: Specialized Cells that Support Nerve Function
Schwann cells are cells that play a vital role in nerve function. They are responsible for myelinating axons and helping to ensure the transmission of electrical signals between neurons. Schwann cells also have an important role in nerve regeneration. In this guide, we will take a closer look at the structure and function of Schwann cells, as well as some of the key marker proteins involved in their differentiation. By understanding more about these cells, we can gain insights into the causes of neurodegenerative diseases and potentially develop new treatment approaches.
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "BlogPosting",
"mainEntityOfPage": {
"@type": "WebPage"
…
20th Jul 2023
Fibroblast Markers
Fibroblasts, essential components of connective tissues, play vital roles in maintaining tissue structure and function. Their remarkable ability to produce and organize the extracellular matrix forms the foundation for tissue integrity and repair processes. Identifying and characterizing fibroblasts amidst complex biological environments rely on fibroblast markers, specific molecular indicators that aid researchers in distinguishing these cells. In this blog post, we delve into Fibroblast, their markers and their significance in cancers. fibroblast markers in research, their potential applications in disease investigation, and their implications in regenerative medicine and therapeutic
…
20th Jul 2023
A Quick Guide to Myelin
The myelin sheath is an insulating layer around nerve cells. It is made up of a substance called myelin, which is produced by special cells called oligodendrocytes. Myelin protects the nerve cells and to keep them maintain their function. Myelin is important for the proper function of the nervous system. It helps to speed up nerve impulses and prevents them from becoming mixed up. Without myelin, nerve impulses would move slowly and would be easily confused. Myelin is also important for the repair of damaged nerves. When a nerve is damaged, the myelin sheath around it is also damaged. The oligodendrocytes that produce myelin can also repair the myelin sheath. This process is called myeli
…
19th Jul 2023
Converting RPM to G-force in Centrifugation
Centrifuges play a pivotal role in scientific research and various industries, enabling efficient separation and isolation of components within a sample. Understanding the relationship between rotations per minute (RPM) and gravitational force (G-force) is crucial for optimizing centrifuge settings and achieving desired results. In this blog, we will focus on the principles behind RPM and G-force in centrifugation, provide practical insights for accurate conversions, and offer valuable tips and best practices.
Table of Contents
Jump to a section:
- RPM and G-Force
- Conversion
- Illustration
- Factors
- Right Settin
…
19th Jul 2023
An Overview of the glycoprotein GM-CSF
This article breaks down the glycoprotein Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) detailing its structure, function and therapeutic uses. It also describes its role in immunity, inflammation and diseases such as cancer and AIDS.
What are Colony Stimulating Factors?
Colony stimulating factors (CSFs) are a group of glycoprotein cytokines that stimulate the production of blood cells. They are important for the treatment of cancer and other blood disorders. CSFs were first discovered in the 1960s, and since then, they have been used to treat millions of patients worldwide. There are four main t
…
18th Jul 2023
T cell Immunophenotyping - A Guide
Introduction T lymphocytes are type of white blood cell that plays a crucial role in the immune system. There are many different types of T cells, and it is important to be able to distinguish them accurately in order to study their function. Immunophenotyping is the process of identifying and classifying these different types of T lymphocytes. In this guide, we will discuss the different markers that are used to identify T cells, as well as how to sort them using flow cytometry. We will also look at the different helper T cell subsets and their activation markers. By understanding the basics of immunophenotyping, you can effectively diagnose and treat immune-related diseases
…
18th Jul 2023
Cleaved Caspase-3 and Apoptosis
Delve into the role of Cleaved Caspase-3 in programmed cell death and its implications in disease pathologies, unraveling its regulatory mechanisms and potential as a therapeutic target. Key Takeaways: Cleaved Caspase-3 is a central enzyme in apoptosis, orchestrating cell dismantling. It's activated by initiator caspases and is key in executing the apoptotic process. Cleaved Caspase-3 has roles in diseases like cancer and neurodegenerative disorders. Its regulation involves various factors, including IAPs and the Bcl-2 family. Targeting Cleaved Caspase-3 offers potential therapeutic strategies for various diseases. Table of Contents Jump
…
18th Jul 2023
von Willebrand Factor and Cancer
What is von Willebrand Factor?
Von Willebrand Factor (VWF) is a crucial glycoprotein that plays a fundamental role in blood clotting and hemostasis. Produced by endothelial cells and megakaryocytes, VWF circulates in the bloodstream as large multimers. Its primary function is to mediate platelet adhesion at sites of vascular injury, forming a temporary platelet plug to stop bleeding. VWF also serves as a carrier protein for Factor VIII, protecting it and extending its availability during the clotting process.
Von Willebrand Disease (VWD) is an inherited bleeding disorder caused by deficiencies or abnormalities in von Willebrand Factor.
{
"@context":
…
18th Jul 2023
Comprehensive Guide to Mononuclear Cells
Mononuclear cells, as the name suggests, refer to a group of white blood cells characterized by the presence of a single nucleus. Understanding the nature, function, and significance of mononuclear cells is essential for comprehending the complex workings of our immune system and overall health.
Throughout this article, we will explore the definition of mononuclear cells, examine their functions in different biological contexts, discuss their presence in blood and bone marrow, and highlight their clinical implications. Additionally, we will dive into the world of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and their role in immunology and research.
Table
…
17th Jul 2023
Antigen Presenting Cells (APCs) and cancer immunotherapy
Explore antigen presentation's crucial role in adaptive immunity and its impact on cancer immunotherapy, highlighting the diversity and function of MHC class I molecules. Key Takeaways Antigen presentation by MHC class I is key for adaptive immunity. Specialized cells, antigen-presenting cells (APCs), present antigens to T cells. MHC-I molecules' polymorphism enables diverse antigen presentation. Cancer immunotherapy leverages antigen presentation to target tumor cells. What is Antigen Presentation? Our immune system has various mechanisms to defend against pathogens, with adaptive immunity being a crucial component. Adaptive immunity enables our immune syst
…
16th Jul 2023
C reactive protein
Delve into the world of C-reactive protein (CRP), a critical player in the body's response to inflammation, and understand its role in health and disease. Key Takeaways C-reactive protein (CRP) is a marker of inflammation, increasing in response to infection, injury, or tissue damage. Produced by the liver, it's regulated by IL-6 and involved in immune responses. CRP's functions include pathogen recognition, opsonization, activating the complement system, and modulating inflammation. Used as a diagnostic biomarker, CRP levels help assess inflammation and cardiovascular risk. Elevated CRP levels are associated with various conditions, including infections, autoimmune dis
…
16th Jul 2023
Cancer Metabolism: Tumorigenesis, Metabolic Therapy & The Warburg Effect
Cancer Metabolism is the mechanism by which cancer cells make energy in order for them to grow and spread. Even in the presence of oxygen, cancer cells increase glucose uptake and produce lactate, which is defined by the Warburg Effect. This article also discusses areas related to cancer metabolism such as Tumorigenesis and Metabolic Therapy.
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "Article",
"mainEntityOfPage": {
"@type": "WebPage",
"@id": "https://www.assaygenie.com/blog/an-overview-of-cancer-metabolism-tumorigenesis-metabolic-therapy-and-the-warburg-effect"
},
"headline": "Cancer Metabolism: Tumorigenesis, Metabolic Therapy & The Warburg Effect",
"descr
…
14th Jul 2023
Leukemia Inhibitory Factor (LIF)
Leukemia Inhibitory Factor (LIF) is a cytokine that plays a crucial role in various physiological processes within the human body. It has gained significant attention in the field of leukemia research due to its multifaceted functions and potential therapeutic applications. In this blog the molecular structure, biological sources, signaling pathways, and the role of LIF in leukemia will be discussed.
Table of Contents
Jump to a section:
- LIF Expression
- LIF Signaling
- LIF in Leukemia
- LIF Related Kits
- LIF in Stem Cell Culture
.nav__list {
list-style: none;
}
.nav__list a{
font-family: Popp
…
13th Jul 2023
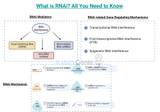
What is RNAi? All You Need to Know
RNA interference (RNAi), also referred to as Post-Transcriptional Gene Silencing (PTGS), is the process by which RNA molecules silence genes in response to double-stranded RNA. RNA interference (RNAi) causes the downregulation or silencing of specific genes at the post-transcriptional level. It can lead to several effects depending on the targeted gene and its biological function.This article discusses RNAi, the various types of RNAi, its mechanism of action and RNAi therapeutics.
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "BlogPosting",
"mainEntityOfPage": {
"@type": "WebPage",
"@id": "https://www.assaygenie.com/blog/what-is-rna-interference-all-you-need-to-know"
}
…
13th Jul 2023
Transfection: A Comprehensive Guide
Transfection protocols play a crucial role in the realm of molecular biology and genetic research, enabling the introduction of foreign nucleic acids into living cells. This innovative technique allows scientists to manipulate gene expression, study protein function, and investigate cellular processes with remarkable precision. This article focusses on the fundamental principles underlying transfection protocols, exploring their significance and various approaches employed for achieving successful genetic delivery
Table of Contents
Jump to a section:
- Cell Transfection
- Applications
- Mechanism
- Transfection vs Tr
…
12th Jul 2023
VEGF: Inflammation and Tumourigenesis
What is VEGF?
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factors (VEGFs) are a group of homodimeric polypeptides, and are master regulators of vascular development, maintenance and angiogenesis. VEGF is also a potent growth factor, and is produced by macrophages and CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. Members of the VEGF family include 5 structurally related proteins (VEGFA-D, and placental growth factor (PIGF), which are further individually subdivided based on alternative splicing. VEGF acts as a potent stimulator of angiogenesis, promoting the growth and survival of endothelial cells, and is essential for embryonic development and tissue repair in adults.
The discovery of VEGF and it
…
12th Jul 2023
Mitotic Catastrophe Review
Delving into the intricate world of Mitotic Catastrophe, this blog unveils its critical role in cell division and cancer therapy, offering insights into its mechanisms and potential treatments. Key Takeaways: Mitotic Catastrophe: A response to abnormal mitosis, potentially leading to cell death. Oncosuppressive Role: Prevents proliferation of genetically unstable cells, guarding against cancer. Mitotic Failure and Slippage: Involves death without mitosis exit or progression to G1 phase. Cyclin B Proteolysis: Key in mitotic slippage, leading to Cdk1 inactivation. Prolonged Arrest: Influences cell fate, with a cutoff point for irreversible catastrophe. Targeting Strategies
…
11th Jul 2023
Cyclins and Cyclin Dependent Kinase – Review
Cyclins and CDKs are central to cell cycle control, with specific cyclin-CDK pairs regulating different phases, ensuring orderly progression and genomic integrity in cell division. Key Takeaways: Cyclins and CDKs are vital for cell cycle regulation. Cyclins A, B, D, E each pair with specific CDKs to control cell cycle phases. Cdk1, the prototypical CDK, partners with cyclin B for mitotic entry. Cyclin B upregulation and Cdk1 substrates play key roles in mitosis. Proteomic analysis reveals extensive Cdk1 substrates in mitosis. Positive feedback loops amplify Cdk1/cyclin B activity. Cdk1-Plk1 phosphorylation cascade is crucial for spindle assembly and mitosis. Cyclin degradatio
…
10th Jul 2023
Immunometabolism – A therapeutic perspective
What is Immunometabolism?
Immunometabolism is an exponentially growing, multi-disciplinary field of research aiming at deciphering the dynamic cellular and molecular mechanisms that interweave metabolic and immunological processes together. Although the term “immunometabolism” first appeared in the literature in 2011, the first studies investigating the connection between immune and metabolic disorders date back to the late 19th century. Our expanding understanding of how different immune cell functions correlate with particular metabolic configurations during homeostasis and inflammation has opened new therapeutic possibilities where the modulation of
…
10th Jul 2023
CD11b: Macrophages and Microglia Marker
The immune system plays a critical role in defending the body against pathogens and maintaining tissue homeostasis. Within the intricate network of immune cells, CD11b, also known as integrin alpha M, emerges as a significant player in immunology and neuroscience. CD11b serves as a cell surface marker that aids in identifying and characterizing specific immune cell populations, particularly macrophages and microglia. Understanding the role of CD11b and its association with these cells provides valuable insights into various disease processes, immune responses, and neuroinflammatory disorders. In this blog post, we will look at the structure and function of CD11b, its significance
…
10th Jul 2023